Itchy Legs – Causes, Pictures, Treatment of Leg Itching
Itchy legs is a common symptom that we all experience at times. The human skin is not just a protective layer but also a highly sensitive sensory instrument which may be afflicted with a number of sensations that can cause discomfort. Itching is one of the more uncomfortable sensations, second only to pain. Itching can vary in intensity and duration, from a mild itch of a few minutes to the severe itch that can last for weeks.
Why do the legs itch?
Itching of the legs is a common ailment that may arise without any underlying disease or obvious skin rash and often no cause can be found. It can nevertheless cause great discomfort and even affect a person’s daily functioning or sleep. Itching of the legs must be clearly differentiated from other sensations like leg pain or leg tingling. Pain may be due to actual injury to the skin and underlying tissue, while tingling may be a sign of neurological conditions.
The itch receptors are intended to serve as a means of warning a person of some irritation on the skin. It usually elicits the scratching action which not only provides some relief from itching but is also intended to remove the surface irritant. However, itching may occur without any irritant triggering these receptors on the surface of the skin.

Poor Hygiene
Proper hygiene ensures that sweat, sebum (oil) and dead skin cells that have not fallen off as yet, do not collect on the skin surfaces. With poor hygiene these substances remain on the skin and can cause irritation. This is one of the common causes of itchy legs.
On the other hand, excessive cleaning can cause the skin to dry and therefore cause itching. The repeated exposure to soap and water in combination with repetitive rubbing when bathing can also irritate the skin of the legs, thereby resulting in itchy legs. It is important to strike a balance to ensure regular bathing with adequate moisturizing.
Keratosis Pilaris (Chicken Skin, “Leg Acne”)
In keratosis pilaris, thickening of the hair follicles result in small, skin-colored, red, or brown bumps (goose bumps, chicken skin, leg acne) on the thighs, arms or other parts of the body. This is also one of the causes of itchy arms. Heat and irritation by clothes can provoke a bout of itching. Bumps in this harmless, genetically predisposed condition can be rubbed off but tend to recur.
Folliculitis
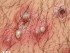
In staphylococcal folliculitis, there is an infection of the hair follicles with Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria). It presents as small red bumps sometimes with white centers which resembles acne, and tends to appear on the thighs, upper trunk, face or other body parts. These small bumps are usually itchy or cause a burning pain. Staph folliculitis, even if not treated, usually heals on its own in few days/weeks.
Picture 1. Staphylococcal folliculitis (source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
Jock Itch
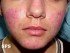
Jock itch is the common term for a fungal infection of the groin region and upper thigh. Jock itch is a red or brown papular rash on the inner thighs, genitals, and buttocks, caused by dermatophytes (tinea fungi). It commonly affects athletes and others who perspire excessively in the groin region. Jock itch, also known as tinea cruris, can be treated with antifungal medication.
Picture 2. Jock itch (Tinea cruris)on the inner thigh (source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
Leg Itch During Running
1. Leg Itch in Unfit Runners
A person who starts vigorous exercise like running after a prolonged period of inactivity can experience intense itch a short while into the activity. In a fit runner, the small arteries in the muscles usually open rapidly in response to high demand to blood, but in an unfit runner arteries may not open properly leading to a low oxygen state. This may cause irritation of adjacent nerves and therefore the sensation of itching (1). The condition tends to ease after a few days to weeks of activity as the body adapts to the increased demands.
2.Cholinergic Urticaria (Physical Urticaria, Heat Rash)
Cholinergic urticaria (hives) are red, swollen bumps or patches appearing on the skin as an allergic reaction to physical stimuli, like pressure of the clothes, exercise, heat, sunlight, cold, vibration, water, spicy food, or emotional stress. Injection with acetylcholine tends to provide rapid relief of symptoms, hence the term cholinergic.
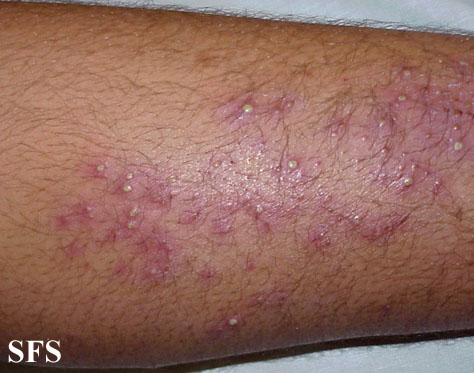
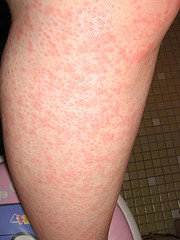 Picture 3. Cholinergic (physical) urticaria on the lower leg
Picture 3. Cholinergic (physical) urticaria on the lower leg
Some people experience intense leg itch during walking, running, after a hot shower or in a hot environment in general (3). The exact cause is not known, but could be related to an allergy to sweat itself. Sweat triggers the release of histamine causing itchiness in the legs or other parts of the body. It may also present with warm skin and small (up to 2-3 mm) bumps, which usually persist from 30 minutes to 2 hours. Some people may respond with a positive patch test to their own sweat.
Treatment. In severe itching, discontinuing exercise and removing tight clothing around the legs is advisable. A shower with lukewarm water can help to cool down the area and remove irritant sweat. If the itching does not stop, antihistamines like oral hydroxyzine may help with symptomatic relief. Read more about using antihistamines in itchy conditions.
Tendency of the skin to develop an urticaria-like rash, when stroked, is called dermatographism. It is quite common, mainly appears in young adults and often triggered by stress. The condition can last for several months and continuous treatment with non-sedative antihistamines is usually effective.
