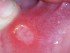
Sore Palate – Causes of Pain on Roof of Mouth
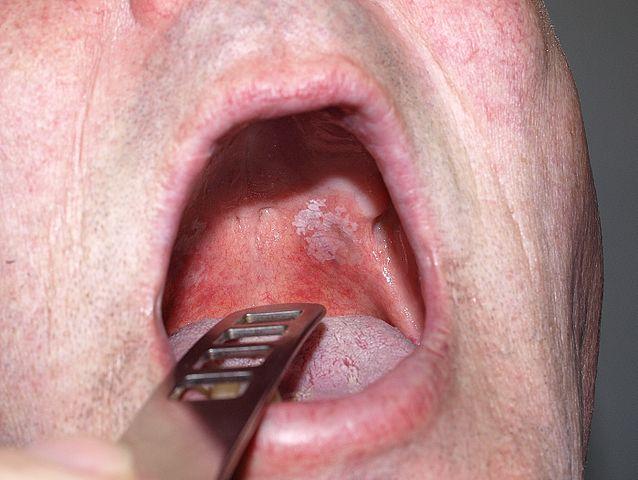
Pain in the mouth is common and can affect the entire mouth in which case it is referred to as stomatodynia or only certain parts like the tongue, cheeks or palate. While the causes of pain in certain parts of the mouth may be overlap, sometimes there are specific causes that only affect a single area. A sore palate refers to discomfort or pain in the roof of the mouth, which separates the mouth cavity from the nasal cavity.
Parts of the Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth that is formed by bone and cartilage. The front two-thirds is made up of bone that is part of the skull while the rear one-third is made up of cartilage. A delicate mucosal tissue lines both the hard and soft palate and is continuous with the rest of the mouth lining.
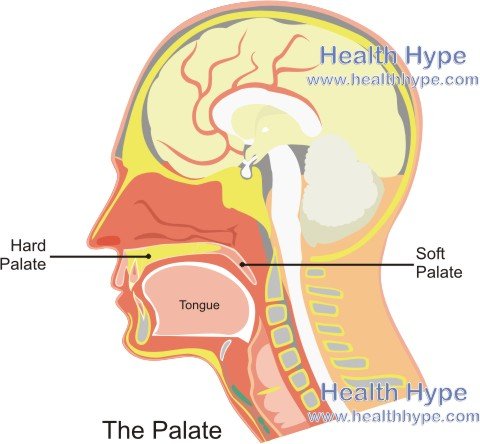
The palate separates the oral (mouth) cavity from the nasal (nose) cavity until these two cavities meet at the back of the mouth where it becomes continuous with the throat. The latter soft palate is free to vibrate although the cartilage ensures that is flexible yet fixed. Read more on palate anatomy.
Causes of Sore Palate
Many of the causes of a sore palate are the same as a sore mouth in general or a sore tongue. Sometimes nasal and throat conditions can also cause palate pain as the mouth is continuous with these cavities. There is a wide range of causes of a sore palate and the more likely causes of both acute and chronic pain or soreness of the palate has been discussed below.

Dry Mouth
Dryness can lead to soreness of the mouth, including the palate in some cases. There are a number of different reasons for a dry mouth. Reduced saliva secretion may be seen with dehydration or conditions like Sjogren syndrome. Sometimes the dryness is due to the flow of air rather than a lack of saliva. This is seen with mouth breathing often due to nasal congestion.
Injury
This is the most common cause of a sore palate. It may mechanical in nature like during tooth brushing, with eating very hot foods that scald the palate and foreign bodies like sharp bones. Chemical causes may include repeated vomiting, tobacco chewing or smoking, very strong alcohol and illicit substances that may be smoked like crystal meth. The soreness is usually preceded by a specific event when these substances are consumed.
Acid Reflux
Acid reflux (gastroesophageal reflux disease) is one of the more common causes of a sore palate that is often ignored. The backward flow of stomach acid can reach as high up as the back of the throat and even the mouth. The corrosive nature of the stomach juices causes irritation and inflammation of the delicate mouth tissues including the palate. Reflux is often worse at night and the soreness of the palate may be most pronounced in the morning upon waking.
Infections
A number of different infections can cause a sore palate, often in conjunction with a sore mouth or sore tongue. This includes bacterial, fungal and viral infections.
- Bacterial infections may be caused by a host of different bacterial species, especially when there is injury or some pre-existing disease of the mouth. Streptococci which can cause strep throat may extend to the palate. Some of these bacterial infections may be sexually transmitted like gonorrhea and syphilis.
- Fungal infections are less common an are usually seen in people who suffer with a severely dry mouth, experience chronic injury to the mouth or have a weakened immune system like with HIV infection or poorly managed diabetes. The main fungus to infect the palate is Candida albicans which causes oral thrush.
- Viral infections may arise with a host of different viral species. One of the more common viruses to cause a mouth infections is herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) which causes a mouth infection known as herpetic stomatitis. Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV) and varicella zoster (chickenpox virus) are other possible causes.
Allergies
Allergies arise when an otherwise harmless substance triggers an immune response which results in inflammation. Hypersensitivity occurs only in certain people. With a sore palate, allergies are often related to food or other ingested substances that make contact with the mouth lining. This includes certain mouthwashes or toothpaste and foods like gluten in people with gluten intolerance.
Autoimmune
An autoimmune disease arises when the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. This may arise for various reasons by often the cause is unknown. Sjogren syndrome and lichen planus are two autoimmune conditions that can lead to a sore palate due to mouth dryness or lesions respectively. Other less common autoimmune conditions include Behcet’s syndrome and Kawasaki disease.
Snoring
Snoring is common problem that occurs when the soft tissues of the mouth and throat vibrate due to movement of air. The soft palate is one of the areas that vibrate and many people experience a sore palate and sort throat after a night of snoring. There are a number of reasons why it may occur. Snoring is linked to alcohol consumption, nasal congestion, a deviated septum, obstructive sleep apnea and obesity.
Burning Mouth Syndrome
As the name suggests, burning mouth syndrome is a condition where there is burning in the mouth and there is sometimes no clearly identifiable reason (primary). With secondary burning mouth syndrome, it is linked to conditions like nutritional deficiencies, food allergies, infections, dry mouth, certain medication, hormonal disturbances, acid reflux and certain mental health conditions.
Nasal Infections
Infection of the nasal cavity often extends to the throat and sometimes the mouth. The palate is usually sore with upper respiratory tract infections like the common cold. It may not always be due to an infection of the palate but can arise with frequent sneezing which strains the soft palate and mouth breathing. The soreness of the palate is usually accompanied by nasal soreness and it is usually short-lived, lasting for a few days to a week.
Other Causes
- Oral cancer
- Ulcerative colitis (inflammatory bowel disease)
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Nerve disorders (compression, infection or injury)
- Eating disorders with repeated purging and nutritional deficiencies
- Pharyngotonsillitis (sore throat and tonsillitis)
- Excessive talking or screaming
References
- Orofacial Pain. AAOP