Oral Thrush (Candidiasis) Mouth Yeast Causes, Pictures, Treatment
Thrush is usually considered to be a vaginal infection with yeasts in women but the fungi can also infect other parts of the body, such as the skin and even damaged skin. Since most of these infections are caused by the Candida species of yeasts, it is also known as candidiasis. Oral thrush or oral candidiasis specifically refers to this type of infection of the mouth. It may be seen in both adults and children for a number of different reasons.
What is mouth thrush?
Oral candidiasis, also commonly referred to as thrush of the mouth, is a fungal infection of the mouth lining and tongue caused by the Candida species of yeasts. The main organism is Candida albicans. It was mainly seen in poorly controlled diabetes, children using oral steroids and newborns. However, since the emergence of HIV it is becoming a more frequently seen mouth infection in people living with HIV and AIDS.
Although mouth thrush can be effectively treated, it tends to recur in people with chronic immune system impairment. Complications are more likely to be seen in these cases. Although uncommon the yeast infection can extend all the way down the throat and esophagus and even reach the intestines. Sometimes it may even extend beyond the alimentary tract to the liver, lungs and heart valves.
Causes and Spread
Oral thrush is caused by Candida albicans. These yeasts are normally found in varying numbers on the skin surface, vagina and mouth and does not usually cause a problem. However, if these environments are affected then there can be an overgrowth of the Candida yeasts. Its growth is also controlled by the immune system and candidiasis is mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems.
Thrush of the mouth affects as many as 4 out of 10 babies about a month after birth but is rare in the first week of life. It is also seen in children and adults who use antibiotics and corticosteroids. Antibiotics destroy some of the normal oral flora (natural mouth bacteria) which allows for a fungal overgrowth. Corticosteroids impairs the immune system.
Apart from poorly controlled diabetes mellitus and HIV/AIDS, candidiasis may also occur with any other condition that weakens the immune system. This include malnutrition, cancer and undergoing cancer treatment. People who wear dentures and suffer with a dry mouth are also at a greater risk of developing mouth thrush. The use of birth control pills and even the hormone changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of thrush.
How is it spread?
Oral candidiasis does not always involve transmission of the organism to an uninfected person as is the case with most infections since most people already have these yeasts residing in the mouth, albeit in small numbers. The infection is largely due to an overgrowth of the yeasts under certain conditions. Newborns may contract the yeast as they pass through the birth canal and it is possible for it to be transmitted during kissing.
Signs and Symptoms
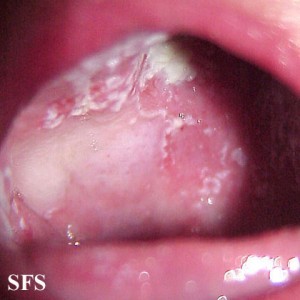
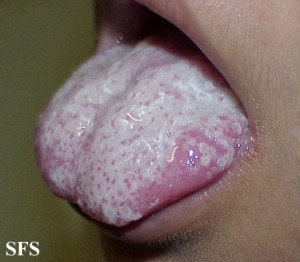
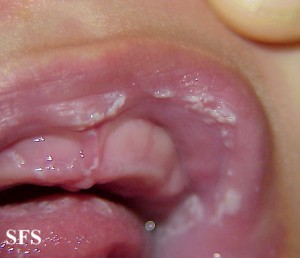
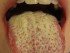
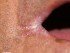
The fungal lesions appear as tiny white spots on the oral mucosa. This may include the inside of the cheek, inside of the lip, palate, gums or tongue and can extend as far back to the tonsils. These spots slowly grow into larger patches. It may have a creamy white appearance that is sometimes said to resemble cottage cheese. Many times there may be claims of a dry cottony sensation in the mouth and even loss of taste.
Unlike some of the other conditions that cause white patches inside the mouth like leukoplakia, the fungal spots and patches can be scraped. However, it may result in bleeding at the site after removal and there is usually significant inflammation under the lesion. This inflammation, evident as redness and swelling, may be seen around the white lesion at times.
Other Symptoms
In children there may also be thrush elsewhere on the body, like a fungal diaper rash that is also caused by yeasts. Oral candidiasis often arises in late HIV infection and it presence is often a poor sign of the progression of HIV infection. Pain and difficulty swallowing may be present with more severe cases and a fever is only seen when the infection spreads beyond the throat into the esophagus.
Pictures of Oral Thrush
Diagnosis of Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is often diagnosed with a physical examination of the lesions in mouth. If necessary, a small scraping may be taken and the sample is then examined under the microscope. In severe cases particularly in people with a very weak immune system, the thrush may extend to the throat and even down the esophagus. In these cases a throat culture or even an endoscopic examination may be done.
It is important to exclude other causes of tongue coating.
Treatment of Oral Candidiasis
The choice of treatment depends on a person’s age and whether there is immune deficiency. Otherwise healthy newborns may not always be treated but there is a risk of recurring infections especially with breastfeeding so treatment may still be advisable. Contrary to popular belief dietary change alone cannot treat existing oral thrush and a medical professional should be consulted.
Antifungal medication is available in different forms and for people with a healthy immune system, a liquid that can be used like a mouthwash may suffice. Fluconazole and nystatin are usually the medication of choice but clotrimazole and miconazole may also be considered. However, in people with a weak immune system stronger medication may be necessary, like amphotericin B.
Prevention of Mouth Thrush
- Good mouth hygiene can help in the prevention of mouth thrush. This includes proper brushing and flossing. However, excessive use of an antimicrobial mouth rinse can contribute to oral candidiasis in predisposed individuals.
- Ensure that dentures fit properly and regular dental checkups is always advisable, especially for people at risk of oral thrush like diabetics.
- Foods that contain sugar and yeasts should be consumed in small quantities. This includes beer and bread, However, as stated dietary modification cannot treat an existing oral fungal infection.
- Remedy mouth dryness depending on the underlying cause. Mouth breathing is a common contributor to dry mouth and often due to nasal congestion which should be treated.
References: