Birthmark Removal – Hemangioma, Nevus, Mole Removal
What Is a Birthmark?
A birthmark is a persistent mark anywhere on the skin, visible at birth or shortly thereafter (in weeks) (1). It represents local accumulation of sin pigment, vessels overgrowth, or other local skin abnormality. Some birthmarks fade, partially or completely, in few years, but other persist for life and may even become more pronounced with time.
Most of birthmarks are painless and harmless, but some may cause complications, like pressure on other organs, they may be connected with congenital diseases, or, rarely, may develop into a cancer, so they always have to be checked by a doctor. Pigmented skin marks that are not birthmarks may be a result of trauma.
What is a Nevus?
A nevus (plural nevi) is a persistent circumscribed mark appearing at birth or at any time in life, anywhere on the skin or mouth mucosa, but not due to external causes (2). It represents localized excess or deficiency of skin connective tissue, skin glands, vessels, or nerves. It may appear as:
- a discoloration (pink, red, violet, bluish, brown, grey, black, or whitish or otherwise pale) in the level of the skin, few millimeters (macule) to several centimeters (patch) in size
- a raised (papule, plaque), or depressed, skin-colored or discolored mark on the skin
What Is a Mole?
A mole is any pigmented lesion on the skin, appearing at birth or later (3). Moles include flat nevi, and raised pigmented masses.
What Is Hemangioma?
A hemangioma is a collection of small blood vessels that appear as a pink or red birthmark on the forehead, eyelids, above the nose, above the upper lip, and the so-called “stork bite” on the nape of the neck. These marks fade or disappear entirely within a few years. Hemangiomas that are not birthmarks may appear later in life from trauma, or various diseases.
Below, several types of birthmarks (4) are described.
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal clusters of veins and arteries, appearing anywhere on the skin (commonly on the lips, head, or neck) as soft, jelly-like lumps that are sometimes painful on pressure.
AVMs can also appear in the brain, brainstem or spinal cord where it can be detected by angiography. AVM’s are usually present at birth, but sometimes they don’t appear until adulthood, and can also result from trauma.
Treatment possibilities:
- Surgical removal
- Before surgery, a substance that clots (obstructs) vessels can be injected into hemangioma, what causes its shrinkage
Café au lait Spot
Pale, tan to light brown (French Cafe au lait= coffee with milk) patch, few to several centimeters in size, can be found anywhere on body. Several (three or more) spots speak for neurofibromatosis.
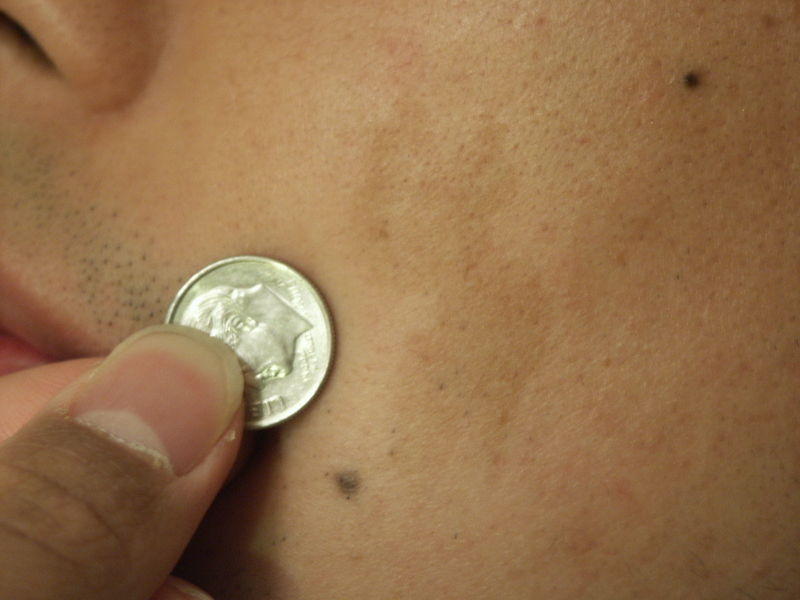
Picture 1. Cafe au lait spot on the cheek
(the light brown patch on the right of the coin)
(source: Wikimedia)
Cavernous Hemangioma
Bluish or bluish-red lump without clear borders grows fast during first 6 months, then slows down, and disappears by 10-12 years of age in most cases.
Treatment possibilities are the same as for strawberry hemangioma.
Congenital Pigmented Nevi
Appear as light to dark brown hairy moles, few to several centimeters in size. Large nevi may become malignant.
Infantile Hemangioma
Infantile hemangioma, or simply hemangioma, appears at birth (or within 4 weeks after birth) as reddish, flat patch with sharp borders, or raised, soft, painless mass, few centimeters in size, on the babie’s forehead, face, lips, neck, or rarely on other sites, like on the sole of the foot. Deep hemangiomas may appear as soft lumps covered with normal skin.
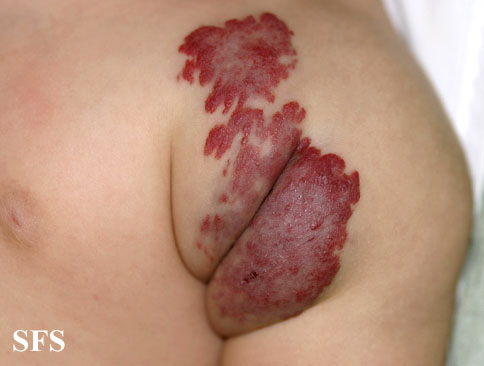
Picture 2. Infantile hemangioma
(source: atlasdermatologico)
More Pictures of infantile hemangioma
Pathology. Hemangioma represents an abnormal overgrowth of vessels in or under the skin.
