Pregnancy Tests Types, Results, Causes of False Readings
How Pregnancy Tests Work
A pregnancy test is used to confirm pregnancy and uses the urine or blood to detect the presence and levels of certain hormones which would be indicative of the pregnant state. There are a number of hormones, including progesterone and early pregnancy factor, which can be used to confirm pregnancy but the hormone that is most commonly evaluated is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Most pregnancy test results can confirm or negate early pregnancy quite accurately, from about two weeks after conception (first day of the first missed period) to about 20 weeks of pregnancy. Detecting the presence of the beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (a hormone secreted by the placenta) in the blood or urine of a woman forms the basis of most pregnancy tests.
A positive test result means that beta-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is detectable in the blood or urine. It most cases it indicates pregnancy although there are certain causes of a false-positive result.
A negative test result means that bet-hCG is not detectable in the blood or urine at a level that can be measured by the specific type of pregnancy tests. It may mean that a woman is not pregnant but there are other causes of a false-negative test result.

Home Pregnancy Tests
A home pregnancy test is a simple test to detect pregnancy using a urine sample and can be easily done within the home environment with little or no technical knowledge. The test may be done with any urine sample but the first voided morning urine sample is preferred since it is likely to have a high concentration of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
How soon can I take a home pregnancy test?
There are various home pregnancy test kits available which may be used and most tests use the immunometric assay. You should consider taking a home pregnancy test about 2 weeks after missing a period and not after having unprotected sex.
Many manufacturers claim that a home pregnancy can be used as early as the day of the missed period or even 3 to4 days before missing a period and that these results are 99% accurate results. This may not actually be the case. The urine hCG level at this time is variable and may lie below the sensitivity of detection, so while some women may test positive, a false-negative result is also quite possible.
The most accurate result is recorded when a test is done 2 weeks after a missed period.
What do I do if the home pregnancy test is negative?
If negative, the test should be repeated after several days. Alternatively you should speak to your doctor about other types of hCG tests which may give more accurate readings in a shorter period of time after conception.
How do I use a home pregnancy test?
All tests come with instructions which should be followed closely to get accurate results.
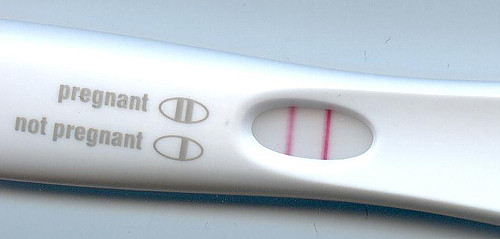
Some tests use dipsticks which are dipped in a sample of urine while others use a test strip in the urine stream. A dropper may be used to put a few drops of urine in the test well. A color change or confirmation mark indicates pregnancy. Some show a single line to denote negative result and a double line to indicate pregnancy. Others may show a plus or minus sign. Always refer to the package insert for the correct information on interpreting a home pregnancy test result.
Home pregnancy tests with digital readings may give better results than non-digital tests. These indicate a “pregnant” or “not pregnant” reading on the test window.
Types of Pregnancy Tests
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Test
HCG is usually detectable in the blood or urine of a pregnant woman within 10 days of fertilization (after implantation of the fertilized ovum in the uterus) and it gradually increases in the first trimester (first 12 weeks) of pregnancy and then falls as pregnancy progresses. Blood samples usually give more accurate results in early pregnancy than urine samples. Accuracy with urine samples increases when the test is done 2 weeks after a missed period.
There are four main types of hCG assays are used :
- Radioimmunoassay
- Sensitivity – 5 mIU/mL.
- It takes 4 hours to complete the test.
- First positive at 10 – 18 days after conception or 3 – 4 weeks of pregnancy.
- Immunoradiometric assay (more sensitive)
- Sensitivity – 150 mIU/mL.
- It takes 30 minutes to complete the test.
- First positive at 18 – 22 days following conception or 4 weeks of pregnancy.
- Immunoradiometric assay (less sensitive)
- Sensitivity – 1500 mIU/mL.
- It takes only 2 minutes to complete the test.
- First positive at 25 – 28 days after conception or 5 weeks of pregnancy.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay – ELISA (more sensitive)
- Sensitivity – 25 mIU/mL.
- It takes 80 minutes to complete the test.
- First positive at 14 – 17 days after conception or 3.5 weeks of pregnancy.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay – ELISA (less sensitive)
- Sensitivity – less than 50 mIU/mL.
- It only takes 5 – 15 minutes to complete the test.
- First positive at 18 – 22 days following conception or 4 weeks of pregnancy.
- Fluoroimmunoassay
- Sensitivity – 1 mIU/mL.
