How Do You Know If You Have Gallstones
Some 20 million American adults have gallstones and gallstone complications account for as many as 10,000 deaths per year. It is by no means a rare or insignificant disorder but since most people with gallstones are asymptomatic (without symptoms), gallstones often does not get the same attention as other common medical conditions. Many people are not familiar with the symptoms of gallstones as they would be with the symptoms of more common ailments. However, spotting gallstones early and getting medical attention as soon as possible can in some cases even make the difference between life and death.
Some people are at greater risk of gallstones than others. The most common type of gallstones is cholesterol stones. It is more likely to occur in middle-aged overweight Caucasian women who have had several pregnancies or use hormone replacement therapy (HRT). A common mnemonic taught to medical students to remember the high risk group is known as the 5 F’s – fair (Caucasian), female, forty (middle aged), fertile (pregnancy/HRT) and fat (overweight or obese).
Picture of cholesterol gallstones
The symptoms of any condition are mainly related to the diseased organ’s location and its function. This means that symptoms are in and around where the gallbladder sits and causes disruptions in the activity of the gallbladder. Remember that most people with gallstones are asymptomatic. Therefore there is no abnormalities around where the gallbladder is located and there are also no disturbances in its functions.
Where is the gallbladder?
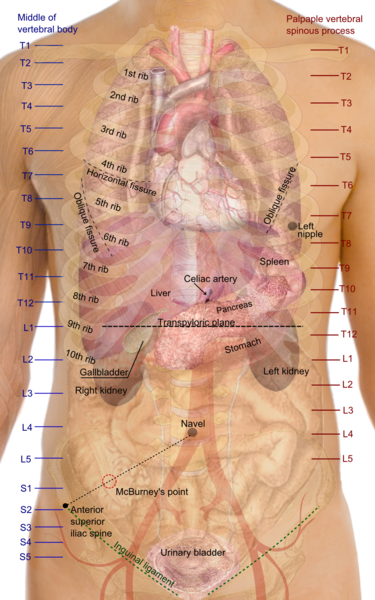
The gallbladder location can be described in many ways depending on perspective. Medical students may use more technical anatomical terms. But for most people, it is sufficient to know that the gallbladder is located in the upper right side of the abdomen. It sits just under the liver and is midway between the right flank and midline of the body. Often symptoms are felt in the upper middle part of the abdomen, slightly to the right. Symptoms my also be felt under the right lower ribcage.
Picture of gallbladder (green) location
What does the gallbladder do?
The gallbladder holds bile. It can stretch to a substantial degree to accommodate bile that is produced and drained from the liver. Bile is one medium to excrete wastes and byproducts of metabolism. The gallbladder can contract to expel this bile into the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) where it mixes with food and is eventually expelled with stool. Bile is also an emulsifier in that it helps break down fats. Therefore the gallbladder is more active and more bile is secreted when you eat a fatty meal.
Gallstone Abdominal Pain
Gallstone pain is one of the typical symptoms and it is known as biliary colic. It generally occurs as attacks that arise very suddenly and last for anywhere between 30 minutes to 2 hours. In rare cases it may last as long as 5 hours. The pain is said to be very intense and excruciating. Some people find mild relief of pain by bending forward. Pain that persists for more than 6 hours may be indicative of acute cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation) or acute pancreatitis – two common complications of gallstones.
Picture of abdominal organs
Right Sided Shoulder Pain
Another common symptom is right shoulder pain which may seem surprising since it is a distance away from the gallbladder. This is known as referred pain. Sometimes right shoulder pain is present without upper abdominal pain. At other times shoulder pain accompanies the abdominal pain without any significant discomfort between the abdomen and shoulder. Apart from pain at the right shoulder, some people may also feel pain between the shoulder blades – at the midline of the back.
Swelling and Tenderness
Abdominal distension (swollen abdomen) may also occur with gallstones. It is usually a symptom of a more severe case and sometimes a mass may be felt in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. This mass is usually not the gallbladder itself but the swelling of the tissue (peritoneum) surrounding the gallbladder. Tenderness is also typical. Two fingers or the entire hand should be placed over the tender area on the right side of the abdomen and if there is a pain when a person breathes in then it is indicative of gallbladder disease. This is known as Murphy’s sign but must only be considered as a positive sign if the same technique on the left side of the abdomen does not elicit pain.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is another common symptom of symptomatic gallstones and usually correlates with the pain. The more severe the pain, the more intense the nausea. However, some people experience severe nausea with mild pain and vice versa. Nausea tends to worsen after eating any food and not only fatty foods which tend to exacerbate the pain. Vomiting is also possible and when it starts it should also raise concern about acute pancreatitis. The lack of nausea or vomiting does not mean that the other symptoms are not due to gallstones.
Jaundice and Fever
Jaundice and a low-grade fever are two other gallstones symptoms like nausea and vomiting which are non-specific. This means that these symptoms are not indicative of gallstones or gallbladder disease and can arise with a range of different illnesses. Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes as bilirubin accumulates in the body. Normally bilirubin is excreted in bile but if gallstones blocks the bile outflow, the bilirubin may be retained in the body. Fever with gallstones is low-grade and not usually due to an infection. Sometimes it can be high but this should raise concerns of secondary infections following an obstruction of the bile ducts by a gallstone.
Diagnostic Investigations
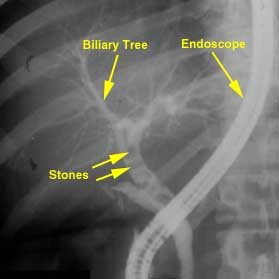
One of the best ways to confirm that you have gallstones is to undergo diagnostic investigations. In this way even small gallstones that may not cause any symptoms can be identified. A range of gallbladder tests may be selected by your doctor when gallstones or gallbladder disease is suspected. An abdominal ultrasound, CT (computed tomography) scan, HIDA scan (cholescintigraphy), ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography) or abdominal x-ray may be used to identify the presence and location of gallstones. Normally these tests are done once gallstone symptoms arise but can be conducted even if a person is asymptomatic.
Picture of ERCP indicating gallstones