Itchy Face and Facial Rash – Causes, Treatment, Pictures
Facial Itching
Itching of the face is a common symptom that every person experience, often on a frequent basis. In most case it is a mild it that is quickly relieved with rubbing or scratching. The face is the most exposed part of the body as it is almost never covered. It is constantly bombarded by the environment through dust, dirt, microbes, wind, heat, cold and other irritants. These are easily removed with washing.
Sometimes the skin is very sensitive and even a mild irritant, that may not irritate every person, can cause itching. It may be associated with allergies or even skin diseases. An itchy face usually does not need any specific medical treatment unless it becomes persistent of if it is associated with a skin rash or other symptoms that indicates a problem.

Causes of Itchy Face
There are various causes of itchy skin either with or without a rash. These conditions may not always be specific for the skin on the face. This means that it can cause itching anywhere on the body. However, some causes are highly specific for the face due to certain factors that are unlikely to affect skin elsewhere on the face.
Poor Hygiene
Dirt, dust and microbes are constantly making contact with the face. These contaminants if not removed can irritate the skin. An unwashed face tends to be itchy. It men this may sometimes be associated with facial hair which tends to trap and hold contaminants. Treatment involves good hygiene by regularly washing the face.
Dry Skin
Dry skin is a very common cause of an itchy face, second only to poor hygiene. It can occur at any time in the year but is more common in winter. Seasonal dryness and itching is therefore often referred to as the winter itch. However, the constant exposure to air conditioned environments particularly in settings like the workplace can dry out the skin. Facial itching due to climatic conditions is also more likely to occur in windy environments.
Dryness of the skin leading to itching may also occur with :
- Excessive washing of the face, particularly with hot water and harsh soaps can also dry off your facial skin. Most soaps, particularly heavily scented varieties, and facial washes dry out the skin on the face.
- Alcohol based products, like men’s aftershave and antiseptic soaps, are known to cause excessive dryness.
- Acne products also tend to dry out the skin as part of its chemical action to combat pimples.
- Sun exposure, which does cause initial oil secretion and sweating, eventually has a harsh drying effect on the skin. It is further aggravated by sunburn.
Treatment would involve proper moisturizing of the skin, avoiding any conditions or products that dry the skin and using sunscreen for adequate protection.
Allergies
An allergy, or hypersensitivity, may be a result of allergic skin diseases or irritants to the face in a person who otherwise does not have these conditions. Allergic skin diseases that are more likely to present with itching includes atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis or urticaria (hives). Substances (allergens) that may be responsible for an allergic reaction even in the absence of skin diseases includes :
- Hair dyes (itchy scalp, front, eyelids, neck, and often marked facial swelling)
- Shampoos (itchy scalp and/or face)
- Cosmetics (itchy face)
- Food and medications (itchy lips, mouth, throat, and upper body)
- Head lice (itchy scalp, neck, shoulders, face)
- Pollen, dust and other inhaled allergens (itchy eyes and itchy nose)
- Jewelry (itch and rash at the site of skin contact)
Treatment may involve the use of antihistamines and corticosteroids. Severe cases associated with anaphylaxis require adrenaline (epinephrine). A more important measure, however, is to prevention by avoiding the trigger.
Psychological Causes
Facial itching is at times imagined or associated with nervous behavior. Sometimes a person may not experience any itching yet scratch the face regularly. Apart from a nervous disposition, itching or scratching the face can arise with anxiety as do many other nervous tics. Treatment may involve counseling or the use of anti-anxiety or antidepressant medication. In most cases though, no specific treatment is needed.
Infections
The skin and hair follicles may become infected by a number of different microbes. Itchiness is a common symptoms in some of these conditions. The infectious causes of an itchy skin may include :
- Childhood viral infections often present with skin rashes that may cause itching in many cases. In chickenpox (Varicella zoster), measles (Rubeola virus) or German measles (Rubella virus), itchy papules or vesicles appear on the face and trunk. These skin lesions crust over and disappear or peel off after about a week. These infections will resolve on its own with no specific treatment being necessary. Treatment may involve the use of anti-inflammatory drugs like acetaminophen to reduce any inflammation and various types of skin applications like calamine lotion, urea creams or just plain emollients.
