Heart Attack or Heartburn (Acid Reflux) Chest Pain, Causes, Symptoms
It is one of the most common conditions mistaken for a heart attack and accounst for many anxious emergency room visists. However, heartburn is not life-threatening and actually has nothing to do with the heart, unlike a heart attack. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) also known simply as acid reflux has become so common these days that as many as 4 in 10 Americans experience symptoms like heartburn at some point. In fact up to 1 in 10 Americans contend with symptoms like heartburn on a daily basis.
Is Heartburn a Heart Problem?
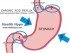
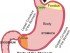
Despite the term heart, heartburn does not involve the heart in any way. Heartburn describes a burning chest pain which arises when stomach acid enters the esophagus (food pipe). The esophagus cannot withstand the corrosive effects of the stomach acid and enzymes. It becomes irritated, inflamed and ulcers (open sores) may therefore form in the esophagus.This typically causes a burning sensation or pain. Since this pain is not due to a heart problem (despite the name ‘heartburn’), it is also referred to as non-cardiac pain.
Read more on how to spot heart pain from heartburn.
Since the esohagus runs in the middle of the chest, the burning sensation is therefore experienced in the chest. Heart problems may also lead to chest pain since the heart is located here as well. However, heart-related pain is usually not burning in nature. It can range from a crushing or constricting chest pain to a sharp pain. Nevertheless, sometimes heart problems can present with a burning pain and similarly acid reflux may at times present with a sharp, piercing or even crushing pain.
Causes of Heartburn vs Heart Attack
It is important to understand that heartburn is a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (HERD) which is also known as acid reflux. Therefore we have to look at the causes of acid reflux which is the main reason for heartburn. A heart attack on the other hand is not a symptom but a condition where a portion of the heart muscle dies. A heart attack is medically referred to as a myocardial infarction.
Causes of Acid Reflux
Normally food and fluids pass from the throat, down the esophagus and into the stomach. Eventually it is passed out from the stomach into the small intestine. The food, beverages, acid and enzymes in the stomach should not pass backward from the stomach into the esophagus (food pipe). To prevent this from happening, a valve at the bottom of the esophagus remains closed to keep the stomach contents within the stomach.
However, if this valve weakens then backward flow (reflux) may occur. The valve is known as the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and problems with it can occur for various reasons. The LES gradually weakens in many people and can become temporarily impaired for several reasons, such as alcohol consumption or with overeating. It is problems with the LES that allows for acid reflux to occur which in turn results in heartburn.
Causes of Myocardial Infarction
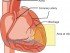
Myocardial infarction, or a heart attack as it is commonly referred to, occurs due to entirely different reasons. This is a heart problem. It is usually due to coronary artery disease (CAD). The coronary arteries supply blood the muscular heart wall. It can become narrowed over time due to the buildup of fatty plaques. Eventually a blood clot may block the blood supply through the coronary arteries.
The lack of blood to a portion of the heart means that it does not receive sufficient oxygen. Eventually this area of the muscle dies and this is known as a heart attack or myocardial infarction. Less commonly, a heart attack can occur even without coronary artery disease like if there is an injury to the heart, blood oxygen levels drop very low, illicit drug use or inflammation of the coronary arteries (arteritis).
Symptoms of Heart Attack vs Heartburn
There may be some degree of similarlity in the signs and symptoms of acid reflux and a heart attack. Therefore these two conditions are often mistaken for each other despite being such different conditions. However, the slight variation in these symptoms may also provide some indication of one condition over the other. In addition the response to medication can also provide some clue to the underlying cause – acid reflux symptoms may ease with antacids while there would be no relief in heart attack symptoms with antacid use.
Read more on cardiac vs non-cardiac pain.
Heartburn and Other Symptoms
As mentioned, heartburn is a symptom. It is a burning chest pain due to acid reflux. There are several other symptoms that may accompany heartburn and which are typicaly of acid reflux. This includes:
- Nausea
- Regurgitation and sometime vomiting
- Excessive belching
- Sour taste in mouth
- Bloated sensation
- Sore throat
- Dry cough
- Lump sensation in throat
Symptoms like dizziness and shortness of breath would almost never occur in acid reflux. Even if all of the symptoms point toward acid reflux yet there is dizziness or shortness of breath, then a heart attack should be suspected.
Chest Pain and Other Heart Attack Symptoms
Chest pain is only one symptom of a heart attack. Typical of cardiac pain, it is usually felt in the center of the chest and is often described as constricting, squeezing or tightness in nature. In addition, the chest pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Pain in the left arm, neck or jaw.
- Excessive sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and sometimes vomiting.
- Dizziness
- Anxiety
Loss of consciousness or paleness to a blue skin tinge are other very serious signs of a heart attack. However,a heart attack may not always present in this typical manner. Sometimes the symptoms are atypical and more indicative of acid reflux than a heart attack. In a silent heart attack, there may be little to no symptoms that are characteristic of a heart attack.
NOTE: A heart attack can lead to death within minutes to hours. It is therefore important to seek medical attention when heart attack symptoms arise even if these symptoms are suspected to be due to acid reflux. A doctor will assess the symptoms and conduct relevant diagnostic investigations to confirm a heart attack.