Avoid Eyestrain from Light, Screens and Reading
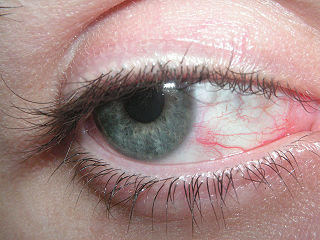
Eyestrain or eye fatigue has become common place in everyday life for many of us. Most of the time it is nothing more than an annoyance but for some people it can be quite debilitating. Fortunately eyestrain does not lead to any permanent complications but the symptoms may recur on such a frequent basis that it affects a person’s life and even their ability to work. Eyestrain is often a result of ignorance rather than just being overworked. A few simple measures that will take only a few minutes can prevent eyestrain, even amidst a busy work schedule.
Causes of Eyestrain
There are several causes of eyestrain and it is important to understand why eyestrain arises in order to prevent it. Eyestrain is not a permanent condition. It arises with prolonged activity that involves the eye. Keeping the eye fixed on an object at a set distance, too much or too little light and even blinking infrequently can all contribute to eyestrain. It is more likely to occur when conducting one of the following activities for a prolonged period of time :
- Reading and writing.
- Staring at a computer screen, watching TV or play video games.
- Working in very dim light.
- Exposure to glare without protective eye wear.
- Delicate work involving a microscope or magnifying glass.
Rest the Eyes
The eyes like any part of the body needs to be rested every now and then. You do not necessarily have to close your eyelids and fall asleep to rest the eyes. When you look at fixed objects for prolonged periods of time, you strain the eyes more than walking around and looking at objects at varying distances. If you cannot get away from office desk then there is a simple way to rest the eyes without ‘sleeping on the job’.
The 20-20-20 rule for taking an eye break says that after every 20 minutes you should look at an object about 20 feet (about 6 meters) for at least 20 seconds. Measure a distance about 20 feet away from your desk and find something pleasant, yet not intrusive on others, to look at. Keep a clock or even a 20 minute hourglass on your desk. It will help you to remember when to take an eye break.
The Right Eyewear
Even if you have perfect 20/20 vision, eyewear can still be beneficial in protecting your eyes. Bright light and UV rays can strain or even damage the internal structures of the eye. The right eyewear should offer protection and it is best to speak to an optician or opthamologist before you select the appropriate eyewear.
It is not entirely about sunglasses. There is a host of eyewear these days that can fulfill multiple functions – reducing glare and protecting your eyes from UV rays – without looking like stylish shades that your boss would not approve of. Photochromic lens, also known as self-darkening lens, will clear up and look like regular spectacles when you are indoors but darken when you are in the sun. These days newer lenses can make the transition very quickly.
Blink Frequently
People tend to blink less when they are concentrating intently on some activity. But blinking is one of the essential actions for eye protection. It stimulates the release of tears and wipes away any dust and debris on the surface of the eye in much the same way as windscreen wipers. Blinking less frequently allows the eye to dry out further irritating the strained eye.
It may seem rather simplistic but blinking frequently can help ease eyestrain. So just how many times should you blink? Humans blink about 15 times a minute, sometimes more and sometimes less. It is helpful to stick a note next to your computer screen to remind you to blink and with time it will become second nature. But even if you don’t, whenever you feel your eyes burning or aching, then blink a few times in succession.
Eye Coolers
A modern invention to cater for an very common problem in the modern world, eye coolers can help soothe the eyes to some extent. These modified eye goggles or eye shades have a gel that can stay cool for long periods after being placed in a fridge. Eye coolers work in essentially the same ways as placing slices of cucumbers over the eyelids – it has a cooling effect on the eye. Never place ice directly on the eyelids.
A cold application over the eyelids may not completely relieve eyestrain but it does relieve some of the symptoms like a burning sensation in the eyes. It can also ease some of the eye redness by causing the tiny vessels to constrict. Any cooling agent placed over the eyelids should not be cold but rather cool – if you cannot bear it on your skin then do not use it. Use these applications for only a few minutes at a time.
Artificial Teardrops
There is a wide range of artificial teardrops that can be purchased without a prescription. These eye drops are not medicated and simply help to lubricate and moisturize the eyes. Water is not a good alternative over synthetic teardrops for dry eyes. If you use contact lens, you may need special eye drops that will not damage or interfere with the lenses. Rather speak to a doctor about the artificial teardrops taht best suits your specific needs.
Go for an eye exam
Sometime eyestrain may arise in the backdrop of other eye problems, especially refractive errors of the eye. These eye problems are where your eyes can no longer focus as it normally should leading to visual defects like shortsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia) or astigmatism. Age-related vision problems (presbyopia) can also be a cause of eyestrain.
Fortunately all of these eye problems can be easily treated with spectacles. Sometimes other eye problems like a cataract or glaucoma may also play a role in what may seem like eyestrain. It is important to see an optician or opthamologist for a thorough eye examination and diagnosis of any underlying eye disorders. Prompt treatment can spare you very serious complications which may initially just seem like simple eyestrain.
Correct the lighting
Glare or dim lighting are two common problems that lead to eyestrain. It is important to find the optimal lighting that is comfortable to the eyes. Where glare cannot be removed like during the day in bright sunlight, the correct eyewear can remedy the problem. Sometimes sunlight can reflect off walls particularly light-colored walls. If the sunlight cannot be blocked, walls may need to be painted in dark colors.
When working in dim light, use artificial lighting that is not too bright but sufficient for proper vision. In many instances, however, glare is from computer and TV screens. Simply altering the brightness and contrast of the screen or using an anti-glare filter can easily correct the problem. Lenses with anti-reflective coating can also help reduce glare where sunglasses are not practical.
References :
www.mayoclinic.com/health/eyestrain/DS01084