Non-Digestive Causes of Abdominal Pain
The abdominal cavity is largely occupied by the digestive tract. This includes the alimentary tract that runs from the mouth to the anus, and other organs associated with digestion like the liver, gallbladder and pancreas. Most cases of abdominal pain is associated with the digestive tract, particularly the part of the tract that lies within the abdominal cavity. Abdominal pain can be a common non-specific symptom meaning that the cause may not involve the abdominal cavity, its organs or structures. This is known more accurately as non-alimentary abdominal pain and some of the causative factors may be associated with serious and even life-threatening conditions.
Most of us will experience abdominal pain several times in life – from childhood right through adulthood. Often acute bouts of abdominal discomfort and sometimes even pain has no clear cause and may pass spontaneously in a short period of time with no need for treatment. At other times, abdominal pain is largely associated with the alimentary tract and this will present with typical features including indigestion, belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, borborygmi (loud abdominal sounds), flatulence, diarrhea, and constipation. Changes in appetite and even weight may be prominent in more chronic causes of alimentary abdominal pain. With non-alimentary abdominal pain, the presentation is not always clear. Abdominal pain is present and digestive symptoms are absent. This can be even more confusing when abdominal pain and digestive-related symptoms are not due to any disturbance within the digestive tract specifically.
Understanding the possible causes of non-digestive abdominal pain, identifying concurrent symptoms, risks that make certain people more likely to be suffering with these conditions and seeking medical attention as early as possible can be life-saving. Self diagnosis should be avoided as far as possible but knowing what these symptoms may mean is important.
Non-Alimentary, Non-Digestive Abdominal Pain
Non-digestive abdominal pain, or more accurately non-alimentary abdominal pain, is any discomfort or pain in the abdomen that does not emanate from the alimentary tract and is not associated with the activities and functions of the tract. Any pain, irrespective of the location, that is accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, breathlessness, pale or bluish discoloration of the skin and associated with confusion and/or loss of consciousness should be treated as a medical emergency. Immediate medical attention is therefore required.
Causes of Non-Digestive Abdominal Pain
The more common diseases of certain non-digestive organs and systems presenting with abdominal pain are discussed below. Some of these conditions may only affect males or females.
Heart
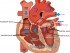
A myocardial infarction, or commonly heart attack, is the death of a portion of the heart muscle most frequently as a result of a severed interrupted blood supply. Risk factors include obesity, hyperlipidemia (high level of fats in the blood), hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes mellitus, cigarette smoking and advancing age. Other signs and symptoms may include :
- Central chest pain radiating to the arm (usually left), neck and jaw.
- Excessive perspiration.
- Nausea.
- Breathlessness.
- Dizziness.
- Fainting.
Blood Vessels
An aortic dissection is the accumulation of blood in the middle layer of the aortic wall due to a tear in the inner lining. It is an uncommon condition associated with risk factors such as an aortic aneurysm, hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis, aortic valve defect and coarctation of the aorta. Other signs and symptoms may include :
- Severe chest pain radiating up to the neck or down the back.
- Upper back pain.
- Perspiration.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Fainting.
- Muscle weakness or paralysis.
Lungs and Pleura
Pleuritis, also known as pleurisy, is inflammation of the lining surrounding the lungs. Most cases are due to an infection any may be associated with the flu (seasonal influenza), pneumonia, tuberculosis, chest trauma, radiation exposure, cancer or pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung). Other signs and symptoms include :
- Chest pain when breathing, only during inhaling and exhaling.
- Dry cough.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Fever (not always).
Skin
Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a painful skin condition associated with the reactivation of the varicella zoster virus. It is not common and is more likely to occur in older patients and immunocompromised individuals. Shingles is actually a condition of the nerves but presents with prominent skin symptoms. The virus causes chicken pox, which is more common in children, and then may remain latent among the nerves for years or decades. The typical distribution involves dermatomes – areas of the skin supplied by a single spinal nerve. Signs and symptoms may include :
- Blistering skin rash.
- Pain, burning and tingling, sometimes numbness.
- Itchy skin.
- Fever.
- Headaches.
Spinal Column and Cord
Spinal collapse or vertebral collapse is a fracture of the vertebral bone leading to injury of the soft tissue and nerves. It can occur gradually and is often painless. However, acute vertebral collapse is a painful condition. It is often associated with osteoporosis, cancer, hemangiomas (benign blood vessel tumors) and severe trauma. Mid-thoracic vertebrae and T10 to L2 vertebrae are more commonly affected. The signs and symptoms include :
- Back pain
- Muscle weakness and/or paralysis
- Restricted movement due to pain
- Tenderness over affected vertebrae
Spinal cord compression is pressure on the spinal cord from surrounding tissue or protruding structures. It is a medical emergency that can arise with trauma, tumors, abscess, bulging intervertebral disc, inflammatory diseases and hematomas. Other signs and symptoms may include :
- Abnormal sensations (paresthesia)
- Paralysis of limbs
- Urinary retention or incontinence
- Fecal incontinence
- Hyper-responsive reflexes
Females
Several conditions of the ovaries and fallopian tubes may cause abdominal pain, sometimes without any other symptoms. The main causes include inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis), ectopic pregnancy and ovarian torsion. The symptoms may be sometimes difficult to identify if there is no vaginal discharge or bleeding.
Salpingitis is more commonly due to an infection. Symptoms may include :
- Lower back pain
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Intermenstrual bleeding/spotting
- Severe period pain
Ectopic pregnancy involving the fallopian tubes (tubal pregnancy) is the most common and occurs when the fertilized egg implants in the tube and not the uterus.
- Vaginal bleeding in a pregnant woman
- Lower abdominal pain or cramping more on one side
- Dizziness
- Fainting
Ovarian torsion arises with rotation of the ovaries to an extent that interrupts its blood supply.
- Sudden severe one-sided pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
Males
Testicular torsion is the rotation of the testes causing the spermatic cord to twist and the blood supply to the testes is interrupted. It is more frequently seen in teenage boys and less frequently in young children or even infants. Other signs and symptoms may include :
- Severe testicular pain radiating to the abdomen
- Swollen testes
- Tenderness of the testes