Pain Under Right Rib Cage
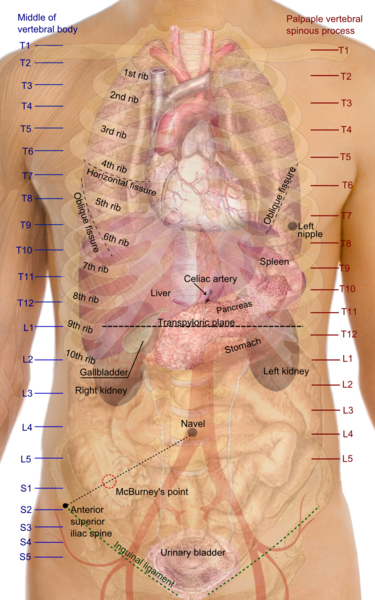
The rib cage is the part of the axial skeleton that protects the vital organs within the thoracic (chest) cavity and the upper part of the abdominal cavity. It is made up of the ribs that articulate at the back with the vertebral column (vertebrae) and at the front with the breastbone (sternum). Numerous costal cartilages bridges the ends of the ribs at the front with the breastbone.
There are 12 ribs on each side (left and right) and a clavicle (collarbone) on the left and right as well. Various organs are located behind the rib cage which are either located in the thoracic cavity or abdominal cavity. Often the organs of the thoracic cavity are described as sitting ‘behind’ the rib cage while the organs of the abdominal cavity are considered to be ‘under’ the rib cage.

Organs Under Rib Cage
The rib cage shields the entire thoracic (chest) cavity and part of the upper abdominal cavity.
Chest Organs
The following organs are within the thoracic cavity.
- heart covered by the pericardium and the great vessels (center)
- lungs and pleura (either side)
- trachea (center) and bronchi (originating at the center and extending to either side)
- esophagus
- diaphragm
Abdominal Organs
The following organs lie partially or completely under the lower part of the rib cage and may descend slightly downwards when standing up straight.
- kidney (right and left)
- liver (right)
- gallbladder (right)
- stomach (left)
- spleen (left)
- transverse colon (right and left corners – hepatic and splenic flexures)
- pancreas (partly under the left)
Causes of Pain Under Right Rib Cage
The various causes of pain behind the rib cage, usually referring to chest pain or pain in the thoracic cavity have been discussed further under :
The causes of pain under the rib cage, usually referring to abdominal pain, have been partly discussed further under :
These causes have been discussed here further with specifically as pain under the right rib cage, similar to pain under the left rib cage.
Liver
The liver is the largest organ in the abdominal cavity and occupies most of the area under the right rib cage. The various causes of liver pain include :
- Trauma to the liver may occur with any blunt force or sharp force injury to the abdominal wall or less commonly through surgery or diagnostic procedures.
- Viral hepatitis which is an infection of the liver caused by a specific type of virus. Other infections of the liver may be due to less commonly seen viruses, or bacteria, fungi and parasites.
- Alcoholic liver disease is a broad term to describe many stages of liver disease due to chronic alcoholism. Alcoholic hepatitis is more likely to present with abdominal pain and tenderness. End-stages like cirrhosis is usually not painful.
- Fatty liver disease, also referred to as non-alcoholic liver disease, is the accumulation of fat in the liver associated with obesity, high blood cholesterol, hypertension (high blood pressure) and diabetes mellitus.
- Pyogenic liver abscess is an accumulation of pus within a localized area in the liver. It may arise with other infections within the abdominal cavity like acute appendicitis, after injury to the abdomen and liver, blood-borne infections, bile duct infections and endoscopic procedures such as ERCP.
- Liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant tumor that develops in the liver. It may also arise as a result of metastatic spread of a malignant tumor elsewhere in the body in which case it is referred to as secondary or metastatic cancer. Pain is usually present in the late stages.
- Liver cysts or hepatic cysts are thin-membraned fluid-filled sacs in the liver. It may occur as a single cyst (simple cyst), several cysts (polycystic liver disease), neoplastic cysts or hydatid cysts.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis (ICP) is a condition where bile is backed up into the liver and may be due to problems within the liver itself or bile ducts.
