Car Accident Injuries – Symptoms, Diagnosis, Pictures, Prevention
Head and Brain Injuries
Hitting the windshield or falling out from the car, when not being harnessed with a safety belt, are main reasons for head injuries in car accidents.
Apart from unconsciousness, head pain, bleeding and visible head deformities, the following symptoms may speak for a head or brain injury:
- Tenderness or instability of head bones upon pressing
- Painful mouth opening (temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain)
- Problems with memory and concentration
- Pupils of unequal diameter, or excessively wide or narrow
- Nosebleeds or clear liquid (liquor) leaking from the nose
- Impaired vision, hearing, smelling or unusual sensations in any body part
- Weak or paralysed limbs
Retinal Detachment
One common car accident injury that often remains unnoticed until becoming severe, is retinal detachment. Suddenly appearing blurred vision and flashes, floaters and “curtains” in your visual field are most obvious symptoms. Blurred vision after a car accident is an emergency; retinal detachment should be surgically treated promptly to prevent permanent vision loss.
—-
In most cases, neurological examination performed by a neurologist, and X-ray, CT or MRI of the head are required to determine exact organs damage in a car accident.
FIRST AID: Any unconscious person involved in a car accident should be checked for “ABC”: are airways free (by looking into the mouth, is breathing present (by closing the face to victim’s nose), is circulation active (by checking the pulse of the carotid artery on the neck)? If a victim breathes and has a palpable pulse, he should be put in the “recovery position” (Picture 1).
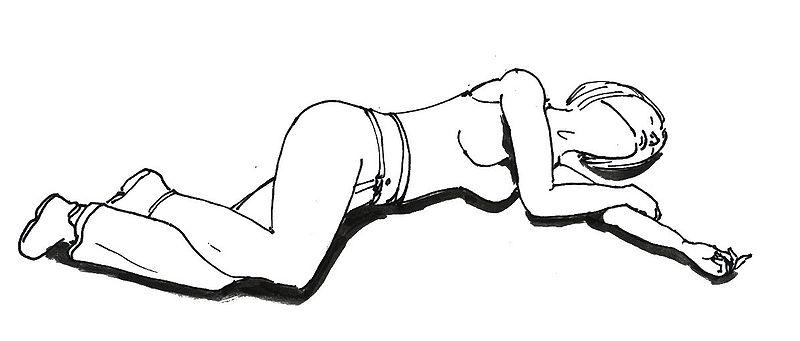 Picture 1. Recovery position
Picture 1. Recovery position
(source: Wikimedia)
Whiplash
Whiplash is a neck pain from strain of the neck muscles, tendons or ligaments, occurring when the neck moves beyond its normal range of motion (flexion-extension injury). An usual cause is a front or rear impact car accident, especially when the car sit has no head rest or this is positioned low.
NOTE: Whiplash may be accompanied with concussion, which is commonly overlooked. Anyone having headache after neck injury should be examined by a doctor.
Back Muscles, Spine and Spinal Cord Injuries
When back muscles, tendons or ligaments are strained, but the spine and spinal cord remain intact, an accident victim may experience back pain, which may resemble pain from a disc injury (see below).
Cartilaginous disc(s) lying between spinal vertebra may bulge, herniate or slip during a back injury and pinch one or more spinal nerves. This may result in a back pain and pain, numbness or tingling in one or both arms or legs.
One or more vertebra (spinal bones) may be broken or cracked without spinal cord being injured. Symptoms may vary from no pain to back pain or pain and tingling in limbs.
Spinal cord or one or more roots of spinal nerves may be compressed or partially or completely cut. Complete spinal cord cut results in loss of sensations and inability to move any body part below the level of the cut; the cut in the neck will affect trunk and all four limbs and the cut in the lower back will affect body below the waistline.
FIRST AID: When a conscious injured person does not feel any sensations in legs when touched or can not move legs, then spinal cord injury is highly suspected. In this case, four persons have to lift the victim and put him carefully on the firm board and then into an ambulance car. Any unconscious persons involved in a car accident should be treated like they possibly have a spinal cord injury until proved otherwise.
CT or MRI of the spine is usually required to diagnose injury of the spine or spinal cord.
Injuries of Ribs and Internal Organs
Steering wheel or other hard object hitting the chest or stomach may result in:
- Broken ribs causing rib pain, or instability when pressed upon ribs or during breathing, coughing or moving.
- Pneumothorax (Greek pneumo = air; thorax= chest). When a lung membrane covering the inside of the chest wall is punctured (in car accidents mostly by a broken rib) the lung collapses and the air fills the affected half of the chest cavity. This is called pneumothorax, which does not necessary cause any additional pain or breathing problems, so it can be easily overlooked and is often discovered only when X-ray of the chest is done. Pneumothorax affecting both lung wings at the same time is usually deadly, though.
- Splenic rupture. A strong blow to the left flank may result in a rupture of the spleen. Severe internal bleeding may follow and urgent spleen removal is usually required.
- Rupture of abdominal aorta. When the stomach is severely compressed, aorta may rupture, and death follows in few minutes in most cases.
- Kidneys, liver and other internal organs may be also injured and cause internal bleeding.
Symptoms of internal bleeding are: abdominal pain, paleness, fatigue, thirst, feeling cold, lightheadedness.
Injury of Bones and Joints
- Broken arms and legs, and injured shoulders, knees and ankles are common car accident injuries.
- Foot or ankle is often injured by break pedals.
Prevention of Car Accident Injuries
The following may greatly reduce the possibility of injuries in car accidents:
- Not driving fast in a dense traffic
- Not driving under influence of alcohol, drugs or certain medications
- Not using a mobile or smoking during driving
- Using sunglasses in sunny weather
- Replacing worn out tires and breaks
- Using automatic safety belt that grabs immediately after your trunk starts to move forward quickly
- Headrest, adjusted to support the most prominent part of the back of the head
- Using a type of automobile, known by its safety
