Breast Swelling – Tender, Sore & Painful Swollen Breasts
Definition of Breast Swelling
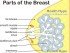
Breast swelling is an enlargement of the breast or both breasts compared to the regular breast size and may be accompanied by other symptoms like tenderness (soreness), pain, lump(s), changes of the areola or nipple and any secretion from the nipple. Swollen breasts may be a normal physiological process as seen in puberty or pregnancy or may be a sign of a medical disorder.
Tender or Sore Breast
Breast tenderness or soreness is a mild to moderate discomfort of the breast, sensitive to touch or pressure and often accompanied with redness. Tenderness and soreness should be differentiated from breast pain although this may be subjective and dependent on an individual’s pain tolerance levels.
Breast Pain
Breast pain should be differentiated from soreness or tenderness of the breast. Pain usually indicates serious pathology that needs to be investigated and treated. Breast pain may be referred to other areas on the body like the axillae (armpits), abdomen, neck and back.
Causes of Swollen Breasts
Symptoms associated with the following conditions may not be present with every case of breast swelling. Always consult with your medical practitioner for further investigation or to confirm a diagnosis.
Sx = symptoms. Ddx = differential diagnosis.
- Puberty. Sx may include increasing bust size, androgenic hair (pubic hair and/or hair of the armpits), onset of menstruation (menarche), fat accumulation on the thighs, buttocks and/or lower abdomen. (1) Ddx = use of oral contraceptives.
- Menstrual Cycle. Sx may include irritability and mood changes (premenstrual syndrome/PMS, premenstrual tension/PMT), bilateral (both sides) breast swelling and tenderness prior to menses, period pain (menstrual pain), discomfort or cramping, headache, leucorrhea / leucorrhoea (vaginal discharge). Ddx = use of oral contraceptives, fertility drugs.
- Pregnancy. Sx may include breast tenderness, amenorrhea / amennorrhoea (cessation of menstruation – regular periods), nausea and vomiting (morning sickness), lactation, leucorrhea (clear vaginal discharge), frequent urination, darkening and/or enlargement of the areola (area around the nipple), headache, fatigue. (2) Ddx = use or contraceptives, gonadotropin releasing hormone drugs (like goserelin acetate), premature ovarian failure, menopause.
- Lactation (breast feeding). Sx may include milk production and secretion, colostrum production and secretion before and after delivery, tender or sore breasts, palpable nodules in the breast. A differential diagnosis (ddx) would only be considered if there are other signs and symptoms like excessive pain, unilateral (one-sided) breast swelling or pus secretion from the nipple. Breast swelling and tenderness is a normal symptom of pregnancy and post-delivery.
- Menopause. Sx include erratic periods or amenorrhea (cessation of periods), breast tenderness, weight gain, hot flushes/flashes, mood changes. Ddx = pregnancy, premature ovarian failure, gonadotropin releasing drugs, hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
- Drugs like gonadotropin releasing hormone, contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy (HRT), anabolic steroids.
- Lymphadenopathy & Lympedema. Sx include enlarged lymph nodes/glands (lumps in the breast) that is usually movable. Ddx = breast infection (mastitis), breast abscess, pregnancy, lactation and most other causes of breast swelling.
- Mastitis (breast infection) often occurs when breastfeeding. Sx may include breast pain, tenderness/soreness, redness, heat or warmth of affected area. Ddx = breast abscess, drugs. (3)
- Breast Abscess is a collection of pus within the breast tissue. Sx = severe breast pain, fever, chills, redness, heat/warmth, discharge of pus, deviated nipple, visible lump or ‘bump’ on breast surface, deviated nipple and/or areola. Ddx = breast cancer, mastitis.
- Breast lump. Most breast lumps are benign and may appear or disappear spontaneously. Sx may include palpable breast lump, fixed or movable lump, visible lump or ‘bump’, single enlarged lump or many small breast lumps and bumps. Ddx = breast swelling and lumps due to lactation, lymphadenopathy, breast abscess, breast cancer, breast fat necrosis, breast cyst, fibroadenomas, papillomas.
- Breast cancer. Sx may include painless breast lump, usually fixed and increasing in size. May be visible on the surface as a lump or bump. Deviated nipple and/or areola. Swollen lymph nodes of the surrounding area – around the clavicle, axilla (armpit) or even of the upper arm. Ddx = benign breast lump, breast fat necrosis, papilloma, fibroadenomas, lymphadenopathy, breast abscess, swelling and lumps due to lactation. (4)
- Breast Augmentation (enlargement or implants). Breast swelling is an enlargement due to elective cosmetic surgery. Postoperative breast infection (mastitis), breast abscess or allergic reactions may be possible and can cause further breast swelling with breast pain, tenderness or soreness.
- Breast Reduction. Breast swelling may occur due to inflammation of breast tissue. Postoperative infection of the breast is also possible.
- Gynecomastia is the abnormal breast swelling in males. May occur at any stage of life and should be clearly differentiated from enlarged pectoral muscles (‘pecs’) in muscular males.
Related Articles :
- What Is Swelling?
- Swollen Lymph Nodes & Glands – Lymphedema and Lymphadenopathy
- Causes of Breast Pains – Diagnosis of Breast Pain Symptoms
References :
1. Symptoms of Puberty. NHS Choices.
2. Pregnancy Symptoms. American Pregnancy Association.
3. Breast Infection (Mastitis). Emedicinehealth.com.
4. Breast Cancer. Merck.