Sulfonylurea (Glimepiride, Glyburide, Glipizide) Drug Information
What are sulfonylureas?
Sulfonylureas were the first oral medication to be used for treatment of diabetes mellitus (sugar diabetes). It encompasses a group of sulfonamide-related chemicals that can stimulate the release of insulin from the beta cells in the pancreas. Sulfonylureas are therefore known as insulin secretagogues and there has to be a sufficient number of beta cells present and functioning in order for this drug to have an effect.
The first generation of sulfonylureas are rarely ever used these days and include drugs like tolbutamide, chlorpropamide and tolazamide. The second generation sulfonylureas include glimepiride, glyburide (glibenclamide), glipizide, and gliclazide and are widely used as these are much safer and more potent than first generation drugs.
Actions of Sulfonylureas
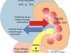
Sulfonylureas bind to sulfonylurea receptors (SUR1) and cause the pancreatic beta cells to release insulin. It may also have some effect on delaying the breakdown of insulin by the liver. Sulfonylureas produce a sustained reduction on blood glucose levels with prolonged treatment. This may result from the improved insulin effects on insulin receptors snd may also be due to a reduction in serum glucagon levels due to the sulfonylureas.
Side Effects of Sulfonylureas
The side effects of second generation sulfonylureas are considerably less than the first generation agents. The most prominent adverse effect of sulfonylurea drugs is hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels) which can even be serious enough to cause a coma. Hypoglycemia is more common with long acting first generation agents like chlorpropamide.
Since sulfonylureas are taken before meals, there is an increased risk of hypoglycemia if a meal is skipped, if the meal contains inadequate carbohydrate or if the ingested meal is vomited out. Oral or intravenous (IV) administration of glucose or glucagon is used to treat the resulting hypoglycemia.
Other side effects, which are seen mostly with first generation sulfonylureas, include :
- nausea and vomiting
- jaundice
- hypersensitivity reactions
- skin rash
- low white blood cell counts
- aplastic and hemolytic anemia.
Concomitant intake of chlorpropamide and alcohol can lead to reactions similar to that caused by anti-alcohol abuse agents (antabuse drug disulfiram). Chlorpropamide may also cause low sodium levels in blood. Weight gain may be seen with the use of sulfonylureas.
Contraindications for Sulfonylureas
- Pregnancy
- Lactation
- Certain infections
- Severe trauma
- Major surgery
- Significant liver or kidney insufficiency
- Type 1 diabetes
Other Insulin Ssecretagogues
Repaglinide and nateglinide are two drugs that have gained wide acceptance as fast-acting agents to reduce high blood sugar levels after eating (post-meal hyperglycemia). These drugs are taken with each meal or just before the meal.
Both repaglinide and nateglinide stimulate insulin release from pancreatic beta cells in response to glucose.vLike with the sulfonylureas , these drugs can only have an effect if there are sufficient functional beta cells present in the pancreas. It is particularly useful in the management of isolated post-meal hyperglycemia, but it has minimal effect on fasting glucose levels.
The major side effect with these drugs is hypoglycemia but since the drug is short acting, hypoglycemia is milder and short lived. Due to the short duration of action, these drugs are fairly safe. Patients with liver disease however, should be cautious about using these drugs.