Nicotine Withdrawal Symptoms, Timeline, Treatment
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance and once a person becomes addicted to it, sudden deprivation (‘going cold turkey’) can cause unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The severity of these symptoms may be significantly reduced if there is a gradual weaning off nicotine or the simultaneous use of nicotine replacement products.
There are both physical and psychological symptoms of withdrawal which may persist for varying periods of time. These symptoms are usually more intense and persist for longer periods of time in a nicotine user who is dependent on large quantities of nicotine on a daily basis or who has been using nicotine since early in life. Cessation of these symptoms are not a guarantee of overcoming the addiction, and as with any substance dependence, a person who quits nicotine has to be vigilant not to return to the habit.
Symptoms of Nicotine Withdrawal
Symptoms of nicotine withdrawal may arise after quitting any form of nicotine administration and will usually only occur in a person who is addicted to nicotine and using it on a regular basis for a prolonged period of time.
Effects of nicotine deprivation usually start within a few hours of the last dose and can reach their maximum intensity within two to three days. The symptoms are usually short-lived and a person may experience only some of them.
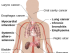
The symptoms of nicotine withdrawal which are commonly reported include :
- Irritability, anxiety, aggression and agitation.
- Mood swings.
- Depression and anhedonia (inability to enjoy oneself).
- Craving for nicotine – this can become intense and may persist for a long time.
- Sleep problems such as insomnia, excessive drowsiness or nightmares.
- Increased appetite often leading to weight gain.
- Decreased alertness.
- Inability to concentrate.
- Impaired performance level.
- Bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
- Fatigue.
- Constipation.
Newborn babies, born to women who smoked heavily during pregnancy, often show signs of nicotine withdrawal soon after birth. This can be confirmed by neurological assessment of the baby after birth and by markers of nicotine exposure.
How Long Does Nicotine Withdrawal Last?
The timeline for nicotine withdrawal symptoms varies among individuals with most physical withdrawal symptoms lasting between 3 to 10 days. Psychological symptoms may persist for months and the craving for nicotine can last for even longer.
Nicotine addiction is not entirely physical and long term users will often report a need to mimic the method of administration. For example, many cigarette smokers who quit smoking tend to snack excessively, chew gum, or play with objects in their hands. This may not be related to suppressing cravings but rather to ‘occupy’ the mouth or hands.
Nicotine users, especially smokers, tend to develop social habits which usually involves other smokers. This may result in the desire to partake in the method of administration, like cigarette smoking, rather than in a craving for nicotine itself.
Treatment of Nicotine Withdrawal Symptoms
- Nicotine replacement therapy can reduce many of the withdrawal symptoms by using low doses of nicotine in the form of gums, patches, nasal sprays, lozenges or inhalers. These are especially helpful in relieving craving till the body adjusts to the absence of nicotine.
- Medicines to help quit smoking like bupoprion hydrochloride.
- Antidepressants and antipsychotic drugs.
- Psychotherapy, including counseling and joining a support group.
To cope with nicotine withdrawal symptoms it is important to remember that it is just a temporary phase and with persistence it is possible to break the nicotine addiction.