Numbness and Tingling of the Tongue (Paresthesia)
What is tongue paresthesia?
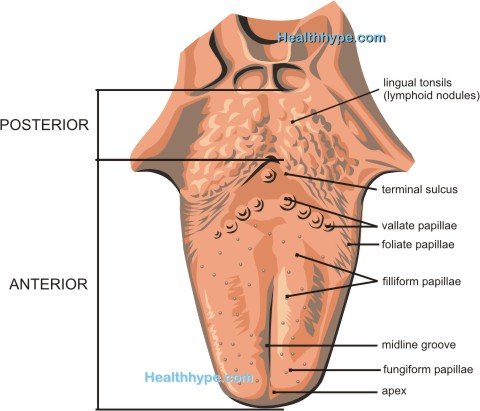
Paresthesia of the tongue is any abnormal sensation from the tongue which includes sensations such as numbness, tingling or prickling (“pins and needles”). The tongue is one of the most sensitive organs of the body. Sensations of temperature, pressure, texture and pain are often heightened on the tongue when compared to the skin and the tongue is also capable of a unique sensory function – taste. The tongue has a rich nerve supply and part of the reason why the tongue is so sensitive is that it is lined with a delicate mucuous membrane. As with any part of the body, there may at times be abnormal sensations from the tongue. When this involves the sense of taste, it is known as dygeusia. If it affects the other sensory components of the tongue leading to sensations such as numbness, tingling, prickling (“pins and needles”) or burning then it is known as paresthesia.
Meaning of tongue parestheia
Abnormal sensations on any part of the body indicates a problem with the receptors, nerves or brain centers responsible for processing the signals. Receptors on the tongue are the nerve endings that have special functions. Some are able to detect changes in temperature (thermoreceptors), others can detect pressure and texture (mechanoreceptors) and there are also receptors for pain (nociceptors). The taste buds have the receptors for the sense of taste. When these receptors are exposed to specific stimuli, it elicits electrical impulses. The strength of these impulses depend on the degree of stimulation. For example, exposure to very firm pressure on the tongue will cause stronger impulses from the mechanoreceptors than light pressure. These impulses then travel along the lingual nerve to specific areas of the brain where it is decoded and experienced as a specific sensation. This process is similar in every part of the body. The only exception with the tongue is that it is also capable of detecting the chemical composition of different substances it is exposed to which is known as the sense of taste.
Paresthesia can affect any part of the body, and does not only occur on the tongue. It indicates a problem with a receptor or nerve, and less often with the brain. This means that the receptor or nerve is stimulated although there is no stimulus present on the tongue. In these instances, a person may feel heat, cold, pressure or even pain for no clearly evident reason. Tingling, prickling (pins and needles) or burning of the tongue are other sensations that may be present which is a more clear indication of a disorder with the receptor or nerve. Sometimes, as is the case with numbness, the disorder with the receptor or nerve means that it is not able to detect different stimuli to the same degree as is normally the case. Irrespective of the type of sensation, the presence of these abnormalities indicates a problem with a receptor or nerve that may be a sign of nerve inflammation, compression or damage. Similarly these may be an underlying problem in the sensory center within the brain where the nerve impulses are received, decoded and interpreted as specific sensation.
Causes of tongue numbness and tingling
Medication and Substances
Although the mechanism of tongue numbness and tingling has been attributed to disorders of the receptors, nerves or brain centers thus far, there are instances where these sensations may occur due to substance use. Ingesting caustic agents, topical anesthetics, certain types of alcohol, prescription drugs and illicit substances (narcotics) may cause abnormal sensations when exposed to the tissue of the tongue. This is usually short term and should pass on its own unless it permanently damages the tissues of the tongue or nerves. Numbness and tingling of the tongue with prescription medication is more likely to be due to a side effect or drug interaction and does not usually cause damage to the tongue or nerves.
Poisoning and Toxins
A number of natural or artificial toxins can cause numbness or tingling of the tongue. In most cases these are substances that are ingested and directly exposed to the tongue. One of the more common of these natural poisons is the ciguatera toxin which is found in certain types of fish and marine life, like baracuda, sea bass and eel and causes ciguatera fish poisoning. Another types of poisoning is scombroid food poisoning which may arise with eating decayed fish that were not properly refrigerated.
Fugu is a pufferfish that contain large amounts of a deadly toxin known tetrodotoxin. It is concentrated within the skin, liver and ovaries of the fish. Fugu can only be prepared by licenced chefs or it can be lethal. It is, however, common practice for a small amount of the toxin to be retained in the fish to enhance the culinary experience. This can cause numbness and tingling of the tongue and lips which passes shortly thereafter. However, these symptoms may also be present with poisoning and if not prepared properly with just a minimal dose of the toxin, it can be lethal.
Poisoning with other substances, particularly heavy metals, may also cause numbness and tingling of different parts of the body including the tongue.
Dental Surgery
Numbness of the tongue, lips, the inner parts of the mouth and face is a common effect of anesthesia use in dental procedures. As it wears off there may be some tingling, later followed by aches and pain as a result of the trauma to the mouth. This is temporary and will pass as the tissue heals. However, in some cases there may be nerve damage during the course of the dental procedure. This can lead to permanent numbness and/or tingling of the tongue. Such complications may arise with major dental procedures such as a root canal, wisdom tooth extraction, dental implants where there is injury or damage of the lingual nerve that supplies the tongue.
Trauma
Any injury to the tongue may cause pain as well as other abnormal sensations like tingling as a result of inflammation of the tongue (glossitis). Severe injury that damages receptors or nerves of the tongue may lead to numbness, which may follow acute pain. Common injuries may be a result of eating or drinking very hot foods and beverages, strong acids or alkalis, tongue piercings or biting the tongue. Very cold foods or beverages may also cause temporary numbness or tingling. In these cases, the cause is usually clearly identifiable. Radiation exposure to the mouth, usually as a part of cancer treatment, can irritate the tissues of the tongue, receptors or nerves. Another possible cause is tobacco chewing or areca nut and betel leaf chewing but numbness and tingling of the tongue is more likely to occur in occasional users.
Infections
A number of infections may involve the tongue or nerves supplying the tongue thereby leading to pain more commonly or paresthesia. The most notable of these is a herpes simplex virus (oral herpes) or reactivation of varicella zoster (chickenpox virus) causing shingles (herpes zoster). Other common tongue infections like oral thrush (candidiasis) is unlikely to cause symptoms like numbness or tingling of the tongue but it is possible.
Vitamins and minerals
An excess or deficiency of certain micronutrients may also lead to paresthesia of the tongue. The main imbalances that may lead to numbness and tingling of the tongue is an excess of deficiency of calcium, sodium or potassium. A deficiency of vitamin B12 may also cause numbness and tingling of the tongue.
Other causes
There are various other causes which can cause paresthesia of the tongue although numbness and tingling may also be experienced on other parts of the body as well, and not specifically in the tongue.
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Tumors pressing against the nerves or a brain tumor
- Burning mouth syndrome
- Hypothyroidism
- Migraines
- Facial palsy