Immune System – Structure and Function
The immune system of our body consists of series of cells, called white blood cells, which act in a sequential manner, like a planned military defense system. The various cells have specialized functions which are performed in a highly accurate and controlled manner. Though, the immune system is known to erroneously destroy one’s own body tissues, a process called autoimmunity. However, this can never overshadow the silent and sturdy protection offered by its cells from a variety of threats.
Organs of Immune System
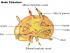
The bone marrow forms an integral part of the immune system by producing the different types of white blood cells. Bone marrow is stimulated during periods of excessive requirement to produce more quantities of a particular white blood cell. Thus, bone marrow is a positive regulator of the composition of blood, as it matches the production of a particular cell type with its requirement. Continuous production of cells (by replication) in bone marrow make it a common site for genetic instability, which can cause various cancers, like leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and so on.
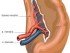
The lymph nodes are small training centers for the immune cells. They are also primary sites for analysis of destroyed cells and infecting organisms to find antigens. Antigens are specific marker proteins which are unique for a cell type or an entire infecting organism. Antigens stimulate the production of cells and chemical substances, specific to the infecting organism or cell. Thus, the immune response is highly specific in its destruction. This is highly important as the immune cells have the capacity to destroy even the normal cells of the body. Lymph nodes are present in groups in various parts of the body. Their involvement in the form of swelling or pain, generally gives a clue regarding the location of a disease.
The spleen can be considered a large lymph node, which acts as a non-specialized filter for infections, tumorous, or senescent blood cells. The spleen receives abundant blood and lymph supply, which helps it in controlling the quantity of blood cells present in circulation. Spleen can be considered as a negative regulator of the composition of blood, as it destroys the excessive and malfunctioning cells. The destroyed cells are segregated and the intact components are sent to the bone marrow or liver for reuse during the formation of new cells. Thus, spleen can also be called as a recycling department of our body.
Cells of Immune System
White blood cells (WBC) or leucocytes, can be broadly divided as granulocytes and agranulocytes, depending on the presence of granules in their cytoplasm. White blood cell count of a normal human is around 4000 – 11000 / 100 ml. of blood. The differential count of each type of WBC is an important investigation, that is routinely done along with WBC count. The relative dominance of granulocytes or agranulocytes, or a particular type of cell, in the differential WBC count, gives important clues towards correct diagnosis. The granulocytes carry destructive enzymes in their granules, which enable them to take quick action against the invading threats, like infections, tumors, and so on. Thus, granulocytes form the primary line of defense and make way for the action of the agranulocytes (lymphocytes), which have a further sophisticated mode of action.
Related Articles
- White Blood Cells – Granulocytes
- White Blood Cells – Lymphocytes
- Bone Marrow – Structure and Function
- Multiple Myeloma – Bone Cancer
- Multiple Myeloma – Symptoms and Staging
- Multiple Myeloma – Treatment