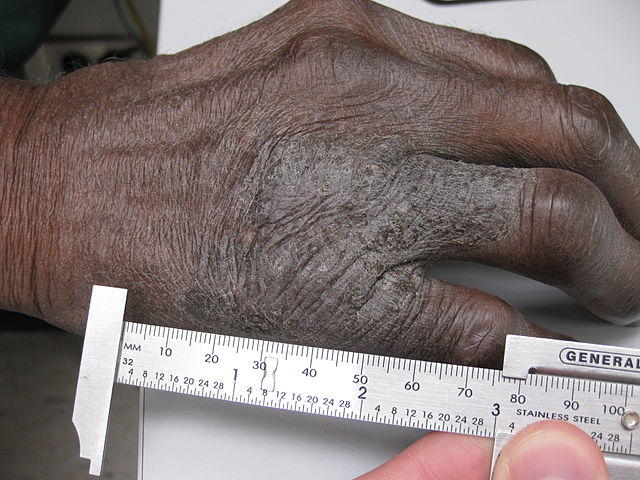
Neurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronicus) Chronic Scratch Rash
We all experience itching now and then. Sometimes it is due to skin irritation while at other times it occurs for no known reason. Intense and persistent itching, especially where there is a rash, is usually a skin disease. However, sometimes ongoing itching has no physical cause. It can be related to nervousness or anxiety but is just temporary. If the itching is ongoing and skin is scratched constantly over a long period of time, it can eventually lead to changes in the thickness and texture of the skin.
What is neurodermatitis?
Neurodermatitis is a disorder where the skin becomes thickened due to chronic itching. This thickening of the skin is known as lichenification and this condition is therefore also known as lichen simplex chronicus. The reason for the chronic itching is not always clear. In most cases there does not appear to be any other underlying skin problem. It is believed that a vast majority of cases arise with psychogenic itching or nervous itching. Although neurodermatitis is often focused around the symptom of thickening and leathery skin, it is itching that is the main symptom. The thickening and leathery skin occurs as a consequence of long term scratching. Therefore it is also known as chronic scratch rash.
Picture of lichen simplex chronicus (neurodermatitis or scratch disease) from Wikimedia Commons
Neurodermatitis Reasons
Lichenification is a medical term for thick and leathery skin. Repeated injury and irritation of the skin can cause lichenification. Scratching is one such form of injury and trauma. While most of us do not give the act of scratching much thought, the reality is that it causes minor injury to the skin. When this is ongoing, it causes structural changes in the skin. Some people are more likely to experience lichenification especially if they have skin diseases like atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Chronic Nervous Itching
The exact reason for the chronic itching that leads to neurodermatitis is often unclear. It is believed that it may have psychological origins as it is more often seen with anxiety and nervousness. However, it also appears that the nerves may actually be stimulated so the perception of itching is not imagined as such despite there being no clear cause of the itching.
It is thought that there is some inflammatory chemicals that causes stimulation of these nerves although there is no other signs of inflammation like redness, swelling and heat with scratching. Whether the itching is psychological in origin entirely or due to undetectable irritation and stimulation of the nerves is difficult to differentiate. It is also being questioned whether psychological stress and anxiety only aggravate the itching but do not actually cause it.
Itchy Skin Diseases
Recent studies that have indicated that when certain hair products like PPD (P-phenylenediamine) are stopped then the itching ceases. PPD is used in hair coloring products and is the main reason for conditions like hair dye allergies. Since chronic itching even without a rash can occur in people who have had atopic dermatitis (eczema) and psoriasis, it is possible that there is an underlying skin disease. However, only itching is present and the skin appears normal causing the skin disease to remain undiagnosed.
Lichen Simplex Chronicus Causes
The exact cause of the condition is unknown. The thickening and leathery appearance of the skin in neurodermatitis (lichen simplex chronicus)is secondary. This means that it is just a consequence of the primary condition – itching and scratching. The conditions discussed below may not be the cause of itching but some are a likely risk factor meaning that it increases the chances of pruritis (skin itching).
- Anxiety
- Dry skin (xerosis)
- Existing skin diseases like asteatotic dermatitis
- History of skin disease like atopic dermatitis (eczema) and psoriasis
- Insect bites and stings
- Medication like lithium
- Pollution (air) with traffic exhaust
- Poor circulation especially in the legs (venous insufficiency)
- Psychological stress
- Shingles scars
- Wound scars
Lichen Simplex Chronicus Symptoms
Scratching and Itchiness
It is often debated whether the chronic scratching is always due to itching. Since itching is a subjective symptom it can not be conclusively substantiated that it is present. It is possible that a person may scratch excessively despite not feeling any actual itch. Nevertheless, most people with neurodermatitis report constant itching usually at a single area. Most of the time the persistent itch does not extend beyond this area.
Nervousness and anxiety are popular trigger and exacerbating factors. Activity is another factorseems to alter the itching in most patients. Being still or quiet tends to bring on the itching or worsens it. On the other hand, being active seems to ease the itching. However, this may not be due to a physical reason. Instead activity may distract the person who then does not focus on the itch. Once again, this is a largely subjective experience. Although persistent, the itch comes and goes (intermittent). Scratching provides short term relief.
