Flat Feet – Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of Flat feet
Flat feet are of 2 types – physiological (normal) and pathological (diseased). The physiological flat feet are due to imbalances in growth, and correct themselves over a period of months to a few years. Though they may give rise to transient symptoms of pain and swelling, they are self-limiting. Pathological flat feet are abnormalities in the bones or muscles of the foot, which are fixed, and do not correct themselves over time.
Pathological flat foot is caused by
- Tarsal Coalition
- Congenital Vertical Talus
- Accessory Navicular
- Hypermobile flat foot
- Tight Achilles tendon
- Peroneal spastic foot
- Z-foot or Skew foot
A simple way to distinguish between normal and diseased flat feet is to check for flexibility. A physiological flat foot is flexible, and using a little force one can bring the foot in a normal position. A pathological flat foot, on the other hand, is rigidly flat because of the bony or muscle abnormality. A normal foot is always hollow in the middle part because of the arches of the foot. A physiological flat foot is flat but the middle part can be made hollow using a little force. A pathological flat foot can never be made hollow and one can even feel a hard fullness in the middle part of the foot in place of the hollow.
A doctor may ask for an x-ray of the foot in standing position, in order to pinpoint the flatfoot towards one of the above diseases. This is not only helpful in diagnosis but also in knowing the extent of disease process and planning the type of treatment (medical or surgical).
Treatment of Flat Feet
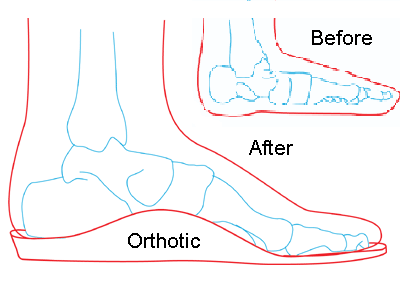
Physiological flat foot is a self-limiting condition, hence no treatment is necessary. However, if a child has severe pain and swelling, it necessitates treatment in the form of restriction of activity and painkillers for a period of 3-4 weeks. Children may also benefit from orthosis (braces)(Picture 1), which keep the foot in the normal position and hasten the recovery. However, these are highly uncomfortable, especially for a restless child. Foot exercises help to improve the tone of the foot muscles, which in turn strengthens the arch of the foot.
Picture 1: Flat foot Orthotic
(source: docpods )
Pathological flat feet are treated depending on the root cause of the flatness. They generally respond well to a combination of orthosis and foot exercises. If treatment has been delayed for many years, surgical repair becomes necessary. Flat foot surgery consists of lengthening the shortened muscles and releasing the contracted capsules of the foot joints. It is generally performed by an orthopedic surgeon experienced in foot disorders. After surgery the foot is kept in normal position using an orthosis. The recovery time is around 4 weeks after which the person is encouraged to walk with the orthosis. After 5-6 months the person can walk without any orthosis or crutches and the recovery is complete.