Itchy Rectum and Anus – Causes and Treatment
About the Anus and Rectum
The anal canal is the last 2 to 4 cm (approximately 1 to 2 in) part of the large intestine that ends with the anal opening (anus). The rectum is about 12 cm (approximately 4 to 5 in) long and lies between the sigmoid colon and anal canal. Both the rectum and anal canal (along with the anus) form the very last part of the large intestine.As with any other part of the digestive tract, a host of irritants and diseases can cause pain, a burning sensation or even itching in these parts.
An itchy anus or itchy rectum is not an uncommon symptom. We all experience itching in this area every now and then. However, when it is persistent then it needs to be medically investigated. Lesions in the rectum do not usually itchy as there are not itch receptors in this region. Itch receptors are responsible for the sensation of itching when it is activated. However, there are pain receptors in the rectum and therefore sensations such as pain may occur here.
Itching of the anus is possible and is known as pruritus ani which simple means anal itching. Sometimes it may feel deeper and thought to be originating fom the rectum but the itching is either from the anus or anal canal. It may also extend to the skin around the anus which is known as the perianal area. The itching can also continue to the perineum and even involve the groin. Most of the time itching in this region is not a cause fo concern but in rare cases may occur with serious diseases.
Common Causes of Itchy Anus or Rectum
Some of the more common causes of itchy anus and itchy rectum are everyday factors that can be easily remedied. It is a combination of lifestyle factors and non-disease causes that can result in itchy skin anywhere on the body.
Poor Hygiene
Dried feces, dust, dead skin and sweat are some of the particles that are present on the anus and perianal area during the course of everyday life. These substancs can irritate the skin and cause itching in the anal region. It can be easily removed with regular bathing and proper cleaning of the area. Moistened tissues should also be used to clean up after a bowel movement so as to minimize the build up of these substances.
Dry Skin
Dry skin may also cause anal itching. This can occur in any person with, particulaly with the use of harsh soaps, excessive washing of the area and age-related drying of the skin. Do not clean the anal and perianal region excessively and use mild soaps with lukewarm water. Dry skin can be protected with a water-resistant topical applicaion such as petroleum jelly which should be applied generously to the skin surface.
Foods and Beverages
Certain foods such as hot spices, caffeine, beer, wine, prunes, figs, milk products, nuts, popcorn, chocolate, tomatoes and citrus fruits may also cause anal itching for various reasons. This can be due to localized irritation caused by certain chemicals within these foods, diarrhea induced by these foods or an allergic reaction to certain foods and beverages.
Scratching
Scratching is one of main reasons for an itchy anus even when there is no underlying medical cause. Scratching aggravates existing itching and should therefore be avoided as far as possible. Where itching of the anus occurs due to a medical condition, treatment needs to be directed at the underlying cause in order for the itching to subside.

Diseases that Causes Itchy Anus or Rectum
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is skin inflammation due to excessive excretion of oil by the sebaceus (oil) glands. This causes a subsequent overgrowth with Malassezia yeasts. Itchy, scaly yellowish patches of skin appear in groin, armpits, around the nose or ears, and on the scalp. Treatment includes ointments and shampoos containing selenium sulfide, pyrithione zinc, ketoconazole, terbinafine, sodium sulfacetamide, and corticosteroids.
Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are enlarged anorectal veins that may become inflamed. These veins are located either inside the rectum and anal canal (internal hemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids). Internal hemorrhoids usually cannot be felt but may bleed. It may become enlarged to the point that it can protrude through the anus. If hemorrhoidal veins get thrombosed (clotted), itching and sometimes severe pain may occur.
External hemorrhoids appear as tender, soft lumps that bulging out from around the anus. These veins may cause itching or a burning sensation, especially after prolonged sitting or straining during a bowel movement. Hemorrhoids may develop in obesity, prolonged sitting, constipation, repeated straining at bowel movements, and in pregnancy.
Lack of dietary fiber and fluid, insufficient physical activity and several drugs may contribute to chronic constipation which in turn can lead to hemorrhoids. Mild to moderate hemorrhoids may resolve on its own. Over-the-counter hemorrhoidal creams can be obtained in pharmacies. Chronic, non-resolving hemorrhoids can be treated with different non-surgical (rubber banding, arterial ligation, freezing) or surgical methods.
Diarrhea and Bowel Incontinence
An itchy anus is not an uncommon symptom with diarrhea or fecal incontinence. The repeated exposure of the anal lining to feces and wiping can cause irritation and damage to the tissue. This may give rise to pain, burning sensation, bleeding and itching. Removing or treating the cause of diarrhea or incontinence should be the priority A Sitz bath, thorough but gentle cleaning of the anal region and soothing applications including hemomrrhoid creams may help.
Fungal Infection
Fungal infections of the skin with dermatophytes is a common condition. The groin is a frequently affected area and this is known by many names, including tinea cruris, groin ringworm or jock itch. Sometimes this fungal rash can extend to perianal area and even the anus. Typically these fungal infections cause itching.
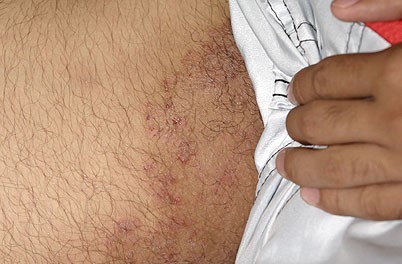
Less commonly an yeast infection of the skin (usually candidiasis) can also in this region and is typically a deeper skin infection. Itching of the buttocks may also be present. Treatment is with over-the-counter antifungal ointments, or in severe cases with prescription antifungal agents, both topically or orally.
