Causes of Swollen Groin Lymph Nodes
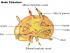
The lymph nodes of the groin, or inguinal lymph nodes, are located in the crease between the leg and pelvis. There are two types of inguinal lymph nodes – superficial and deep. These groin lymph nodes often swell due to an infection or cancer in the areas from which they drain lymph (lymphatic fluid). For this reason, swelling of the groin lymph nodes is an important clinical indication of certain diseases within the organs of the lower abdominal cavity, legs, groin, buttocks, anus, perineum and external genitalia.
Anatomy of Inguinal (Groin) Lymph Nodes
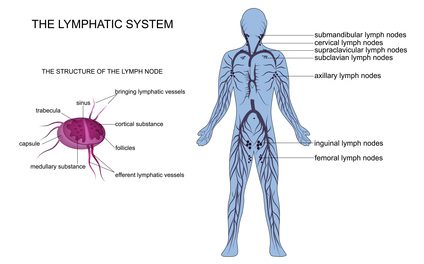
Lymph nodes are located throughout the body with each group being responsible for draining a particular area. The common lymph nodes that swell are found in the neck (cervical), armpit (axillary), and groin (inguinal), as well as in numerous other areas of the body.
There are about 10 lymph nodes that collectively form the group known as the superficial lymph nodes. They drain the skin and subcutaneous tissue (which lies just beneath the skin) of the lower abdominal wall below the level of the umbilicus, gluteal region (buttocks), perineum, lower part of anus, external genital organs and the leg.
The superficial lymph nodes thendrain into the deep inguinal lymph nodes. There are about 3 to 5 of these deep inguinal lymph nodes which filter the lymph and return it to the circulation. As with lymph node swelling anywhere in the body, increased immune activity in the groin and pelvic region will lead to swollen groin lymph nodes.
Causes of Enlarged Groin Lymph Nodes
The superficial lymph nodes are more likely to be felt and even seen when swollen. However, when not swollen it is usually not visible or palpable. Nevertheless it is constantly functioning to filter lymphatic fluid, neutralize infectious agents like bacteria and even isolating and destroying abnormal cells that are potentially cancerous.
Infections
Infections of the leg or genitals may cause swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. Systemic infections may also cause lymph node swelling of the three main groups – groin, neck or armpits.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as syphilis, gonococcal infection, chancroid, herpes simplex, lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) may cause swelling of the inguinal lymph nodes. Swollen groin lymp nodes are one of the main STD symptoms in men and women.
- Bubonic plague caused by Yersinia pestis, may cause extremely tender lymph node enlargement in the groin, accompanied by redness and inflammation of the overlying skin. Lymph nodes of the armpit and neck may also be involved. The bubonic plaque is uncommon in modern times compared to other viral, bacerial and protozoal infections that may cause swollen groin lymph nodes.
- Viral infections such as infectious mononucleosis may affect the whole body and cause generalized lymph node swelling in various parts of the body, such as neck, armpit or groin. However, viral infections of the groin region are more likely to cause isolated swelling in the groin region.
- Bacterial infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, muscles and bone of the leg or pelvis may also cause swelling of the groin lymph nodes.
- Toxoplasmosis caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii may also result in swollen lymph nodes. Most people do not exhibit any signs or symptoms of the disease and no treatment may be necessary but in babies born to infected mothers or in immunocompromised patients such as those with HIV/AIDS, it can turn into a serious infection. Flu-like symptoms such as body ache, headache, fever, fatigue and sore throat may be accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes.
Cancer and Tumors
Many forms of cancer occurring within the area drained by the groin lymph nodes will lead to swelling (lymphadenopathy). Lymph node swelling usually occurs due to malignant tumors.
- Leukemia is the cancer of the body’s blood forming tissues, including bone marrow and lymphatic system. There are several different types of leukemia and swelling of the lymph nodes may not only occur in the groin region, when it is present.
- Lymphoma is the cancer of the lymph node. It usually starts in the lymph node and may spread to other parts of the body. It may involve groups of lymph nodes in various parts of the body. There are two types of lymphomas – Hodgkin’s disease and Non-Hodgkin’s disease.
- Pelvic malignancy (cancer) and metastasis (spread) from cancer of anus or vulva may result in swollen lymph nodes, not related to a lymphoma. Lymph node enlargement developing in a known case of cancer will indicate its spread. If it develops in a case already treated for cancer, it will indicate recurrence of the disease.
- Melanoma is one of the types of skin cancer which may cause swelling of the lymph nodes around the affected area. Therefore if this malignancy occurs in the groin region then the groin lymph nodes may be swollen.
Drugs and Vaccines
- Medication. The side effects of certain drugs may cause lymph node enlargement although this is not a common occurrence. Some drugs that may contribute towards lymph node swelling include certain medicines for gout (like allopurinol), epilepsy and bipolar disorder (like phenytoin and carbamazepine), infections like penicillin for bacterial infections and pyrimethamine for malaria and sulfonamides (sulfa drugs). Lymph node enlargement due to drugs is more likely to be generalized.
- Certain vaccinations such as MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) and typhoid vaccination may also cause generalized lymph node enlargement. This means that the lymph node swelling is not isolated to the groin region but may occur throughout the body. However, it is more likely to occur in the neck, armpit and groin. Read more on vaccination side effects.
Systemic
- Patients with known systemic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE/SLE) may develop a swollen lymph nodes later in the disease. It is usually generalized lymph node swelling. However, this may not always be present with these diseases and is therefore not a reliable sign for diagnosis.
- Lymphadenitis or inflammation of the lymph nodes resulting in swelling of the nodes is common in children and is often due to a local or generalized infection, usually viral in origin. Tuberculous lymphadenitis may be seen more often in developing countries, with generalized lymph node enlargement indicating widespread dissemination of the disease.
References
- Lymphadenopathy. Medscape