Itchy Wrists Causes and Remedies for Wrist Itching
Itching of the skin is a common symptom that can occur anywhere on the surface of the body. Most of us experience it a few times in a day but it is short term and quickly relieved with slight scratching. However, there are times where itching may persist and even progressively worsen with or without a skin rash. In these cases itching is most likely a symptom of some underlying medical condition and usually it is related to a skin disease.
Causes of Itchy Wrists
Itching at the wrist may be due to the same reasons as itching anywhere else on the body, and specifically with itching of the hands and itching of the palms. However, there are some factors that may be somewhat unique to the wrist which can cause itching without it spreading beyond the wrists.
Clothing
Allergies to textiles is not uncommon. It will usually affect any part of the body where the clothing makes contact with the skin. The folds, like the neck and wrists, often react more quickly than others parts of the body. With regards to the wrists, the cuffs of a shirt or sweater may be the reasons why there is itchy wrists due to clothing without affecting other areas of the arm or torso to the same degree.
Wrist Apparel
Watches, bracelets and wrist bands are another common cause of wrist itching. Often the itching is due to an allergic reaction when the materials these wrist wear is made of comes into contact with the skin. This is known as allergic contact dermatitis. Some people are sensitive while others are not.
However, another factor to consider is irritation of the skin without any allergy. This can happen when wrist apparel is too tight, used for too long periods of time, may be sharp or rough or is chaffing the skin during movement. Sweat and water trapped between a wrist watch and the skin can also serve as irritants.
Hand Washing
Washing the hands and wrists can also be a cause of itchiness with or with a skin rash. Excessive washing or very vigorous washing can cause mechanical irritation but even the water and soap may be a problem. Water that is not dried off properly may act as an irritant. Certain soaps, particularly soaps with strong fragrances and antibacterial soaps, may also be irritants for some people. The latter can also cause dry skin.
Eczema
Eczema is a common term used to refer to the different types of dermatitis. Irritation or allergic reactions to clothing, water, sweat, soaps and so on are usually part of contact dermatitis. Another common dermatitis is atopic dermatitis which is more frequently seen in children. This is a result of hypersenstivity to certain inhaled or ingested allergens and tends to cause a rash at the folds of the body. It may be associated with asthma or allergic rhinitis.
Also refer to hand eczema.
Medication
Wrist pain and soreness is not uncommon these days given the widespread use of keyboards, mobile devices and video game controllers. It is often thought to be related to carpal tunnel syndrome where the median nerve that travels through a bony tunnel in the wrist is compressed.
The application of topical agents which may be massaged into the area can sometimes be the cause of skin irritation. Some people are more sensitive to these topical applications than others. Oral medication can also cause itchy skin as a side effect but it is usually not isolated to a specific part of the body like the wrist.
Toxins
The hand comes into contact with many toxic substances in the environment either accidentally or intentionally. The latter is more likely to occur among people who work with toxic substance in an industrial setting. Although protective wear is usually advised, these substances may still be able to make contact with the skin.
It is uncommon for the wrists to be affected alone in these cases without involving the hands as well or even the a portion of the forearms. However, in cases where loose fitting gloves are worn of if there is a gap between the protective gloves and the rest of the gear, the wrists may be exposed.
Fungal Infections
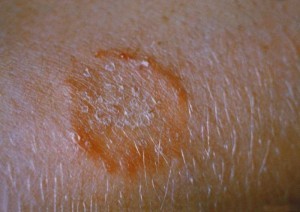
Fungal infections of the skin are common although these infections on the wrists alone are not frequently seen. However, wrist fungal infections are usually an extension of a hand fungus (tinea manuum). These infections are caused by a type of fungus known as dermatophytes and is more likely to affect the feet (athlete’s foot), scalp (scalp ringworm) and groin (jock itch).
These fungi may sometimes be transferred from these infected areas to the hands and wrists. However, fungi are widely prevalent in the environment and may be passed on from one person to another, less commonly from animals or directly from the environment to a person. It is often referred to as a ringworm due to its characteristic red ring-like lesions.
Other Causes
There are a number of other causes of itchy skin but it may not always be isolated to the wrist. Nevertheless these causes need to be considered when the other possible conditions mentioned above have been excluded.
- Hives (urticaria)
- Infections like chickenpox
- Infestations like scabies
- Liver and/or biliary disease
- Nummular dermatitis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Psoriasis vulgaris
Remedies for Itchy Wrists
Wrist itching especially when it is persistent and a rash is present should always be investigated by a medical professional. Depending on the diagnosis, the appropriate treatment is then prescribed. Some simple conservative measures that may be helpful includes:
- Wash the hands thoroughly after touching potentially irritant substances and this should extend above the wrists. Protective wear should be used as far as possible.
- Dry the washed area thoroughly and always ensure that there is no residual water or soap before wearing a watch or other wrist apparel. Ideally watches and other wrist apparel should be avoided until the itching resolves.
- Use an emollient for dry and itchy skin. These applications should be hypoallergenic with minimal additives like fragrances for a pleasant scent.
- Avoid scratching as far as possible. It may exacerbate the itching. Instead attempt to rub the area gently and apply a thick application like petroleum to reduce skin irritation from scratching.