Head Pain Causes
Head pain or cephalgia refers to pain in any part of the head or of the entire head. This differs from a headache which is traditionally accepted as only referring to pain on the upper part of the head including the temples (sides), frontal (front), parietal (top) and occipital (back of the head) regions.
Despite this difference, the terms ‘head pain’ and ‘headache’ are often used synonymously.
Causes of Head Pain
Many of the causes of a head pain may also be the cause of a headache. However some of these causes may result in pain in the head without a headache as defined in the traditional sense. It is common that many causes of localized pain in the head may also result in a headache – for example, an abscess in the gum may cause pain in the mouth/gum area (localized) as well as referred pain to the forehead (which will be called a headache).
Head pain can be divided by pain of the structures :
- Inside the cranium or cranial cavity. The cranium is the part of the skull that surrounds the brain and this is known as intracranial causes of head pain.
- Outside the cranium and this includes other organs of the head or at times neighboring parts of the body that results in referred pain to head. This is known as extracranial causes of head pain.
Extracranial Causes
It is important to first identify the area of the head where the pain is located as this will give an indication of a possible cause. At times, the pain may feel like the entire head is paining, which is often described as head congestion, and this may be an indication of systemic causes. Understanding the characteristics of the different types of headaches may also help in isolating the cause of the pain.
The causes below are not the only causes but are the most common for the specific regions.
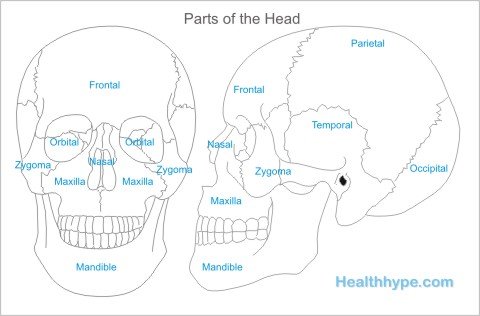
Parietal Head Pain
Pain on the top of the head may be due to :
- Hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Eye strain.
Occipital Head Pain
Pain at the back of the head may be due to :
- Neck muscle spasm (particularly spasm of the trapezius muscle)
- Whiplash
- Hypertension
- Occipital neuralgia
Temporal Head Pain
Pain on the sides of the head (temples) may be due to :
- Otitis media (ear infection/inflammation)
- Sore throat
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction
- Bruxism (constant teeth clenching)
Frontal Head Pain
Pain at the front of the head (forehead and above) may be due to :
- Sinusitis
- Eye strain
- Glaucoma
Orbital Head Pain
Pain around or at the back of the eye, including pain of the eye itself, maybe due to :
- Eye strain
- Glaucoma
Nasal Head Pain
Pain at the nose may be due to :
- Sinusitis
- Other causes of nasal congestion
Maxillary Head Pain
Pain of the upper jaw and below the cheek bones may be due to :
- Sinusitis
- Dental abscess
- Dental cavities
- Bruxism
Mandible Head Pain
Pain of the lower jaw – chin, sides of the jaw, angle of the lower jaw – may be due to :
- Dental abscess
- Dental cavities
- TMJ dysfunction (side of the mandible)
- Bruxism
- Mumps
Infection
Infections of the skin, connective tissue or individual organs of the head. For example sinusitis, strep throat or a gum abscess. Generalized infections, like influenza, are also known to cause head pain.
Mechanical Disorders
This may be due to disorders with the movable body parts in the head and/or neck area. For example – temporomandibular joint dysfunction (jaw), cervical spondylosis (neck).
Nerve Pain
Compression of nerves of the face and head, diabetic neuropathy or neuritis.This may also include cervicogenic head pain which is a result of pathology of the upper (cervical) spinal column, neck or shoulders. For example – occipital neuralgia (nerve pain) may cause headaches felt on the top, back and sides of the head. Also refer to facial pain spine for information on facial pain as a result of nerve compression.
Tumors
Benign or malignant tumors of the head and face which may also cause compression of the nerves.
Trauma
Injury to the head during impact, assault or falls. This may also relate to post-operative pain after surgery to the head. This may result in soft tissue inflammation, hematomas, inflammation of individual organs or bone fractures.
Strain or Exertion
Overuse may result in inflammation with accompanying pain. For example – clenching of the teeth may strain the masseter and/or temporalis muscle often causing jaw, cheek and forehead pain.
Systemic and Other Causes of Head Pain
- Hypertension
- Hypothyroidism
- Dehydration
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Hormonal causes like PMT and menopause although this may be linked to intracranial pain.
- Tetanus
- Fibromyalgia
- Arterial dissection (tear), particularly of the vertebral arteries, basilar and/or carotid artery.
- Constant coughing
- Fever
- Kidney failure
- Fatigue
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypercapnia
- ‘Blood poisoning’ like bacteremia, viremia
- Giant cell arteritis
- Food sensitivities
Drugs, Chemical Toxicity Head Pain
Head pain is among the common side effects associated with the use of pharmaceutical drugs. It is also a common withdrawal symptom.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPI’s)
- Statins
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI’s)
- Nitrates and other vasodilators
- Certain NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like indomethacin
- Diuretics
- Hormones (hormonal replacement therapy, oral contraceptives)
- Weight loss drugs containing sibutramine and ephedrine
- Overuse of medication (rebound headaches), especially painkillers
- Stimulant withdrawal (nicotine, caffeine)
- Alcohol and narcotic withdrawal and abuse
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Herbal supplements (example – ma huang, ginseng, St. John’s wort)
Psychiatric Head Pain
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Psychogenic
Intracranial Causes
Tumors
This will include benign and malignant tumors of the following intracranial structures :
- Brain
- Pituitary gland
- Meninges
- Skull (bone)
Infections
An infection of the intracranial may be primary or secondary due to the spread of the infection from other sites.
- Encephalitis
- Meningitis
- Abscess
- Subdural empyema
- Other infections like syphilis, cryptococcosis and tuberculosis (TB).
Hemorrhage (Bleeding)
Bleeding within the brain tissue itself or around the brain thereby causing compression.
- Intracerebral
- Subdural
- Subarachnoid
- Aneurysm rupture
Swelling
Swelling within the brain tissue or an increase in the fluid around the brain may be due to :
- Non-infectious meningitis
- Concussion and post concussion syndrome
Vascular
Fluctuations in the blood supply to the brain, resulting in increased blood flow to some areas and restricted flow to other regions.
- Intracranial hypertension
- Vasculitis
- Cerebral embolism
- Cardiovascular accident (CVA or stoke)
- Vascular malformations
Nerves
The cranial nerves originate from the brain and compression or irritation of these nerves may cause head pain.
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Optic neuritis (including diabetic neuropathy)
Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Hormones and neurotransmitters may have a multitude of effects that could result in head pain but it is more likely that these chemical alter the blood flow to the brain (vascular).
- Serotonin (low levels)
- Dopamine (low levels)
- Estrogen