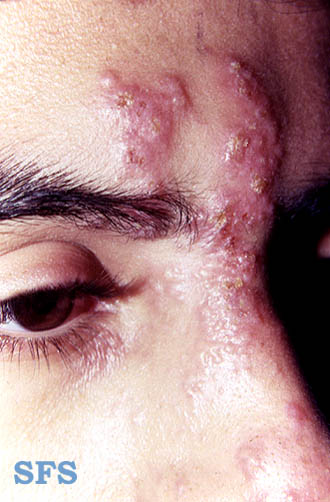
Picture 1. Herpes zoster
(Sourced from Dermatology Atlas,
Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D.
atlasdermatologico.com.br)
- Herpes simplex infection usually appears as a group of small, translucent, burning blisters around the mouth (cold sore). Severe infection may be treated with antiviral drugs (acyclovir).
- Herpes zoster infection (shingles) may present with a chronic burning or itchy rash which tends to follow the course of the trigeminal nerve branches. It is usually only on one side of the face. Treatment is with oral acyclovir.
- Dengue fever is a self-limiting viral disease with fever, itchy rash and small bleedings on the skin. It is transmitted from human to human by mosquitoes. It appears worldwide, except in Europe and Antarctica.
- Bacterial infections are commonly caused by bacteria that normally live on the skin and can result in impetigo. This includes staph skin infections (like staphylococcal folliculitis), streptococcal infections (scarlet fever, erysipelas).
- Tinea barbae is a fungal infection of the bearded area in men. It can be passed from person to person but may also be contracted from animals. It is caused by a number of Trichophyton and Microsporum species of fungi, some of which naturally reside on human skin. A tinea infection of the skin of the face is known as tinea faciei. Treatment is with anti-fungal drugs applied on the skin (topical) or ingested (oral).
Skin Diseases
A number of skin disease may present with itching of the face. These skin diseases also present with a skin rash in most cases and other symptoms that allow it to be differentiated from less obvious causes. Excessive scratching in these cases often leads to permanent discoloration of the skin.
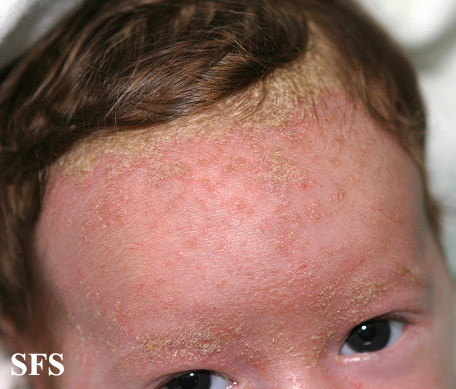
Picture 2. Seborrheic dermatitis.
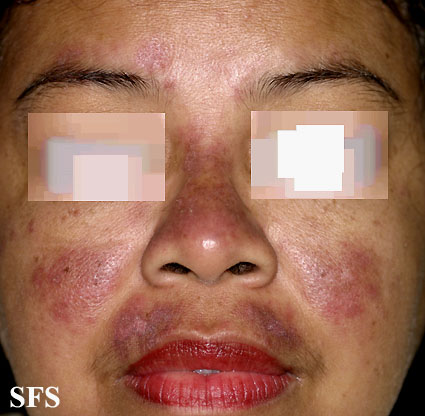
Picture 3. Systemic lupus erythematosus.