Thick and Leathery Skin
Thickening of the skin with a leathery texture and appearance is another defining feature of neurodermatitis. It occurs secondary to the itch. Initially there is redness of the skin due to the constant irritation caused by scratching. Since it occurs in areas that are easy to reach, lichen simplex chronicus rash is more often seen on the :
- Scalp
- Back of the neck (nape)
- Wrist
- Top of the forearm (extensor surface)
- Inner elbow
- External surface of genitalia
- Upper inner thigh
- Back of knee
- Lower leg
- Ankle
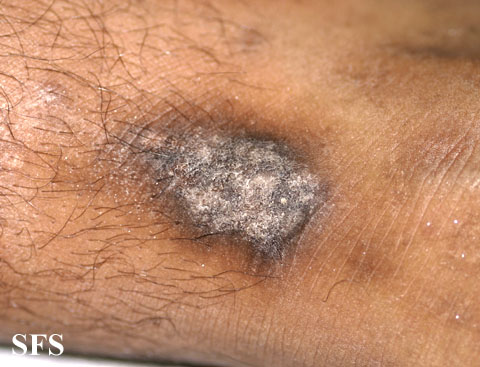
The thickened area is typically red but with time the skin becomes discolored – dark brown to almost black in some people (hyperpigmentation). It is a clearly demarcated patch and there may be signs of scratching on and around it as well. There may also be some degree of scaling of the affected skin but it is not as severe as with other skin conditions like psoriasis.
Neurodermatitis Pictures
Pictures from Dermatology Atlas Brazil courtesy of Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D.
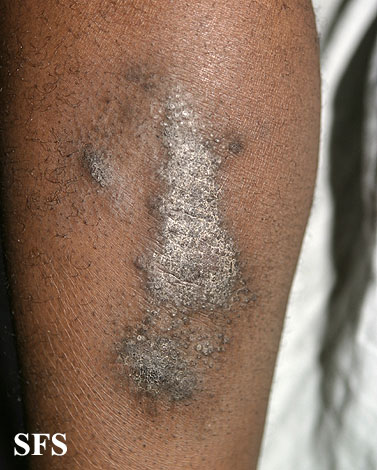 | 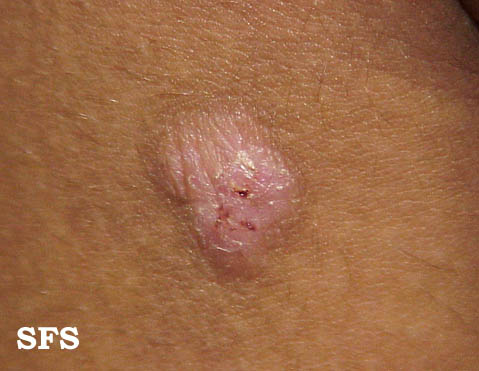 |
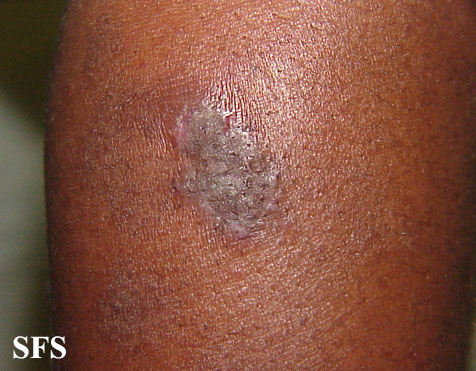 |  |
Neurodermatitis Diagnosis
Neurodermatitis cannot be diagnosed definitively without excluding other skin diseases. Although the appearance of the skin rash and the history of scratching are the main indicators, many other skin diseases may have similar signs and symptoms.
Neurodermatitis Tests
The main tests that are done for neurodermatitis includes :
- Patch testing to exclude diseases such as allergic contact dermatitis.
- IgE blood test which will indicate an allergic condition.
- Skin biopsy to exclude skin diseases like psoriasis.
- Microscopic examination of potassium hydroxide wet mounts of skin scrapings to exclude fungal infections. Fungal cultures may also be helpful.
Differential Diagnosis
There are a range of skin diseases that appear similar to neurodermatitis. The more common of these conditions include :
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Atopic dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis – allergic or irritant
- Dermatophyte (fungal) infection
- Plaque-type psoriasis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Stasis dermatitis
Neurodermatitis Treatment
There are a number of different treatments utilized for neurodermatitis. However, the key to treatment is stress management and behavioral therapy to reduce scratching. Therapy in this regard is a long term approach. For short term relief, the following measures may be implemented :
- Antihistamines help reduce the itching and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids suppress inflammation and can be used orally (tablet or capsule) or topically (creams and ointments).
- Antidepressants may help reduce itching and scratching. Sedatives and tranquilizers may be beneficial as well.
- Salicylic acid and coal tar applications may helpful for the thickened skin.
- Moist dressings can be applied over the affected skin which have been treated with medicated creams to increase absorption.
Thick Leathery Skin Prevention
There is no definitive preventative measures for neurodermatitis as the exact cause is unclear. The same contributing factors may exist in many people yet not all will develop the condition. Once the primary symptom of chronic itching starts, the key to preventing the thickening of the skin is to not scratch. However, it is unavoidable for most people. One of the preventative measures in this regard is to apply thick layers of barrier applications like petroleum jelly. This reduces the friction caused by scratching.
References :