Abdominal Pain, Pictures, Quadrants, Severe Abdomen Pain Causes
Abdominal pain is a common symptoms that afflicts every child and adult at some point in their life. For some, it is a common occurrence and can be debilitating when severe. However, most of us experience abdominal pain occasionally and it is usually linked to an underlying condition. The pain may be accompanied by a host of other symptoms including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation or excessive flatulence.
What is abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain is any pain, ache or discomfort in the abdomen (also referred to as the belly). It can arise from the abdominal organs like the gallbladder or appendix, the tissues in the abdomen like the peritoneum or the abdominal wall consisting of connective tissue, subcutaneous fat, muscles and skin.
Sometimes abdominal pain may emenate from the spine or even from the organs in the chest cavity or pelvic cavity. Dull aches or discomfort is often referred to as a sore abdomen although this also technically falls within the scope of abdominal pain.
The severity of abdominal pain does not always correlate with seriousness of an underlying disorder. For example constipation or trapped gas may cause debilitating pain yet it is not life threatening. One the other hand pancreatic cancer may present with little or not abdominal pain but is very serious.
Most of us refer to pain in the abdomen as upper abdominal pain or lower abdominal pain but there are more specific ways to locate and identify the areas in the abdomen. Although the term ‘stomach’ is often used interchangeably with ‘abdomen’, the stomach is a specific organ whereas the abdomen is a section of the torso.
Abdominal Quadrants
The abdomen can be broadly divided into four quadrants by an imaginary vertical and horizontal line running across the navel (umbilicus). These imaginary lines divide the abdomen into four abdominal quadrants: right upper (RUQ), right lower (RLQ), left upper (LUQ) and left lower (LLQ) quadrants.
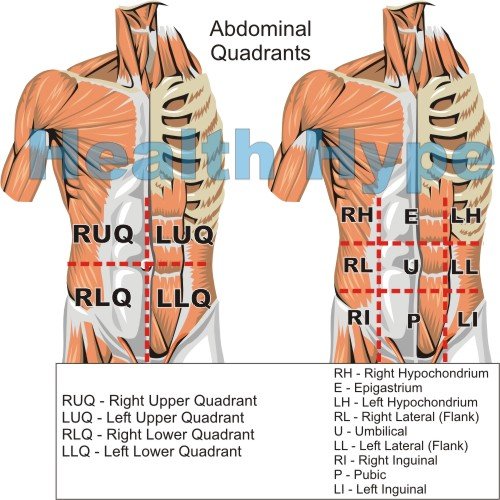
The abdomen can also be divided into nine regions for identifying more specific locations. These nine quadrants (as illustrated above) include the:
- Right hypochondrium (right hypochondriac region)
- Epigastrium (epigastric region)
- Left hypochondrium (left hypochondriac region)
- Right lateral region (right flank)
- Umbilical region
- Left lateral region (left flank)
- Right inguinal region
- Pubic region
- Left inguinal region
Organs in the Abdomen
The abdominal cavity contains the most number of organs compared to any other cavity in the body. Naturally, it is also the largest cavity. Most of the abdominal organs are part of the digestive system with the gastrointestinal tract (gut) occuping most of the space within the abdomen.
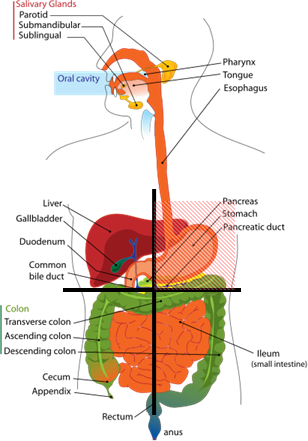
Organ in the four abdominal quadrants
Abdominal pain can be denoted according to abdominal quadrant in which it appears:
- Right Upper Quadrant or RUQ pain may arise from the liver, gallbladder, main bile duct, upper part of the ascending colon, right part of the transverse colon, stomach, duodenum, right kidney, ureter or adrenal gland, right lung membrane (pleura), lower right ribs, abdominal muscles, skin or spinal nerves.
- Left Upper Quadrant or LUQ pain may arise from the pancreas, stomach, left part of the transverse colon, upper part of the descendent colon, second part of the small intestine (jejunum), left kidney, ureter or adrenal gland, spleen, heart, left lung membrane, lower left ribs, abdominal muscles, skin or spinal nerves.