Bacterial Infection
In perianal streptococal dermatitis (1), a bright red and itchy rash appears in the groin area. It is moe common in children between 6 months and 10 years of age. Blood streaks may appear in the stool and when wiping after a bowel movement. The cause is infection with group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. Treatment with antibiotics is effective but recurrence is common.
Erythrasma is an infectious skin rash that appears in the skin folds (armpits, groin and toes). It is caused by Corynebacteria minutissimum. Erythrasma mostly affects people in hot climates and those who are immune compromised as may be seen with HIV infection or poorly controlled diabetes. The rash is typically itchy but there may be no other symptoms. Treatment is with antibacterial ointments.
Intestinal Parasites
Thee are several human intestinal worms and protozoa that can cause an itchy anus. Sometimes there may be no other symptoms apart from the itching.
- Pinworms are intestinal parasites that often reside in the colon or rectum in children. These worms may exist the rectum at night and deposit eggs on the surrounding skin. As a result it can cause anal itching. Antihelmintics may be prescribed to eradicate the worms.
- Blastocystis hominis (3) is a microscopic parasite that may cause diarrhea and anal itching. However, in most case it is often present without any symptoms. Antibiotics and antiprotozoal drugs are used to treat the infection.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Common symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) include burning during urination, uretheral discharge or bleeding, swollen groin lymph nodes and sometimes a fever. Typically these infections may extend beyond the genitalia and also causes itching between the goin and thigh. The following STDs may also cause anal itch:
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Gonorrhea
- Genital herpes
- Anal warts (condyloma)
- Molluscum contagiosum
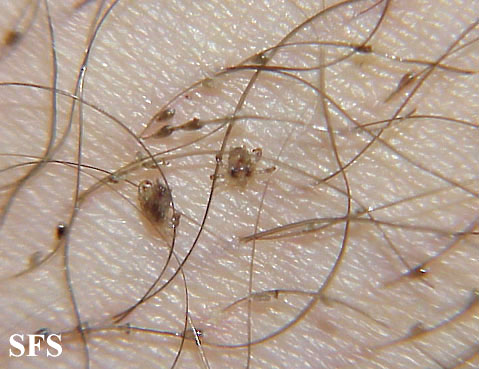
- Pubic lice (crabs)
- Syphilis
Picture 2. Pediculosis pubis
(source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
Treatment may require certain antibiotics, antiprotozoal drugs or other antimicrobial agents. Various HIV skin infections should also be considered in people who are infected with the virus.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis in the groin and buttock region may appear as an itchy, red rash with flaking skin. It may be due to irritation by diapers, underwear, constant irritation by clothes, soaps, water and various other irritants and allergens. Preventing contact with these irritants or allergens is an essential part of treatment. The ras may be treated with various topical applications, such as emollients or even corticosteroid creams.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is inflammation and infection of hair follicles, oil and sweat glands. Itchy and painful lumps may burst and dicharge fluid from the skin between buttocks. These lumps also often appear in the inner thighs, armpits or on the nape of the neck. Treatment is with corticosteroids, antibiotics, and surgery.
Abnormal Anus Tissue
Anal Skin Tags
Anal tags are small soft fleshy bumps of the anal or perianal skin. These lesions are common. It usually does not cause any symptoms but mild anal itching may be present. Although anal skin tags are not usually a problem, it can be removed surgically.
Anal Fissure
Anal fissures are painful linear cracks of the anal mucosa and skin near the anus that may result in straining during defecation, injury, or inflammatory conditions of the rectum and anus. Fissures are common and often heal on its own without futher complication.
Perianal Abscess
A perianal abscess is accumulation of pus in tissues that surround anus. It is usually a result of chronic bowel inflammation or infections. Sometimes a perianal abscess may be seen as a bulge from the skin near the anus, or may be felt during a rectal examination. Treatment is with antibiotics and/or surgical drainage.
Anal Fistula
An anal fistula is a small tunnel that forms between the anal or rectal mucosa and opens onto the skin beside the anus. It may itch and bowel contents may exit through it. Surgery is usually required for the treatment of an anal fistula.
Bowel Diseases that Cause Itchy Anus
Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are inflammatory bowel diseases that appears to be immune-mediated. It mostly affects adults. Ulcers and fissures affecting the anal mucosa may be itchy or painful and can bleed. Corticosteroids and other immune suppressants as well as immune-modulating drugs may be used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Anal Cancer
Anal carcinoma (cancer) may be painful, itchy and may bleed. It is a rare form of cancer when compared to colorectal cancer. Most of the time it occurs after 50 years of age. Teatment requires a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy and/or surgery.
Prevention of Anal Itch
- Gentle but thorough wiping after a bowel movement is essential. Moistened tissues may be used.
- Wash the anal region with lukewarm water when bathing. Soap should be avoided if it is an irritant.
- Never scratch the anus and perianal region as the mucosa and skin in this area is very delicated.
- Avoid applying perfumes, deodorants and medicated powders in the anal and perianal area.
Treatment of an Itchy Anus
Treatment of an itchy anus or itchy rectum may vary depending on the underlying cause. It is important that the area is assessed by a medical professional in order for the most appropriate treatment to be prescribed.
- Topical moisturizing creams can help to soothe affected area. Sometimes a corticosteroid cream may be used by these applications should not be used continually as it can cause thinning of the anal mucosa.
- Suppositories should be avoided unless it has been specifically prescibed for rectal and anal conditions that may cause itching.
- A high fiber diet with sufficient water intake on a daily basis is important to avoid constipation and keep the stool soft. This will help with minimizing strain during a bowel movement.
References
- Perianal streptococcal dermatitis. American Family Physician
- Erythrasma. Dermnet NZ
- Blastocystis hominis infection. Mayo Clinic
- Anal abscess. WebdMD.com
Last updated on 16 August 2018.