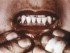
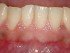
Swollen Gums – Diseases that Cause Gum Swelling
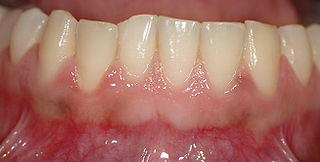
Healthy gums are pink and firm that surround the root of the tooth. As with any part of the body, gum tissue may become irritated and inflamed. This can cause a host of symptoms, including pain, bleeding and swelling of the gums. Sometimes this may be linked to serious conditions which can result in extensive damage of the gum, teeth and even underlying jaw bone.
Swelling of the gums (gingival swelling) is a common occurrence and is quite frequently accompanied by gum bleeding and/or pain and tenderness of the gums. Identifying the cause of swelling is essential for the proper treatment. If left untreated, it can progress to more severe conditions.
Symptoms with Swollen Gums
Gum swelling is a sign of some gum disease. It may be accompanied by a host of other gum symptoms depending on the underlying cause. These symptoms may include:
- Bleeding gums
- Gum pain and tenderness
- Unusually red or dark gums
- Erosion of gums
- Loose teeth
- Bad breath
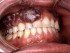
Abnormalities of the gum may not always be easy to spot. The tissue can become eroded or overgrown apart from the swelling. Hyperplasia of the gums (gingival hyperplasia) is a condition where there is overgrowth of gum tissue. The triangular-shaped portions of the gums between adjacent teeth, known as papillae, may become swollen, enlarged and protrude abnormally.
In extreme cases, excessive swelling of the gums may overlap the teeth and cover it completely. Gum swelling may involve only one or two papillae or there may be generalized swelling of the gums. It may develop gradually or may have an acute onset. The history often points to the cause of gum swelling.
Causes of Gum Swelling
It is important to investigate gum swelling to identify the exact cause. It may not always be serious or due to any disease. For example, trauma (injury) to the gums is a common cause of swelling and may be due to causes like vigorous brushing. The swelling should resolve once the inflammation settles. However, at other times swelling of the gums can be serious and require medical attention.
Mouth and Gum
Gum disease is the most frequent cause of swollen gums.
- Gingivitis is a common type of gum disease that tends to be mild. Periodontitis is a severe form of gum disease which may even lead to loss of teeth.
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) is a more severe type of gingivitis and may cause an acute, generalized, and rapidly progressive gum swelling.
- Mouth ulcers are open sores that form in the inner cheek lining, tongue, palate and/or lips.
- Poor oral hygiene is one of the leading causes of gingivitis. Apart from brushing twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste, the use of an antibacterial mouthwash and flossing is also important.
- Viral, bacterial or fungal infections vary in severity and complications and can present with gum swelling along with other symptoms.
Teeth
- Pericoronitis is inflammation of the gum tissue surrounding an impacted or partially erupted wisdom tooth. It should not be confused with periodontitis.
- Periapical abscess is a collection of pus that is located in the gum near the root of the tooth. It may cause gum swelling.
- Impacted food particles between gums and the teeth.
Drugs and Toxins
- Medication can cause gum thickening (gingival hyperplasia). This includes drugs like phenytoin (for seizures) and nifedipine (antihypertensive).
- Heavy metal poisoning, like mercury, lead or arsenic poisoning.can cause a host of gum symptoms from swelling, bleeding and tender or painful gums to redness and darkening of the gums.
- Fetal valproate syndrome is a rare congenital disorder caused by exposure of the fetus to valproic acid (used to control seizures in the treatment of epilepsy) during the first 3 months of pregnancy. Among other features such as spina bifida, distinctive facial appearance and mental retardation, gum hypertrophy may be an additional feature.
Dental Appliances and Products
- Poorly-fitting dentures and other mouth appliances can cause gum swelling due to constant friction with the gums, and also due to trapped food particles within them which encourages bacterial growth and infection.
- Sensitivity to toothpaste or mouthwash can also be a problem. These products for good dental health and should not be avoided. Instead other brands or variants should be considered.
Hormones
Hormonal changes occurring during pregnancy and puberty can have an effect on orodental health and increase the risk of gum swelling due to various causes.
Tumors
- Immune-compromised individuals like those suffering from HIV/AIDS or uncontrolled diabetes.
- People undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Involvement of gum tissue, causing swelling and other features, is a very common finding in leukemia.
- Oral (mouth) cancer is one of the most serious causes and can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early.
- Pyogenic granulomas or pregnancy tumors are benign vascular lesions in the mouth, often seen in the gum area during pregnancy.
Diet and Lifestyle
- Severe malnutrition.
- Prolonged and severe vitamin C deficiency (scurvy).
- Excessive smoking or tobacco chewing.
Other Causes
Serious systemic illnesses may result in swollen gums. This could be due to :
- Blood disorders
- Genetic conditions
- Infections like HIV
- Metabolic disorders
Sometimes, gingival hyperplasia may be idiopathic, meaning no cause can be identified.
Treatment for Swollen Gums
The exact cause of gum swelling needs to be diagnosed by a medical or dental professional. The appropriate treatment can then be prescribed. This may require various medication and dental surgery. There are several dietary and lifestyle changes that can be helpful for common causes of gum swelling, like gingivitis. However, this should not delay seeking medical attention.
How to Prevent Gum Swelling
The following measures focuses on the prevention of gingivitis, one of the most common causes of gum swelling. However, it may also be beneficial for the treatment and management of other conditions which may or may not cause swollen gums.
- Teeth should be brushed at least twice daily. A soft toothbrush or an electric toothbrush are ideal and a fluoride toothpaste should be used.
- Flossing and rinsing with a mouthwash should also be part of the daily dental regimen. Dental picks may also be helpful to clean between the teeth.
- Avoid tobacco. Both smoking and chewing tobacco are major risk factors for the development of gingivitis.
- See a dentist at least every 6 months, even if there are no dental problems. Regular cleanings can also be helpful.