- It takes 2 – 3 hours to complete the test.
- First positive at 14 – 17 days after conception or 3.5 weeks of pregnancy.
The sensitivity of the assay will determine how early a pregnancy can be detected. The most common pregnancy tests currently used are sensitive to 25 mIU/mL. Pregnancy tests can be broadly divided into those that are conducted at home (usually a urine test) and tests conducted in a laboratory by using blood specimens.
What is Qualitative HCG Blood Test
A qualitative beta-hCG test confirms the presence or absence of hCG in the blood. This test only confirms if a woman is pregnant or not. HCG levels of 25 mIU/mL and more is usually detected by this method.
What is a Quantitative HCG Blood Test
A quantitative beta-hCG test measures the exact amount of hCG in the blood and is a very sensitive test for pregnancy since even very small amounts of hCG can be detected by this test, even as low as 1 mIU/mL. However, this test is not done routinely and is not necessary in all pregnancies.
Quantitative HCG Levels and Reference Range
HCG levels increase rapidly in the first trimester of pregnancy and then gradually declines. The amount of beta-hCG detected will be a pointer to the stage of pregnancy. In early pregnancy, the amount of hCG (usually 1200 mIU/mL or less) doubles every two days, so serial blood tests may be conducted every 48 hours can determine if the pregnancy is proceeding normally or not. Even if it does not double, there should be at least a 66% increase in 48 hours. HCG levels between 1200 and 6000 mIU/mL double every 72 to 96 hours, while hCG levels above 6000 mIU/mL take over 4 days to double.
A quantitative test should not be conducted to gauge the stage of pregnancy but is rather used as a method of monitoring the progression of a healthy pregnancy in the first trimester. If the result is :
- less than 5mIU/mL then this is considered negative for pregnancy.
- between 5mIU/mL to 25mIU/mL is inconclusive and a repeat test is necessary.
- greater than 25mIU/mL confirms pregnancy.
Low Levels of Quantitative hCG Test
Information regarding viability of a pregnancy can be obtained by a serial quantitative hCG test. Falling hCG levels will indicate a non-viable pregnancy.
A serial quantitative hCG test which does not show the expected rise of hCG may indicate :
- An impending miscarriage (threatened abortion).
- Incomplete abortion.
- Complete abortion – after a miscarriage, the hCG level usually returns to the non-pregnant range in about 4 – 6 weeks but this will depend upon the stage of pregnancy when the miscarriage occurred.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Fetal death.
- Drugs such as diuretics and promethazine.
High levels of Quantitative hCG Test
HCG levels which are higher than normal may indicate :
- Multiple pregnancies such as twins or triplets.
- Normal pregnancy.
- Hydatidiform mole or molar pregnancy.
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus.
- Cancer of the ovary.
- Drugs such as anticonvulsants, anti-Parkinson drugs, phenothiazine and promethazine.
Causes of False-Positive Result
A false positive means the pregnancy test shows a positive result even though there is no pregnancy. False positive results are not very common. Some of the causes include :
- Abortion – induced or spontaneous (miscarriage).
- Hydatidiform mole or molar pregnancy.
- Choriocarcinoma – a type of cancer occurring in the uterus which produces hCG.
- Certain other types of cancer, such as cancer of the bladder and ovary, may produce small amounts of hCG, giving a false positive result.
- Improper testing – checking the reading beyond the stipulated time.
- Treatment with hCG hormone, such as while undergoing treatment for infertility.
- Pituitary disorders such as pituitary tumors.
- Corpus luteum cysts of the ovaries.
- Besides drugs containing hCG hormone, other medication like antibiotics and oral contraceptives, do not alter pregnancy test results. Stress, alcohol or narcotic drugs do not affect the test result either.
- Wrong interpretation of results, such as confusing the evaporation line caused by the urine as a positive result.
Causes of False-Negative Result
A false negative result suggests there is no pregnancy even though a woman may be pregnant. False negative results are more commonly seen with urine tests. Some of the causes include :
- The pregnancy test is done too early and the hCG concentration is below the sensitivity threshold of the particular test being used.
- Wrong date – miscalculation about the date of the last menstrual period (LMP).
- Delayed periods due to early pregnancy loss (miscarriage).
- Delayed ovulation.
- Delayed implantation of the fertilized ovum.
- Interstitial tubal pregnancy.
- Using diluted urine, such as after drinking too much water or by use of diuretics.
A doctor will consider doing both a quantitative and qualitative beta-hCG blood test to confirm pregnancy and assess the levels of hCG in the blood. Follow up tests are always advisable to exclude a false-positive or false-negative result or possibly identify a miscarriage.
Last updated on Septemer 1, 2018.
