How To Relieve Eczema And Live With It
Eczema is a broad term that is used to describe a range of different skin conditions. Most types are chronic. It either persists for years or recurs every now and then. Even milder forms of eczema tends to last for at least several months. Eczema should be treated with medication prescribed by a doctor. But there are a number of things that you can do to relieve or improve the condition. Some factors trigger it and others worsen eczema. The cornerstone of managing eczema is to avoid these factors or at least minimize exposure to it.
In most cases we know eczema to mean atopic dermatitis, the skin condition that tends to start from childhood and it often associated with hay fever and asthma. It is a result of immune dysfunction where a person becomes overly sensitive to otherwise harmless substances. It is not uncommon for people to refer to irritant contact dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, fungal infections of the skin (ringworm) and urticaria (hives) as eczema. All of these conditions may be different in nature but have common skin symptoms to atopic dermatitis.
Moisturize Skin Regularly

Your skin is unable to retain its normal moisture if you have eczema. It becomes dry and itchy. This irritates and damages the skin further and increases the likelihood of infections. Therefore you have to artificially moisturize the skin on a regular basis. This should be done several times in a day, especially after washing or bathing. It is not just about how often you moisturize but also the type of moisturizer. Always choose hypoallergenic products. If you are unsure whether a moisturizer is hypoallergenic or not, then opt for unscented products that have no additives. Thicker oil-based products like petroleum jelly are better as it protects the skin from the environment and does not easily wash off.
Avoid Scratching The Rash
Most types of eczema are itchy and its only natural to want to scratch the rash. But scratching makes it much worse. You may feel temporary relief from the itching but scratching damages the skin, increases the chance of skin infections and prevents the skin from healing. If you have to do something to relieve the itching then try to rub rather than scratch. Since you may not be able to exhibit the same restraint at night while asleep, keep your fingernails short to limit damage to the skin. Apply thick emollients or petroleum jelly over the area to reduce the friction on the skin in case you do scratch.
Identify Problem Foods

Some eczemas may be triggered or worsen when you eat certain foods. Therefore it is important to identify any foods that may be a problem and avoid it. This link to certain foods is more frequently seen among children rather than adults. Dairy, egg yolk, nuts, soy and wheat are some of the more allergenic of foods. However, there may be individual foods that are a problem specifically for you that are not a problem for others . It may be helpful to keep a food diary in order to isolate potential problem foods. Try an elimination diet and see if staying away from these foods does indeed provide some relief or improvement of the eczema symptoms.
Limit Exposure To Irritants
Apart from food, a host of other factors can aggravate eczema. It is important to identify these irritants and avoid them as far as possible. While it may vary from person to person, common irritants include prolonged exposure to water, dust, strongly scented soaps and lotions, detergents and even clothing particularly if it is made of wool. Therefore a person with eczema has to make significant lifestyle changes and careful product choices in everyday life. These irritants are not like allergens that trigger the immune system in a person with an allergic disposition. However, it does pose a problem when it makes contact with the affected skin which has lost its natural barrier function.
Reduce Environmental Exposure

Human skin is able to withstand a host of environmental factors when healthy. However, eczematous skin does not have the same resilience. Hot or cold, wind, water and sunlight are all irritants to the damaged skin. While the external environment cannot be avoided entirely. limiting exposure to these natural factors is nevertheless important. A thicker barrier cream, sunscreen creams and even clothing may help with reducing the exposure to environmental factors. Special precautions need to be taken on days that are very hot and sunny, cold, windy or wet, above and beyond the measures that most people would take.
Manage Stress Levels
Stress is known to aggravate a number of different chronic skin conditions. It may even serve as a trigger from some conditions that are in remission. Managing stress is therefore an important part of relieving and living with eczema. It requires multiple lifestyle changes not only to avoid stress but also to ease it. Learning proper coping skills, making changes in life to reduce stressful situations and taking the time to relax are some of the main ways to manage stress. Exercise is very helpful in this regard because it helps reduce stress levels in addition to the health benefits. Sleep is another important measure in managing stress as sleeping problems are common in modern life.
Precautions During Bathing
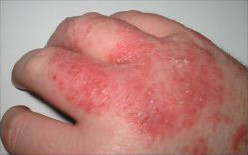
Bathing tends to “weaken” the skin but it is an important part of personal hygiene. The problem that arises with bathing is that many people use strongly scented and antibacterial soaps, very hot water and may scrub the body with abrasive bath accessories. All of these measures either dry the skin out excessively or irritate it. Therefore people living with eczema need to take some precautions when bathing. Firstly opt for only lightly scented or unscented soaps. Baby soap and baby shampoo are ideal. Try to use warm water but very hot water can dry and damage eczematous skin. Avoid abrasives. Rather use a soft sponge and rub gently. Always dry yourself thoroughly after bathing and apply an appropriate moisturizer immediately thereafter.
Treat With Eczema Medication
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that requires proper medical treatment. Although the skin rash and other symptoms may improve, the medication should not be discontinued unless a doctor advises to do so. Medication that has been prescribed for periods of remission – where no rash or other symptoms are present – needs to be continued as directed. Remission does not mean that your eczema has been cured and it may recur months or years later. Even if no medication is prescribed for the remission periods, it is important to continue practicing the simple lifestyle measures discussed above.





