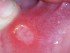
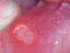
Causes of Mouth Ulcers (Oral Canker Sores)
Mouth ulcers are shallow, painful ulcers that may occur in isolation or as multiple sores inside the mouth. Acute or chronic mouth ulcers may be caused by an number of factors although the reason for recurring canker sores is not known.
Mouth sores may primarily occur due to two factors :
- Any condition causing dryness of the mouth by reducing saliva production. Saliva lubricates the inner lining of the mouth, reduces infections and maintains integrity of the mucosa.
- Any damage to the mucosal lining of the mouth and tongue exposes underlying tissue which may be prone to infection. Contributing factors that may affect healing of the damaged mucosa may eventually lead to a canker sore.
However mouth ulcers due to chronic or systemic conditions may arise due to other factors.
Physical injury
Any damage to the inside of the mouth can result in a mouth ulcer although this may not occur in ever case. Common causes of injury to the inside of the mouth, tongue, and/or inner lip may include :
- chipped, broken or poorly aligned teeth
- braces
- dental procedures and fittings like dental implants, bridges, crowns
- injuries to the mouth – trauma, impact, hard brushing and flossing
Chemical damage
Abrasives or irritants may make contact with the mouth cavity and cause mouth ulcers. Possible chemical irritants include :
- Alcohol especially in excessive alcohol intake or alcohol abuse
- Smoking or tobacco chewing. Smoking is known to cause dryness of the mouth.
- Candy, chewing gum, chewable multivitamins (like vitamin C/ascorbic acid)
- Foods and drinks, especially if acidic
- Certain oral hygiene products like toothpastes and mouth wash.
Working with certain hazardous chemicals like dyes, heavy metals, acid fumes, metal or mineral dust may contribute to the development of mouth ulcers.
Infections
Bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa may cause mouth ulcers in immunocompromised individuals. More commonly, microorganisms may cause a secondary infection of a pre-existing mouth sore.
Some common infectious agents that may be responsible for mouth ulcers or related mouth pathology include :
- Streptococci
- Gonococci
- Coxsackie virus
- Candida albicans
- Corynebacterium diptheriae
- Treponema pallidum
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Herpes simplex
- Varicelaa zoster (chickenpox)
- Morbillivirus (measles)
Nutritional Deficiency
Certain vitamins and minerals including vitamin B12, vitamin C, iron and folate may cause a range of mouth symptoms including canker sores. Nutritional deficiencies may also affect the integrity of the tissue of the mouth or contribute to mouth dryness which can make the area more prone to physical injury, chemical damage or infections.
Drugs
Most drugs may cause mouth dryness making the mouth more prone to infections. Certain drugs like corticosteroids, methotrexate and chemotherapy may impair immune functioning which could contribute to mouth ulcers.
Immune Functioning
Any chronic conditions, drug or lifestyle factor that may impair immune functioning may contribute to the development of mouth stores. This includes stress, autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and immunodeficiency syndromes like HIV/AIDS. Other mouth diseases like oral thrush (candida or yeast infection) and leukoplakia may be referred to as mouth sores or but these conditions do not often cause typical mouth ulcers.
Chronic Diseases
Mouth ulcers may be associated with certain diseases and the exact mechanism of action for the recurrence of canker sores in these cases are unknown. Mouth sores may be related to the following conditions :
- Inflammatory bowel diseases – Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis.
- Food allergies & intolerance – Celiac disease
- Bechet’s disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Lichen planus
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Chronic nasal obstruction resulting in mouth breathing and dryness of the mouth.
Mouth ulcers may occur due to other conditions or contributing factors including changes in hormone levels related to menstruation or pregnancy and in allergy related disorders. Canker sores may be closely related to chronic conditions of the gut although the mechanism of action has not been established. The cause of recurrent mouth sores should be investigated further especially if it is affecting daily functioning like eating and drinking or if you suspect that your mouth ulcer may be related to other conditions and disorders.
Related Article
References :
- Mouth Sores. Medline Plus
- Mouth Ulcers. Wrongdiagnosis
- Canker Sore. Mayoclinic
- Mouth Sores. Merck