Arterial Occlusion Treatment (Diet, Exercise, Medication)
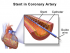
Arterial occlusion is the blockage of the blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood (artery) to different parts of the body. The occlusion obstructs blood flow either completely or partially thereby starving the tissues of oxygen. A partial obstruction may lead to atrophy (shrinking) or cell injury, which is either reversible or irreversible. A complete occlusion will lead to irreversible cell injury and cell death.
The causes, signs, symptoms and diagnosis of arterial occlusion is discussed further under :
Treatment of Arterial Occlusion
The choice of treatment depends on a number of factors including the location and degree of occlusion. The patient’s age, health status and past medical history are also important to consider when deciding to delay surgery.
There are many cases where conservative management (lifestyle changes without medication) or a medical (non-surgical) approach (lifestyle changes + medication) may be sufficient to limit the extent of the narrowing and even reverse it. Opting for these approaches is dependent on individual cases and predisposing factors.
Surgery may be necessary in severe arterial occlusion or if there is failure to respond to these measures.
Lifestyle Changes
The main known risk factors for atherosclerosis related to lifestyle are :
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Sedentary (inactive)
- Diet high in saturated fats and refined carbohydrates
Making lifestyle changes that remove or minimize the impact of these factors may be sufficient to limit the progression of the narrowing or even reverse some of the changes. However, each case has to be assessed by a doctor who will determine if a patient can consider conservative management rather than commence with medication or undergo more invasive procedures immediately.
Diet
- All of the following dietary approaches may be relevant to most patients with arterial occlusion. However, specific cases require definitive dietary approaches for the most effective results.
- Low calorie : obesity
- Low fat diet : obesity, high blood cholesterol, diabetes
- Low glycemic index (GI) : obesity, diabetes
- Low sodium : hypertension
- Fiber helps to reduce cholesterol uptake from the gastrointestinal tract (high cholesterol, obesity), lower glycemic index (diabetes, obesity) and provide bulk to minimize the quantity of food intake (obesity).
- Protein helps to reduce glycemic index (diabetes, obesity), provide a longer lasting feeling of satiety (obesity) and lower calories ounce-per-ounce than fat or carbohydrates (obesity).
Exercise
- Exercise is beneficial in arterial occlusion to help treat predisposing conditions and reduce blood stasis.
- However, excessive exercise should be avoided as the blood flow through the narrowed artery to the target organ may be insufficient during periods of higher demand. This can lead to ischemia or even an infarct.
- Cardiovascular exercise, like walking, jogging, swimming, should be undertaken for at least 20 minutes 3 times per week. Irregular exercise patterns may strain certain organs rather than proving to be beneficial.
- NEVER start any exercise program without first consulting with a doctor and undertaking a regimen that is supervised by a competent personal trainer who is fully aware of your medical history.
Medication
A number of drugs may be used to treat a clogged artery depending on the causative factor, underlying chronic conditions and severity of the individual case. Apart from atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots (thrombus or embolus) are another major cause of arterial occlusion that are more likely to occur in a case of atherosclerosis.
Cholesterol Lowering Agents
- These drugs when used in conjunction with a diet low in saturated fat and refined carbohydrates* may help to lower blood cholesterol levels.
- This may slow down or stop the growth of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Losing weight and exercising may also help with lowering cholesterol levels.
- Examples : statins, fibrates.
* Refined carbohydrates like sugar have been shown to contribute to elevated blood lipids, particularly triglycerides.
Anti-Hypertensive Agents
- These drugs help to lower blood pressure since hypertension (high blood pressure) is known to be a major contributing factor to atherosclerosis and blood clot formation.
- In conjunction with weight loss, exercising, stopping smoking and a low salt diet, anti-hypertensive drugs may prove to be beneficial in slowing down or stopping the growth of plaques and decreasing the chance of blood clot formation.
- Proper treatment and management of hyperlipidemia and diabetes are important considerations in hypertension.
- Examples : beta blockers, ACE inhibitors
Anti-Diabetic Agents
- Proper blood glucose control is essential in diabetics.
- This is further compounded by the interaction between diabetes and hypertension and/or high cholesterol levels.
- Apart from medication, dietary management is essential in diabetes and this includes a low-fat, low glycemic index (GI) diet.
- Exercise contributes significantly to glucose tolerance, especially in obese patients.
- Examples : metformin, glibenclamide
Blood Thinning Agents
- These drugs reduce the formation of blood clots which can cause an occlusion on its own or compound an existing narrowing as in atherosclerosis.
- Simultaneous treatment and dietary management of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and diabetes is also essential.
- Exercise may help significantly in preventing blood clot formation.
- Examples : aspirin, clopidogrel bisulfate
Agents to Increase Blood Flow
- Certain drugs will help to relax arteries and/or prevent arterial spasm thereby increasing the lumen diameter and allow for increased blood flow to the target area.
- Examples : nitroglycerin (angina), cilostazol (claudication)
Related Articles