Diagnosis. Surface hemangiomas don’t require any tests, deep hemangiomas may require MRI to determine their relation to other organs.
Treatment. Surface hemangiomas usually don’t require any treatment, deep hemangionas may require surgical removal, if they disturb eating, vision or hearing.
Prognosis. Hemangioma can grow for about 1 year, then starts to decrease in size and disappears completely between 5-12 years of age.
Lymphatic Malformation
Abnormalities in lymph vessels may obstruct the flow of lymph that then presses upon lymphatic vessels walls, thus causing their enlargement. Sponge-like masses containing clear fluid may appear under the skin; the fluid may leak out from vessels, causing under-skin inflammation and swelling – cellulitis, most often in head and neck area. In mouth, it looks like frog eggs.
Pictures of lymphatic malformation
Diagnosis is with MRI and CT.
Treatment possibilities:
- Laser treatment
- Sclerotherapy – injecting of substance will obstruct vessels and result in their shrinkage
- Surgical removal
Mongolian Spot
Blue or slate grey discoloration, resembling bruises, commonly appear in babies of African, Afro-American, Mediterranean, Asian or Indian descent. They mostly appear on trunk, or legs.
Treatment is usually not needed, since spots usually fade over time.
Port Wine Stain or Nevus Flammeus
Red or purple patches, flat or slightly raised, found anywhere on the body at birth. Nevi are permanent.
Treatment possibilities:
- Laser treatment may reduce color, and prevent growth of nodules on lips, gums and other tissues.
Salmon Patch or Nevus Simplex
Salmon-colored nevus (“angel kiss” or “stork bite”) is most often found on the nape of the neck, but also on the forehead, upper eyelids, and around the mouth and nose. In most cases it fades completely over time.
Pictures of port wine stain and salmon patch
Strawberry Hemangioma
Raised, red, soft lump of various sizes, built from abnormal vessels may be present at birth or first few weeks thereafter. It may continue to grow for some time, but then turns grey, and fades completely between ages 5-10.
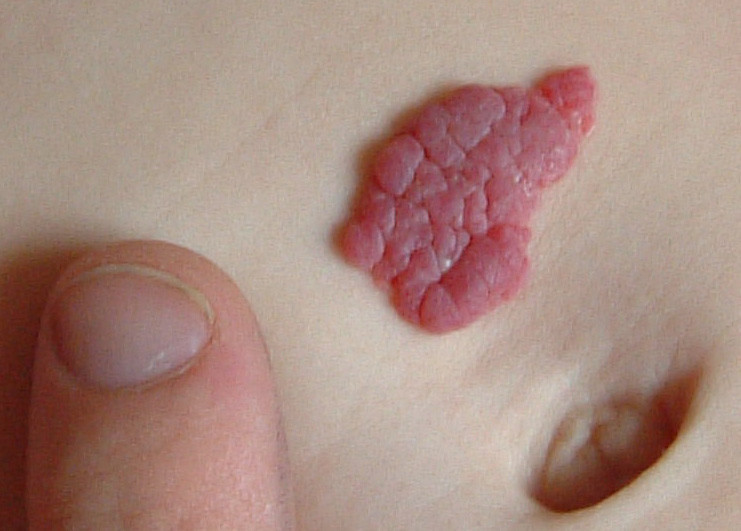
Picture 3. Strawberry hemangioma
(source: Wikimedia)
Treatment is indicated in large lesions, or where it disturbs function of other organs. Treatment possibilities:
- Surgical removal
- Compression and massage
- Laser therapy
- Cryotherapy – freezing of the lesion
- Injection of steroids or hardening substances
- X-ray irradiation
Venous Malformation
A soft, bluish or skin-colored lump, containing abnormal veins is mostly present at birth on the jaw, cheek, lips, or tongue. Both lump mass and color disappear when the lesion is compressed. When the baby cries, the color often becomes more intense.
Congenital Diseases With Birthmarks
Birtmarks may be a sign of a congenital disease:
- Cutis Marmorata Telangiectatica Congenita may be present with undergrowth or overgrowth of a limb, increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma), thin skin, and neurological abnormalities.
- Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome. Nevi represent lack of capillaries between arteries and veins.
- Kasabach-Merritt syndrome. Reddish-brown discolorations and bleeding from impaired coagulation appear as tufted angioma.
- Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome presents with port wine stain on the limbs, and limbs enlargement.
- Neurofibromatosis is present with multiple café-au-lait spots, tumors of nerves, mainly in the head and. It is a genetic disorder, and can appear at any time and anywhere in the body.
- PHACE syndrome is present with Posterior fossa brain malformations, Hemangiomas, Arterial anomalies, Coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects, and Eye abnormalities.
- Sturge-Weber syndrome is present with facial port wine stain, and angiomas on the soft brain membrane (meninges). Other symptoms are headaches, seizures, glaucoma, and mental retardation.
References:
- Definition of birthmark (medterms.com)
- Definition of nevus (mercksource.com)
- Definition of mole (mercksource.com)
