How To Know When You Are Ovulating (Egg Cell Released)
Most women only focus on their period and go by the rest of the month without much concern about the menstrual cycle. But for women who are having difficulty conceiving or use a calender-based method of contraception, the time of ovulation is the most important time in the month. If you are one of these women then knowing when you are ovulating is crucial – it can mean the arrival of that much awaited bundle or joy, or intimacy without the risk of pregnancy. But getting it right is not always an exact science and miscalculations can be disappointing.
Points To Consider
It is important to understand what ovulation is if you are scanty on the details. It is the time in your menstrual cycle when an egg cell (ovum) is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube. Rather simplistically, it means that you are the most fertile during this time of the month, and just before it. Ovulation occurs around 12 to 16 days before menstruation. If the egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell (conception), then you are technically pregnant and the next period should not occur. However, there are several factors to consider when determining ovulation.
Pregnancy possible if sperm enters the body before ovulation
Many women make the mistake of thinking that the only time they can fall pregnant is if they have intercourse during and immediately after ovulation. But it does not mean that intercourse has to occur exactly within this window in order to conceive. It is important to realize that sperm cells can survive for up to 5 days inside a woman’s body although most sperm only survive for 48 to 72 hours. So having unprotected intercourse a few days before you ovulate means that you can still fall pregnant although you were technically not ovulating at the time of the act.
Monthly periods are not a guarantee that you ovulate every time
Not every woman ovulates every month. Here are some of the reasons why women do not ovulate. Women who having problems conceiving may not ovulate at all, for many cycles and possibly even for years. This is known as an anovulatory cycle, the term anovulation meaning ‘no ovulation’. So in these cases trying to time the date of ovulation is pointless. Regular periods are not a guarantee of ovulation. Further medical attention may be necessary to stimulate ovulation or treat any underlying problem that may be limiting normal ovulation.
Calculating ovulation time is difficult in irregular cycles
Ovulation cannot always be calculated with certainty. This is particularly true in women with irregular cycles. The date of ovulation, if it even does occur, can vary significantly. Timing the event will be more dependent on watching for symptoms and doing tests rather than using a calender-based method to calculate when ovulation should occur. Remember that if you had an irregular cycle which is now regular with the use of a hormone-based contraceptive, then you are not ovulating at all.
Spotting The Signs and Symptoms
An ovulation calculator is a handy tool in estimating the date of ovulation. However, it is not 100% accurate. Instead you should depend on several methods to confirm ovulation – calculating the date, spotting the symptoms and using tests. Unfortunately, relying on the symptoms of ovulation alone is not very accurate either. Some signs can be verified by another person or your doctor. But symptoms are largely subjective and sometimes a woman can imagine the symptoms of ovulation. Nevertheless it is worth considering.
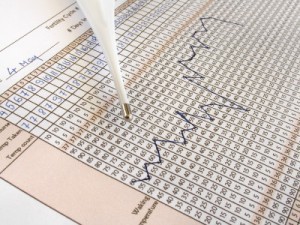
Rise in Basal Body Temperature
There is a slight rise in the basal body temperature when ovulation occurs but it is not detectable without the aid of a thermometer. There are special BBT thermometers for this purpose or a good quality digital thermometer can be used. Expect to see a rise in BBT by about 0.4 to 0.6F.
Clear “Egg White” Cervical Mucus
The normal color and consistency of cervical mucus changes just prior to ovulation. It goes from a cloudy and sticky mucus to a clear and slippery consistency. It appears more like raw egg whites. The amount of mucus also increases substantially during ovulation.
Mid-Cycle Pain, Not Menstrual Pain
Menstrual pain occurs just before and during menstruation. Ovulation pain is different in that it occurs mid-cycle. It tends to be more severe on one side of the abdomen and lasts anywhere from a few minutes to hours. Ovulation pain is also known as mid-cycle pain or Mittelschmerz pain.
Home and Lab Tests For Ovulation
Advances in medical science has led to the development of tests to confirm ovulation. Some can be done at home while others need to be done by a medical professional or at a laboratory. These tests use different methodology to verify pending ovulation, if ovulation has just taken place or whether ovulation occurred in the recent past.
Urine Test
Ovulation predictor kits can be used for home testing. It measures the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) which rises drastically prior to ovulation. A test stick or strip is exposed to urine where it indicates the level of LH in the urine.
Saliva Test
Estrogen is another hormone that rises just prior to ovulation. It can be detected in saliva and is the basis of this type of ovulation predictor kit. A sample of saliva is examined under a microscope to identify a ferning pattern in saliva caused by high estrogen levels. Saliva ferning is not very accurate.
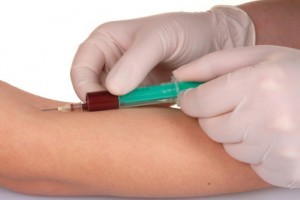
Blood Test
Another more accurate method of testing for ovulation is to assess the progesterone levels. This can be done through a blood test that measures the levels of progesterone in the blood since this hormone rises when ovulation occurs.
Ultrasound Scan
Normally an ovarian follicle matures, ruptures and then releases an egg cell into the fallopian tube. By doing daily ultrasound scans, the follicle can be seen growing. However, it does require a skilled practitioner to be able to visualize these changes.
Biopsy
A sample of the endometrial tissue can be examined to verify the changes that occur with the rise in progesterone levels associated with ovulation. It can be conducted about 7 days before the menstrual period but this test is rarely done to verify ovulation.