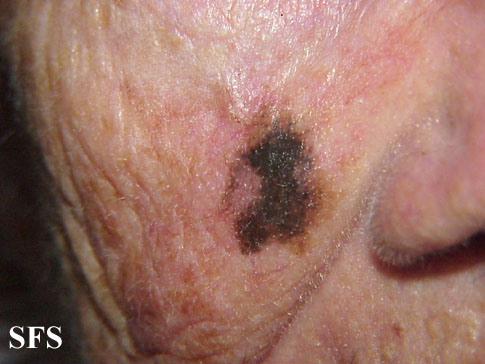
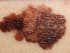
Picture 4. Melanoma on the cheek
(source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D.
Dermatology Atlas)
- Acne vulgaris is the common type of acne seen more often in teens. It is associated with excessive oil (sebum) production, blockage of the pores with blackheads and whiteheads and bacterial infections of the skin. Pimples, or zits, may be painful and the skin may be painful even without pimples in the area. Acne does not always cause skin itching. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. Mild causes can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) soaps, face washes and other drying and antibacterial agents. For more severe cases, treatment may involve oral contraceptives (females), antibiotics and isotretinoin.
- Rosacea is a skin condition marked with severe redness due to widespread inflammation. These areas of redness may appear as patches or slight raised lesions. It is often worsened with sunlight exposure. Treatment is with antibiotics, isotretionin and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae (ingrown hair, razor bumps) is an inflammation of the hair follicle after shaving, and not an infection. It mostly occurs in men with curly hair. Prevention is by avoiding shaving hair close to the skin. Lotion with glycolic acid may be used at night to prevent inflammation. In resistant cases, antibiotics or laser hair removal may be tried.
- Irritant contact dermatitis may occur with contact to any number of substances like cosmetics, sunscreens and even aftershaves. Saliva may also cause skin irritation, and this is more common in children.
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema) appears mostly in children with asthma or other allergies. It runs in families. Rash may appear on the face or anywhere on the body, often on the limbs. Treatment is by avoiding triggering substances, moisturizing creams and corticosteroid ointments.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin with greasy, yellowish, scaly clusters of shed skin cells appear on the scalp, behind the ears, the armpits and groin. It may be associated with skin fungi but is not a fungal infection. Treatment involves zinc, selenium, sulfur, salicylic acid or tar shampoos and ointment.
Other Causes
- Insect bites can occur on any site on the body and the face is more commonly attacked by mosquitoes and other airborne insets. There may be an allergic reaction, infection or localized skin irritation following a bite. Severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis need to be treated with adrenaline. A combination of antihistamines with antiseptic, urea and calamine lotions may be sufficient for treatment.
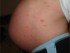
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). A red skin patch in the form of a “butterfly rash” extends over the nose and cheeks. The joints and vessels are often affected. Treatment is with steroid ointments and various other medications. A rash also often appears in other rheumatic diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis, polyarteritis nodosa, temporal arteritis.
- Dermatomyositis is a rare inflammatory muscle disease with skin rash. Violaceus rash and swelling around the eyes, on the back of the fingers and elbows or knees is characteristic.
- Melanoma is highly malignant, fast growing, dark pigmented (brown, black or bluish) tumor, from few millimeters to few centimeters in size. It usually grows in the level of the skin, or appears as a raised tumor. Treatment is with a surgical removal. Squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma usually appear as a crust like tumor on the face, eyelids, ears, lips, or scalp. Treatment may involve surgery or radiotherapy.
Treatment of Itchy Face
The treatment of facial itching is largely dependent on the cause and individual treatments have been discussed above. General measures for treating an itch includes :
- Antihistamines (oral)
- Corticosteroids (topical)
However, the underlying cause needs to be treated or the itching will persist indefinitely. Sometimes simple measures are sufficient if there is no clearly identifying cause of facial itching. This may include :
- Washing the face regularly with gentle soaps like baby soaps and non-scented soaps.
- Drying the face thoroughly after bathing.
- Using a moisturizer or emollient for dry skin.
- Avoiding skin creams and cosmetics on oily skin.
- Protecting the skin with suitable sunscreens.
References:
- Facial rashes. Dermnet NZ
- How to relieve itchy skin. American Academy of Dermatology
Last updated on August 14, 2018.