Human Endocrine System, List of Glands and Hormone Functions
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system comprises the multiple glands that secrete chemical messengers, known as hormones, into the bloodstream. These hormones may act on almost every cell of the body or it may be tissue-specific and only act on certain types of cells. The endocrine system is the body’s regulating mechanism. All of the body’s functions can be influenced in some way or the other by the endocrine system and this includes metabolism, growth, water and electrolyte balance, sexual function, reproduction and even behavior.
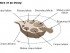
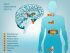
Endocrine Glands
The main endocrine glands include :
- Pituitary gland, pineal gland and hypothalamus – head
- Thyroid gland and parathyroid glands – neck and upper chest
- Pancreas and adrenal glands (on top of kidney) – upper abdomen
- Ovaries (female) and testes (male) – pelvis and perineum
Other sites in the body including organs like the stomach and tissue like adipose tissue can also produce and secrete hormones but are not considered as endocrine glands. In certain disease states, like in cancer, the tumor may secrete hormones into the blood stream – carcinoid syndrome.
Hormones from Endocrine Glands
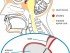
Hypothalamus
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
- Stimulates secretion of TSH and prolactin.
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
- Triggers the release of ACTH.
- Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
- Triggers the release of growth hormone.
- Growth hormone inhibitory hormone (GHIH) (somatostatin)
- Inhibits growth hormone secretion.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
- Triggers the release of LH and FSH.
- Dopamine or prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF)
- Inhibits prolactin secretion.
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary can be divided into the anterior and posterior gland. The hormones below are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, except for ADH and oxytocin, which is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- Stimulates the synthesis and secretion of adrenocortical hormones (cortisol, androgens, and aldosterone).
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) / Vasopressin
- Stimulates the reabsorption of water from urine in the kidneys.
- It also triggers vasoconstriction.
- Both the retention of water and vasoconstriction increases blood pressure.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- In women, it stimulates the growth of the ovarian follicle.
- In men, it stimulates the maturation of sperm in the testes.
- Growth hormone
- Stimulates the synthesis of proteins and growth of cells and tissues.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- In women, it stimulates ovulation, formation of the corpus luteum and production of estrogen and progesterone.
- In men, it stimulates the testes to produce testosterone.
- Oxytocin
- Stimulates the secretion of milk from the breasts.
- Triggers and enhances of uterine contractions.
- Prolactin
- Promotes the development of breasts in women and milk production and secretion.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Stimulates the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine).
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland was believed to play no significant role in the body an was thought of as a vestigial remnant. It is now known that the pineal gland secretes melatonin and related hormones which may play a role in sleep and possibly affect the secretion of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Thyroid
- Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Increases the body’s metabolic rate by acting on most cells.
- Calcitonin
- Promotes calcium deposition in the bones.
- Also reduces the calcium levels present in the blood and tissue fluid.
Parathyroid
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Increases calcium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Triggers the release of calcium from the bones.
- These two effects increases the calcium concentration in the blood.
Adrenal cortex
- Cortisol
- It is a glucocorticoid that has a wide range of metabolic and anti-inflammatory effects as described under natural corticosteroids.
- Aldosterone
- It is a mineralocorticoid that regulates the concentration of essential electrolytes in the body as discussed under natural corticosteroids.
Adrenal medulla
- Norepinephrine and epinephrine
- Has the same effects on target organs as stimulation by the sympathetic nerves but is longer lasting.
Pancreas
- Insulin
- Acts on cells to increase glucose uptake from the blood.
- Glucagon
- Promotes the release of stored glucose from the liver and production of glucose if necessary.
Testes
- Testosterone
- Promotes the development and maturation of the testes, as well as the sexual characteristics of men.
Ovaries
- Estrogen
- Promotes tissue development in the female reproductive system, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and genitalia.
- Increases the growth and development of the and breasts, as well as the sexual characteristics of women.
- Progesterone
- Promotes secretory changes in the uterus and fallopian tubes in preparation of pregnancy.
- Stimulates the development of milk-producing tissue in the breast but does not stimulate actual breast milk secretion.
Thymus Gland
The thymus gland in adults seems to have little functionality compared to early life but plays a role in the maturation of immune cells. It is not an endocrine gland.
The following tissues and organs in the body also produce and secrete hormones but are not endocrine glands.
Adipocytes (Fat Cells)
- Leptin
Heart
- Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Kidney
- Renin
- 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
- Erythropoietin
Placenta
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
- Human somatomammotropin
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
Stomach
- Gastrin
- Ghrelin
Discussed under Digestive Hormones.
Small intestine
- Secretin
- Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Discussed under Digestive Hormones.