Tender Outer Ear (Auricle) and Causes of Pain
The outer ear includes the large skin and cartilage appendages we see on either side of the head (the auricle) and the ear canal until the eardrum (the external auditory canal). When we talk about outer ear pain, most of us are referring to the auricle (also known as the pinna) although the ear canal is technically part of it. Auricle pain occurs for many reasons and along with redness and swelling it may be among the first symptoms to indicate an ear problem.
Sometimes it may be an extension of a problem extending from the middle ear, eardrum or ear canal. However, there are times when auricle pain or tenderness arises entirely from the auricle with no further involvement of other parts of the ear.
Anatomy of the Auricle
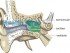
The auricle or pinna is a relatively large appendage on the side of the head. It is prominent in most people and plays a very important role in hearing – it directs sound waves into the ear canal. The auricle is composed of cartilage which is covered by skin. Although human ears are fixed in place for most people, there are muscles that can move it but only some people have functional muscles.
Movement of the ears in these individuals is minor as compared to most other mammals. Pain may involve the entire auricle or only parts of it. Broadly there are five parts to the auricle known as the helix, anti-helix, concha, tragus, lobule and external auditory meatus. There are other features on the auricle but this is usually not of any significance except to the medical fraternity.
Given that the auricle is largely skin and cartilage, pain usually arises from these structures. Injury, infections, allergies, cancers and other skin and cartilage diseases are some of the reasons for ear tenderness or auricle pain.

Causes of Outer Ear Tenderness
Pain or tenderness in the auricle can sometimes be due to simple causes like sleeping on one side against a hard surface. Persistent or recurrent pain should always be investigated as it may sometimes be due to serious causes like cancer even though there is no obvious lesion.
Trauma
Injury to the outer ear is by far the most common cause of tenderness and pain. The injury is usually obvious like with an ear piercing or blow to the ear. Trauma leads to inflammation which is characterized by pain, redness and swelling. If the trauma is not severe then the inflammation is short lived and subsides without any treatment. Pain and tenderness can linger for a while thereafter.
The injury may be caused by mechanical, chemical or electromagnetic forces. Sunburn is another common cause of trauma to the auricle. It can also occur with prolonged exposure to UV light in tanning beds. This is known as phototrauma and is more likely to affect lighter-skinned individuals. Radiation injury to the ear can arise with radiation therapy to the head and neck region for the treatment of cancers.

Infection
Swimmer’s ear is a well known infection involving the outer ear. It is also known as otitis externa. The infection affects the ear canal and the auricle may also be inflamed. However, infections isolated to the auricle are more often seen with piercings that have become infected or secondary infections arising with skin diseases. Most of these infections are due to bacteria and often it is the bacteria that are naturally found on the skin which take the opportunity to infect damaged skin.
Allergies
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system reacts to harmless substances (allergen). With the ear, the allergen usually comes into contact with the skin of the ear as is discussed further under skin diseases. Earrings made of certain metals which are person is allergic to is one of the more common triggers of allergies of the ear. Itching, burning, pain, swelling and redness are typical symptoms. The ear is also a common site for hives (urticaria) which appears to be an allergic response although the exact reason for hives is unclear.
Skin Diseases
- Atopic dermatitis is a common allergy-related skin condition that often starts in early childhood. It tends to affect the skin folds and the auricle, particularly behind the ear, is a frequently involved site. Allergic rhinitis and asthma may also occur with atopic dermatitis.
- Contact dermatitis is inflammation of the skin associated with an irritant or allergen. Irritant contact dermatitis may occur with just about any substance that can irritate human skin. Even prolonged exposure to water can be an irritant. With allergic contact dermatitis the body reacts to harmless substances (allergens) like certain metals in earrings and hair dyes or shampoos.
- Photoallergic dermatitis, sometimes referred to as solar urticaria or photodermatosis, is a skin condition triggered by sun exposure. While strong sunlight can cause skin trauma, in photoallergic dermatitis the sun triggers a reaction with chemicals on the skin. This may include certain drugs, some types of soaps and even sunscreen.
- Psoriasis is an autoiommune-related skin condition where there is thickening of the skin with the formation of silvery-white plaques. It can affect the skin anywhere on the body and the ear is one of the more frequently affected sites especially where there is scalp psoriasis. Certain medication used in the treatment of psoriasis can also play a role in photoallergic dernatitis.

Cartilage Diseases
- Relapsing polychondritis is an autoimmune condition affecting the cartilage. It can involve cartilage anywhere in the body and the joints are a commonly affected site. Since the ears are made up of cartilage, it can also be affected and ear involvement is seem in 9 out of 10 cases of relapsing polychondritis.
- Winkler’s disease is a condition where a painful nodule forms on the upper parts of the ear (not the lobule) due to pressure or trauma. This can include mechanical pressure like with prolonged phone use or with sun trauma. It is also known as chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helices (CNHC). The nodule can sometimes become ulcerated. It is a benign (non-cancerous) lesion.
Cancers
The ear is not an uncommon site for cancers, particularly skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It is exposed to the sun just as much as other areas like the face and hands. In addition, sunscreen may not be applied as it is on the face and hands. However, sun exposure is not the only risk. Radiation exposure and even chronic ear infections could increase the risk of ear cancer.
References
- External Ear Inflammatory Diseases. Medscape
- Ear Tumors. Merck
Last updated on September 25, 2018.