5 Signs of Yeast Infection (Candida) in Women and Men
Yeasts are a type of fungus that naturally occur on and in the human body in small numbers. Most of the time it does not pose any problem to human health but under certain circumstances these fungi can multiply and lead to an overgrowth on the skin surface or within cavities like the mouth or vagina. Although not usually serious or life-threatening, an yeast infection can cause significant discomfort but is easily treatable.
Parts of the Body Infected by Yeasts
Most yeast infections in humansare caused by the Candida species of yeast and specifically Candida albicans. Therefore the term candidiasis refers to an yeast infection with Candida species of yeasts but sometimes this term is used loosely to refer to any type of yeast infection. The more likely areas to be infected with an yeast infection are the vagina, mouth and skin but an overgrowth within the bowels can also occur.
Vaginal Thrush
It is the vagina that is more frequently infected with Candida yeasts which is also known as vaginal candidiasis or vaginal thrush. It affects three in four American women at some time in their life. It is more likely to occur in women who use antibiotics for long periods of time, take hormone medication, douche regularly or have weakened immune systems.
Mouth Thrush
Oral candidiasis (mouth thrush) is not as commonly seen as vaginal thrush. It is more likely to arise in immune compromised people, as is the case with HIV/AIDS and poorly managed diabetes mellitus. The use of immune-suppressing medication also plays a role. The infection involves the tongue, palate, inner cheek and may even extend to the throat and the tonsil may also be affected.
Skin Thrush
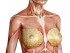
Candidiasis of the skin is less common and tends to arise in the folds of the body or areas that are covered. It usually infects the skin when there is deep break in the skin like where there is chaffing, irritation from heat and moisture or scratching (intertrigo). The groin, armpits and under the breasts are some of the more likely areas to be infected. It also commonly affects the buttocks of babies leading to severe diaper rash.
Most skin fungal infections are not caused by yeasts but by dermatophytes that only cause superficial infections. The feet, groin and scalp are common areas infected. These dermatophyte infections are often referred to as ringworm due the characteristic red ring appearance of the skin rash. The exception is tinea versicolor which can affect the face, arms and torso.
Read more on ringworm.
Intestinal Thrush
Yeast overgrowth can also arise in the bowels but this is uncommon unless a person has a weakened immune system as is seen with HIV/AIDS or has use oral antibiotics for a prolonged period of time. The population of these yeasts are normally kept with limits by the normal intestinal flora (also crudely referred to as the “good bowel bacteria”). The immune system also plays a regulatory role in the yeast population within the bowels.
Can men get genital thrush?
While oral, skin and intestinal thrush can affect both men and women, it is often not known that men can also get genital thrush just as women have vaginal thrush. Genital thrush (candidiasis) in men is uncommon whereas vaginal thrush in women is very common. The Candida yeast infects the tip of the penis, known as the glans penis (head of the penis) and foreskin (if present).
Genital thrush in men can occur for the same reasons as vaginal thrush occurs in women. Thsi includes prolonged use of antibiotics, immune suppressing drugs, weakened immune system (HIV/AIDS, diabetes and so on) and in uncircumcised men who do not practice good hygiene. The yeast can be transmitted to a man from a women with vaginal thrush during intercourse. However, this is not a sexually transmitted infection.
How to spot yeast infections
Since vaginal and mouth yeast infections are the most common, the following signs and symptom may help in spotting these infecions when it occurs. However, it is always advisable to consult with a medical professional who can confirm the diagnosis. At times further diagnostic testing like swabs and scrapings which are examined under a microscope are necessary.
It is important to remember that several other conditions may cause similar signs and symptoms as vaginal or oral thrush. With vaginal thrush, urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted disease need to be considered. With oral thrush, conditions like oral leukoplakia may also need to be excluded. Although thrush is not very serious, it is important to see a medical professional and not attempt to treat these conditions at home without supervision.
Itching
One of the most common symptoms of vaginal thrush is itching. It is felt in the vagina and on the outer parts (labia and vulva). The itching is moderate to severe in most women. Scratching the outer parts may further worsen the condition as it injures the skin. This itching is usually not felt in the mouth in oral candidiasis (mouth thrush) although there are other sensations like a cotton feeling in the mouth.
Pain
Pain and soreness are also common symptoms in the vagina (vaginal candidiasis) and mouth (oral candidiasis). The severity of the pain and soreness can vary. In oral candidiasis (mouth thrush) the pain may be severe enough to make eating and swallowing difficult. In vaginal candidiasis the pain may extend from within the vagina to the vulva with a burning sensation that worsens during intercourse or when urinating.
Discharge and Coating
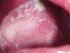
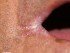
Candidiasis causes the formation of a thick, white discharge that is often described as a ‘cottage cheese’ appearance. In vaginal thrush this appears as a ‘cottage cheese’ vaginal discharge that typically does not have any odor. With mouth thrush there are usually creamy white plaques that coat the inside of the mouth, including the tongue, cheek and roof of the mouth (palate).
Rash
Apart from the discharge and coating, there is also redness and swelling of the vulva (vaginal thrush) and the oral cavity (mouth thrush). The redness is usually worse with severe infections. Any irritation, like scratching, may also exacerbate the redness. This redness may extend to the corners of the mouth in oral thrush. Scraping the coating in mouth thrush also reveals redness and may cause bleeding.
Read more on skin yeast infections.
Other symptoms
- Profuse watery vaginal discharge
- Loss of taste (mouth thrush)