Common Blood Thinners Myths, Facts and Precautions
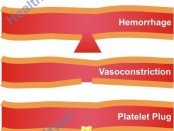
Blood thinning agents are a group of drugs that prevent blood clot formation. With the prevalence of atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries) these days, blood thinners are a commonly prescribed drug. It is a life-saving medication that can prevent a blood clot from blocking one of the arteries to a vital organ. When a >> Read More ...