Additional Pictures of Cholinergic Urticaria
Prevention
- Do not exercise in hot humid weather.
- Take a shower before exercise to remove sweat, oil and any trapped dirt/dust.
- Use a moisturizing cream after bathing to prevent the skin from drying.
- Wear light, airy sportswear made from cotton.
- Wash new underwear or sportswear before the first use to prevent reaction to fabric dyes
3. Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis (EIA)
Anaphylaxis (Gk ana = against, phylaxis = protection) is a severe allergic reaction to certain, very specific allergens (allergy-triggering substances). Rarely, anaphylactic reaction can be triggered by exercise. A person who has ingested specific foods like shellfish or nuts; substances like alcohol; or medication like aspirin, ibuprofen, antibiotics, herbal supplements, diuretics, and started exercising up to 24 hours thereafter, may experience intense leg itch, warmth, fatigue, urticaria (hives) anywhere on the skin, facial swelling, difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or fainting within 30 minutes of exercising.
Symptoms can progress to shock or even death but this is rare. Symptoms of EIA do not appear after eating alone or exercising on its own, but only after a combination of eating certain foods followed by exercising. Symptoms also do not appear after hot shower or during stress as may be seen with hives. Exercising in cold weather or during menstruation can also trigger exercise-induced anaphylaxis in some individuals.
Treatment of severe allergic reaction in EIA is by an intramuscular injection of adrenaline (epinephrine) as soon as possible (3).
Prevention of EIA is by determining trigger foods and medication with skin patch tests and avoiding these triggers on the day of and immediately before the scheduled exercise program. An affected person should wear a medic-alert bracelet and never exercise alone.
4. Itchy Pants Syndrome (Pants Paresthesia Syndrome)
Wearing new pants or trousers made with synthetic material may irritate the skin and cause contact dermatitis. There are two type of contact dermatitis – irritant or allergic. Both these conditions cause severe itching. It can be prevented to some extent by using natural textiles like cotton and washing new clothing before first use. Friction of the pants against the skin may also cause itching.
Leg Itch After a Shower
Reasons for leg itch after a shower (usually hot shower) are similar to other causes of itching after bathing.
- Frequent use of very hot water and certain soaps like antibacterial and strongly scented soaps, removes the protective oily layer lining the skin thereby making the skin dry and itchy.
- Cholinergic urticaria (discussed above).
- Skin diseases like psoriasis or dermatitis.
- Blood diseases like polycythemia vera (rare).
- Psychological reasons.
Prevention. First the cause should try to be isolated. Use lukewarm water, avoid strongly scented and antibacterial soaps and use a moisturizing cream immediately after bathing. If the itch eases with these measures then the cause may have been excessively dry skin. In cholinergic urticaria, an antihistamine like Benadryl by mouth taken 30 minutes before shower usually helps. Skin patch tests may be able to identify topical causes like an allergy to specific soaps or shampoos.
Gravitational Eczema (Stasis Eczema, Venous Eczema)
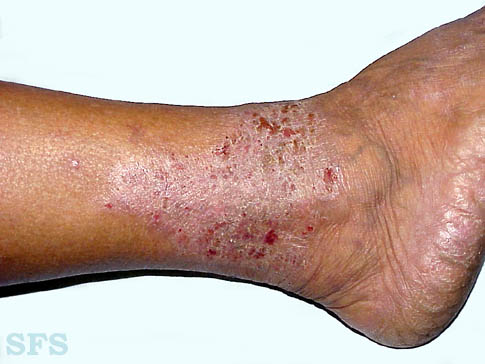
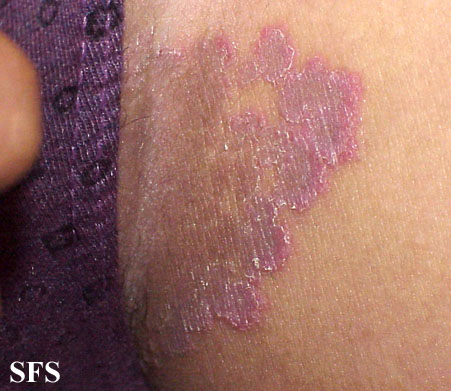
In deep vein thrombosis or in varicose veins, blood can not be pumped efficiently from the leg veins back to the heart. This results in blood pooling within the lower limbs. The lower legs may be red, swollen, itchy, and cracks and scaling may appear.
Picture 4. Stasis (gravitational) eczema on the lower leg. (source: Samuel Freire da Silva. atlasdermatologico)
Treatment. Underlying varicose veins or thrombosis has to be treated. Corticosteroid ointments help in severe inflammation.
Prevention:
- Avoid standing for long periods,
- Legs should be kept clean and drying prevented with moisturizing creams
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is the strong urge to move the legs because of itching and/or tingling that develops during a rest. The condition may severely affect sleeping. Symptoms partly or completely disappear with moving the legs or a short walk. This disorder is of neurological origin and the exact cause is not known.
There is no definitive cure for RLS. Treating underlying disorders is integral in management of RLS. Alcohol and caffeine should be avoided. Medications to treat Parkinson’s disease or analgesics are sometimes effective.
Other Causes of Leg Itch
Leg itch may be a part of generalized itch caused by different disorders, such as xerotic eczema, senile pruritis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, parasites, infections, obstructive biliary disease, chronic renal failure, malignancy, medications, neurodermatitis, diabetes, peripheral nerve damage, emotional stress or psychological disorders. It is therefore not isolated to the legs.
References:
- Dermatology Pictures. atlasdermatologico.com.br
- Rashes affecting the lower legs. Dermnet NZ
- Pruritus. Mayo Clinic
Reviewed and updated on 12 August 2018.