Abdominal Distension (Bloated Belly or Tummy) Causes
What is a bloated belly?
A bloated belly is a visible enlargement of the abdomen and usually associated with gas or fluid. However, any mass in the abdomen may also result in a visible and palpable swelling which may feel soft, spongy, firm or hard and could be mistaken for fluid or gas. Sometimes the term bloating is also used to abdominal fullness, which is a pressure sensation in the abdomen although there may be no enlargement.
Abdominal distension is commonly referred to as stomach bloating but the enlargement may not always be due to the stomach or associated with gas as is often the case with bloating. Any distension or bulging that is evident on only one part of the the abdomen may provide a clearer indication of the underlying cause along with other associated signs and symptoms.
Abdominal distension may be due to a number of reasons which are not always related to any disease. The most common causes of generalized abdominal bloating or a swollen stomach is due to the five F’s – flatus (gas), fat, fluid, feces (constipation), fetus (pregnancy).
Transient Bloating
Abdominal bloating is one of the common symptoms that a person experiences, either with disease or even in the absence of disease, yet it is not always easily explained. In most instances it is fluctuating and therefore referred to as transient bloating. However, sometimes abdominal bloating is persistent, either staying constant, increasing or decreasing distension.
The two most commonly thought of causes for transient bloating is gas or fluid accumulation. However, gas in the gut is rarely able to distend the abdomen to a degree that causes noticeable bloating without the gas first being evacuated through either end of the gut.
Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, or more specifically the abdominal cavity, is unlikely to cause noticeable distention unless it is in excess of 1 liter of fluid. A mass is unlikely to be the cause of transient abdominal distention. Only very large masses can cause noticeable distention and it usually increases with size or may shrink over a long period of time. Therefore abdominal distention that fluctuates on a daily basis cannot be due to any solid or fluid-filled growth.
Functional bloating is a condition where abdominal distension occurs for no known reason. It arises in the absence of any disease. This is often the reason for transient abdominal distention in most people. Some of the more common lifestyle and physiological causes of persistent bloating includes :
- Air swallowing (aerophagia).
- Excessive intake of carbonated beverages.
- Overeating
Persistent Bloating
Persistent bloating, particularly when the abdominal distension is worsening day by day, needs to be investigated. It may often be due to harmless causes similar to that of transient bloating. However, serious causes of bloating need to be excluded. In most cases persistent bloating is due to some underlying disease and other symptoms will inadvertently arise over time. Therefore the bloating along with the other symptoms need to be considered as a whole in order to reach a diagnosis.
The six F’s of abdominal distension should always be considered :
- Flatus – gas.
- Fetus – pregnancy.
- Fat – abdominal obesity.
- Feces – constipation.
- Fluid – ascites.
- Female – menstrual bloating.

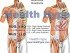
Causes of Abdominal Distension
Many diseases of any of the abdominal organs and structures can result in bloating that is evident as an increase in the abdominal diameter. However, a solid mass, enlarged organ or fluid or gas accumulation may present as a swelling at a specific area (quadrant) of the abdomen which is usually palpable and occasionally visible.
Right Upper Quadrant
- Hepatomegaly (Enlarged Liver)
- Causes
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Primary hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Viral hepatitis
- Heart failure
- Gallbladder
- Causes
- Gallstones
- Cholangitis – inflammation of the gallbladder
- Gallbladder cancer
- Kidney (Right)
- Causes
- Polycystic kidney
- Hydronephrosis – kidney stone, other causes of urinary outlet obstruction
- Renal carcinoma (cancer of the kidney)
- Colon
- Causes
- Feces – refer to Swollen Stomach for a list of causes
- Colon cancer
- Colitis
- Diverticulosis
Left Upper Quadrant
- Hepatomegaly
- An enlarged liver can be detected in the LUQ (moderate to marked enlargement)
- Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen)
- Causes
- Infections, especially blood-borne infections
- Lymphoma
- Lymphatic leukemias
- Hemolytic anemia
- Polycythemia rubra vera
- Myelofibrosis
- Heart failure
- Cirrhosis (liver)
- Thromobosis in the portal or splenic vein.
- Splenomegaly may also be present in a person with inflammatory immune-related disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- An enlarged liver and spleen is known as hepatosplenomegaly.
- Causes
- Amyloidosis
- Cirrhosis
- Lymphoma
- Myeloproliferative diseases
- Left Kidney
- Causes
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Hydronephrosis – kidney stone, other causes of urinary outlet obstruction
- Renal carcinoma (cancer of the kidney)
- Stomach
- Cause
- Stomach distension with food/drink due to delayed gastric emptying – pyloric stenosis, gastroparesis
- Stomach cancer
- Pancreas
- Causes
- Pancreatitis
- Pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatic pseudocyst
- Pancreatic abscess
- Cystadenoma (benign)
- Colon
- Causes
- Feces
- Colon cancer
- Splenic flexure syndrome
- Colitis
- Diverticulosis
- Aorta
- May be more evident in the epigastric region.
- Cause
- Aortic aneurysm
Middle of the Abdomen
- Epigastric Region
- Causes mentioned above :
- Stomach
- Pancreas
- Aorta
- Colon
- Umbilical Region
- Causes :
- Hernia
- Crohn’s disease (small intestine)
- Intestinal obstruction
- Other causes mentioned above :
- Colon
- Stomach
- Spleen (marked splenomegaly)
- Liver (marked hepatomegaly)
- Hypogastric (Suprapubic) Region :
- Bladder
- Causes :
- Distended bladder due to outlet obstruction – bladder stone, prostate (mentioned below)/
- Bladder cancer
- Prostate
- Various prostate diseases may affect bladder emptying thereby resulting in bladder distension.
- Causes :
- Benign prostatic hypertrophy (enlarged prostate)
- Prostatitis
- Prostate cancer
- Uterus
- Causes :
- Fibroids
- Uterine cancer
Right and Left Lower Quadrant
- Appendix (right lower quadrant only)
- Cause :
- Abscess or other mass
- Small intestine
- Causes :
- Crohn’s disease
- Lipoma
- Intestinal obstruction
- Colon
- Causes :
- Feces – refer to Swollen Stomach
- Colitis
- Colon cancer
- Diverticulosis
- Gynecological
- Causes :
- Ovarian cyst
- Tumor of the ovary
- Ectopic pregnancy
Other Causes
There are other causes that may not be related to the organs in the abdomen. It may affect the entire abdomen or it is isolated to one or more quadrants.
- Abdominal wall
- Causes :
- Hernia
- Lipoma
- Trauma
- Peritoneal Cavity
- Causes :
- Ascites
- Peritoneal abscess
- Peritonitis
References
- Abdominal Distension and Bloating. Patient.co.uk
- Swollen Abdomen. Medline Plus