- Right Lower Quadrant or RLQ pain may arise from the lower part of ascending colon, last part of the small intestine (ileum), appendix, right ureter, right spermatic cord, right ovary and uterine tube, abdominal muscles, skin or spinal nerves
- Left Lower Quadrant or LLQ pain may arise from lower part of the descending colon, sigmoid colon, small intestine, left ureter, left spermatic cord, left ovary and uterine tube, abdominal muscles, skin or spinal nerves
Pain in the middle upper abdomen is called epigastric pain and may arise from the stomach, lower part of esophagus, pancreas, heart, spine or aorta.
Pain in the middle lower abdomen is called hypogastric or suprapubic pain and may arise from the bladder, spine or uterus.
Causes of abdominal pain that can appear in any abdominal quadrant: abscess, endometriosis, adhesions, benign and malign abdominal tumors, metastases.
Severe Abdominal Pain
Severe abdominal (stomach) pain is a debilitating pain where a person is unable to continue with daily activities due to the severity of the pain. Abdominal cramps (spasms) are painful contractions of the hollow abdominal organs or muscles in abdominal wall lasting from few seconds to several hours. The cause of the pain or cramp may be indicated by its location and accompanying symptoms. Severe abdominal pain often requires urgent hospitalization but is not always due to a serious or life-threatening ailment.

Causes of Severe Pain in the Abdomen
A person with any of the following symptoms requires immediate medical attention:
- Severe stomach pain, forcing him/her to sit or lie down
- Pain, lasting over 10 minutes
- Restlessness or unusual calmness
- Pale face and lips
- Shallow breathing and weak heart beat
- Fever, chills, nausea or vomiting..
1. Acute Appendicitis
Sudden right lower abdominal pain, which usually starts near the navel and gradually moves few inches toward left and down, tenderness at this spot, nausea, vomiting and fever are main symptoms of acute appendicitis,which can affect a person of any age. Inflamed appendix has to be surgically removed as soon as possible to prevent its perforation and life threatening abdominal inflammation.
Diagnosis in typical cases can be made from history and physical examination; in non-typical cases a CT is the main investigation. Appendix is removed through an inch wide incision in the abdominal wall. Prognosis is excellent; death from appendicitis is rare.
2. Acute Poisoning
Severe upper middle abdominal pain and cramps, vomiting and altered consciousness are main symptoms of acute poisoning due to ingesting of corrosive liquids (e.g. petrol, acids), excessive amount of medications or illegal drugs, inhaling of poisonous gases like war gases or pesticides.
Inducing vomiting with fingers pushed into the throat or drinking a glass of salted water may be tried only in conscious person but not if corrosive substances like petrol or acids were ingested. Stomach pumping, injecting antidots, hemodialysis, and intravenous fluid infusion are some of possible treatments measures.
3. Infections
In the western world, food poisoning by bacteria or parasites in a previously healthy person is rarely serious despite possible dramatic vomiting, abdominal cramps and diarrhea. Food poisoning often heals on its own in few days, and if not, a doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics.
Rotavirus infection causing stomach flu with fever, stomach cramps, vomiting and diarrhea is also usually not a serious disease in the western world, but it is still a major cause of children deaths in Africa, South Asia and South America. Therapy is with replacing lost fluids by oral rehydration solutions or intravenous infusion.
4. Injuries with Internal Abdominal Bleeding
A hit to the stomach (often in car accidents), shot and knife injuries may cause bleeding into abdominal cavity. Abdominal pain, paleness, thirst and feeling of coolness are main symptoms. Urgent surgery is required.
5. Perforation of the Stomach or Intestine
Perforation of the stomach is a complication of advanced stomach ulcer or cancer. Perforation of the small intestine is rare. Perforation of the colon may occur in advanced Crohn’sor ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, Clostridium difficile infection, colorectal cancer and during colonoscopy or surgery. Immediate surgery is necessary.
6. Dissection or Rupture of Abdominal Aorta
In people over 50 years with advanced atherosclerosis, layers in the wall of abdominal part of the aorta may be split what may cause a sudden severe abdominal pain. This tear in the wall of the abdominal aorta is known as an aortic dissection. It can lead to a rupture of the abdominal aorta. These conditions can be fatal within a short period of time and requires emergency surgery.
References
- Acute Abdominal Pain. MSD Manual
- Abdominal Pain, Acute. American Family Physician
- Abdominal Examination. Medscape





