Diseases That Cause Edema (Localized or Generalized Swelling)
Edema is caused by four possible mechanisms. As mentioned in the pathophysiology of edema, the cause of edema may be due to fluid accumulation within the tissue space because :
- High pressure within the blood vessels pushes out fluid into tissue spaces (increased hydrostatic pressure).
- The blood vessel walls are too permeable allowing fluid to easily drain out into the tissue spaces (increased vascular permeability).
- The osmotic pressure within the blood vessels is not high enough to draw out fluid from the tissue spaces (reduced osmotic pressure).
- Excess fluid in the body congests the vessels and tissue spaces (fluid retention).
- The lymphatic vessels cannot drain out interstitial fluid from the tissue spaces (lymphatic obstruction).
Certain diseases may affect the body in a number of ways that can trigger one or more of these mechanisms.
Causes of Edema, Swelling
Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular diseases or impairment may increase hydrostatic pressure or vascular permeability thereby resulting in edema. The possible causes include :
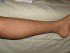
- Heart failure. Some symptoms include swelling of the legs or parts of the body on both sides, pitting edema, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing especially when lying down and bubbling breathing sounds due to fluid in lungs.
- Deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Some symptoms of DVT include signs of inflammation of one leg like swelling, redness, pain and warmth. The leg will usually be tender to touch.
- Chronic venous insufficiency. The leg veins or valves within the veins are weak or damaged and cannot function adequately to assist with returning the blood back to the heart. The blood pools within the legs and this is typical of conditions like varicose veins. Some symptoms include persistent swelling in one or both legs, discomfort or mild pain, dark or dull discoloration of the skin and/or venous ulcers.
Kidney
A number of kidney disorders can cause edema, especially nephrotic syndrome. The kidney condition may cause a reduced osmotic pressure or fluid retention. Some of the symptoms of nephrotic syndrome can be generalized edema evident in the limbs, abdomen and face. The urine may appear foamy (foamy urine), there is a general feeling of being unwell, lack of appetite and measurable weight gain due to the fluid retention.
Liver
Liver damage or failure may reduce synthesis of albumin, a protein that is present in the blood. This reduces the osmotic pressure of blood and leads to edema. Certain liver conditions like cirrhosis may also result in increased blood pressure in the veins from the intestine. Some of the symptoms of cirrhosis include a swollen stomach (abdominal distension), leg swelling, fatigue, nausea and a lack of appetite.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Nutrition
Gastrointestinal conditions like protein losing enteropathy result in the loss of certain blood proteins which will reduce osmotic pressure within the blood. This leads to edema. Protein losing enteropathy may be caused by a number of other gastrointestinal and systemic conditions as well as infections like HIV/AIDS. Malnutrition or undernutrition may also affect the blood proteins thereby leading to edema.
Injury, Infection and Allergy
- Injury may cause edema as a result of inflammation. Depending on the severity and extent of the injury, edema may be localized like in blunt force trauma or burns, or generalized as in poisoning or exposure to toxic chemicals.
- Infections like cellulitis may cause localized edema at the affected site. However in sepsis (‘blood poisoning’) the edema may be more widespread or generalized. Lymphatic filariasis is an infection of the lymphatic system caused by the parasitic African eye worm. Lymphedema may occur in lymphatic filariasis.
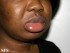
- Allergic reactions may cause angioedema. This is the typical swelling of the skin seen around the eye, lips, hands, feet and throat.
Injury, infection (excluding lymphatic filariasis) and allergic reactions increase vascular permeability which leads to edema.
Drugs, Surgery and Medical Procedures
- Excessive administration of IV fluids (IV drip) may cause edema. This is more likely to occur if the IV fluid is being administered through an infusion pump and the patient is not able to pass out the excess fluid.
- Some drugs that may cause either localized or generalized edema include NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), hormone replacement therapy, corticosteroids and calcium channel blockers which are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Surgical removal of a lymph node will affect the drainage of the surrounding tissues. A lymph node dissection may be necessary in cases of cancer.
Hormonal
- Fluid retention and a slightly raised blood pressure in pregnancy may lead to leg swelling. This is normal and occurs as a result of the hormonal changes. However if the swelling become generalized which may be evident by a swollen face, then it should be attended to as it could be linked to preeclampsia. Here the blood pressure rises significantly and protein is lost through the urine leading to a decreased osmotic pressure. Preeclampsia requires medical attention to ensure the safety of the mother and fetus.
- Premenstrual swelling may be noticed particularly in the feet and ankles. This occurs prior to menstruation and affects many women. It is usually not serious and subsides after menstruation.
- Drugs containing estrogen may also cause localized edema.
Other Causes of Edema
- Bedridden or immobile patients may experience edema due to a lack of activity. This more commonly occurs in the legs because the muscles of the legs assist with circulating blood and lymphatic fluid in the lower extremities. Fluid accumulation may also occur in the lungs of the bedridden patient due to hypostatic pneumonia. Edema may occur in coma or debilitated patients and the elderly who are immobile. Regular physical therapy will reduce the extent of the edema, both in the limbs and lungs.
- Compression of the veins may occur as a result of a tumor, especially benign tumors or the pregnant uterus pressing against a vein. This affects blood flow back to the heart and fluid may accumulate in the tissue spaces leading to edema.
- Standing for long hours (occupational swelling) may cause edema in the legs. This is more likely to occur in there is venous insufficiency like in a case of varicose veins. However any prolonged period of standing or sitting, with minimal movement, may result in some leg swelling even if there is no venous insufficiency.
- Heat, either environmental or applied heat, for long periods of time may cause also swelling.