- Hepatic arterial occlusion is where there is a blockage or narrowing of the hepatic artery thereby reducing the oxygen supply to the liver tissue. It may lead to ischemic hepatitis which is damage of the liver tissue due to an interrupted blood supply.
There are several other causes of liver pain which may need to be excluded as well. Liver problems may or may not present with pain and other symptoms like jaundice, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder is not entirely tucked under the right rib cage but is mainly positioned within the right hypochondrium and epigastric regions. It tends to cause upper middle abdominal pain (epigastric pain) but there may also be pain under the right rib cage.
- Gallstones are sediments of bile that form within the gallbladder and remain largely asymptomatic until large stones partially or completely obstructs the cystic (gallbladder) duct or bile duct.
- Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder caused by gallstones, bile duct obstruction or a tumor.
- Cholangitis is inflammation of the bile duct caused by an obstruction like a gallstone or bacterial and parasitic infections.
- Gallbladder cancer is a malignant tumor that develops within the gallbladder (primary tumor). Sometimes cancer in the gallbladder may be due to metastatic spread from a distant site (secondary cancer).

Kidney
The right kidney sits behind the liver and more to the side. Kidney disease causes right flank and back pain which may be below the rib cage since the right kidney is only partly covered by the rib cage. Conditions that may cause kidney pain includes :
- Kidney stones are solid masses that develop from chemicals in the urine. Large stones may remain lodged in the renal pelvis of the kidney while smaller stones can pass down the ureter causing intense flank pain. Very small stones may pass unnoticed.
- Pyelonephritis is an infection of the kidney most often caused by bacteria and in most cases occurs due to an ascending urinary tract infection.
- Renal hemorrhage is bleeding in the kidney which is mainly due to severe trauma to the abdomen.
- Hydronephrosis is accumulation of urine in the kidney leading to swelling. It may be seen with any obstruction of the urinary tract.
- Polycystic kidney disease is the presence of multiple small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) in the kidney related to genetic factors.
Colon
The ascending colon, hepatic flexure and transverse colon lie partly in the area just under the right rib cage. Diseases that cause colon pain under the right rib cage includes :
- Diverticulitis which is inflammation of the pouches that form in the wall of the colon (diverticula). Inflammation is usually due to an infection.
- Inflammatory bowel disease like ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease which is chronic inflammation of the wall of the large intestine.
- Infectious colitis is the inflammation of the colon due to an infection and is mainly associated with viruses and bacteria.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional disorder mainly affecting the lower part of the gut characterized by changes in bowel habit, abdominal pain, bloating and intestinal cramps.
- Colonic polyps are usually not painful but large polyps can cause an obstruction thereby causing the colonic contents to become backed up and stretch the colonic wall.
- Trapped gas in the colon which can cause distention of the colon and pain is more likely to occur at the bends of the colon (flexures). It mainly arises in the splenic flexure on the left upper abdomen and is therefore known as splenic flexure syndrome. It can possibly arise on the right side – hepatic flexure.
- Fecal impaction may cause the colonic contents to accumulate and distend the colon as will other causes of severe constipation.
- Colorectal cancer is a malignant growth in the large intestine. It mainly affects the lower parts of the colon and rectum. Colorectal cancer is among the more common types of cancer and pain is only seen in the later stages.
Other Causes
- Abdominal wall injury or abdominal muscle strain
- Shingles (herpes zoster)
- Nerve root compression of intercostal nerves
- Fractured rib
- Costochondritis
- Peritonitis
- Intra-abdominal abscess
- Pleuritis
- Pleural effusion
- Tuberculosis of the lung (pulmonary)
- Lung abscess
- Lung or pleural cancer
References
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Merck
- Chest Pain. Mayo Clinic
Last updated on September 24, 2018.
Latest Updated on September 25, 2018 by Dr. Chris
Published on January 18, 2012 by Dr. Chris