Tongue Sores, Lumps and Bumps Causes
The tongue is one of the more sensitive organs in the human body. It is laden with receptors for touch and taste which allows it to complete its relevant functions. The tissue of the tongue does not have the same hard protein covering of the skin. However, the tongue is often exposed to many environmental factors when we eat, drink, talk or breathe through our mouth. It is therefore understandable that the tongue may be easily injured or infected and a number of different lesions may form on it.
What are tongue sores?
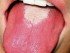
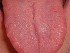
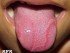
A tongue sore is simply any lesion like a cut or ulcer on the surface of the tongue. Sometimes unusual small growths on the tongue described as lumps and bumps are also referred to as sores. Typically a sore is sensitive or even painful and can affect speaking, eating or drinking to some degree. Even when these functions are not compromised, the discomfort of a tongue sore can be frustrating for a person. The cause of tongue sores can be varied and sometimes the cause is unknown.
Sores can occur anywhere on the tongue. Areas like the tip of the tongue are particularly prone to injury as it is the most mobile part and also the point of first contact with the environment. Normally tongue sores are not serious and usually acute. It may resolve on its own with little or no treatment. However, persistent and recurrent tongue sores can be an important symptom of underlying diseases some of which can be serious or even life threatening.
Causes of Tongue Sores
The most common causes of tongue sores are usually related to mouth problems but sometimes the root cause can be elsewhere in the body or systemic. For example, tongue sores and infections may be related to HIV infection or diabetes. Sometimes there are other symptoms like tongue discoloration that are present along with the tongue sore may be a helpful indicator of the underlying cause. It is also not uncommon for tongue pain or sensitivity to be mistaken for a tongue sore even though there are no lesions.
Trauma
Injury to the tongue is probably one of the most common reasons for tongue sores. Since the mouth is the entry point for food and beverages, and sometimes air, it can be exposed to a host of insults. In addition injury may stem from internal factors like the teeth or poorly fitting dentures. Sometimes every day actions can cause injuries to the tongue, like brushing the tongue excessively as part of the daily oral health regimen. These injuries that can occur may be categorized as:
- Physical, example burns from hot food or drinks.
- Chemical, example stomach acid in GERD.
- Electromagnetic, example radiation in cancer treatment of the head/neck.
Cigarette smoking, tobacco chewing, alcohol misuse and illicit substances that are smoked (like crystal meth) can also cause physical and chemical trauma to the tongue which may lead to persistent or recurrent tongue sores most users are addicted to these substances. The same applies to people who chew areca (betel) nut or other toxic substances.
Canker Sores
Canker sores are ulcers in the mouth that can occur for a number of different reasons. It is linked with viral infections, mouth trauma, nutritional deficiencies, hormones, food allergies and emotional stress. The cause of these sores are largely unknown. Canker sores are not the same as fever blisters which are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). These lesions starts as small red bumps which then become open sores often with a yellowish center.
Mouth Cancer
Most tongue sores and other mouth lesions are not due to any serious causes. However, in rare cases even minor tongue sores may be the start of oral cancer. It is more likely to occur in cigarette smokers, tobacco chewing and with areca (betel) nut chewing. People who have a previous history of cancer or who have undergone radiation treatment to the head and neck are also at a higher risk. Any persistent and enlarging tongue sore especially if it is bleeding should be investigated particularly in high risk people.
Swollen Papillae
The tongue is not smooth. Hundreds of tiny protrusions known as papillae protrude from the tongue surface and it contains the taste buds. These protrusions can become inflamed and therefore swell. Even if not visible, the swollen papillae may cause the tongue to feel rougher than normal. While it is usually not a serious problem the enlarged papillae may feel like bumps and are mistaken for sores. The inflammation may also make the tongue more sensitive or painful.
Eating Disorders
Tongue sores can arise for various reasons in eating disorders. Firstly there is trauma to the tongue caused by stomach acid during purging (intentional vomiting) as is seen in conditions like bulimia. People with eating disorders also suffer with nutritional deficiencies which may lead to tongue sores. Furthermore the compromised nutrition can impact on immune health. As a result infections are more likely to occur and the tongue may be one of the areas that are affected.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Tongue symptoms may be seen in certain nutritional deficiencies like with iron and certain B-vitamins. There may not always be tongue lesions. Instead the tongue may be painful, burning or extremely sensitive which may mislead a person into believing that the discomfort is due to a sore that cannot be seen. Other symptoms may include a swollen, bright red tongue and changes in the sense of taste. Abnormal tongue sensations related to nutritional deficiencies are easily treated with supplementation.
Hormonal Irregularities
Tongue soreness has been linked associated with hormonal changes in some women. There is usually no sores but the tongue feels like it is scalded. This is more often seen in postmenopausal women. The exact cause of this tongue soreness with hormonal fluctuations is not fully understood. The tongues symptoms may resolve with hormone replacement therapy. Similar tongue pain and sensitivity may be seen in endocrine disorders like diabetes mellitus. Also refer to burning mouth syndrome.