Jock Itch – Pictures, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
What is Jock Itch?
Jock itch is a fungal infection of the groin area that is medically known as tinea cruris. The term ‘jock itch’ is derived from this condition occurring frequently in athletes (also referred to colloquially as jocks) and that it presents with significant itching. It is also known as groin ringworm, groin fungus and scrot rot. Despite the term, tinea cruris (jock itch) does not only affect athletes or males for that matter. Any person can develop jock itch, including children and women.
Other regional names for tinea cruris includes ‘dhobi’s itch‘ in India because it is commonly seen among clothese washers (dhobis). The term ringworm is a misnomer. Jock itch like many fungal infections of the skin is due to a fungus that causes a red ring-like lesion on the skin which is said to resemble a curled worm. However, there is no actual parasitic worm involved in the infection.
What are the Symptoms of Jock Itch?
The signs and symptoms of jock itch include a rash, itching, hyperpigmentation and sometimes oozing of the skin.
Rash
The rash, as described, is typically a red ring-like lesion. The skin at the center of the rash may be normal or dry and scaly. However, in the groin region this typical appearance may not always be present. Usually the edge of the rash has a raised red border.
Itch
Itching is also quite pronounced with tinea cruris, hence the term jock itch. The itch tends to worsen when the area is covered and during hot and humid weather. Sratching the area may cause sloughed off skin cells to fall off as tiny sand-like particles.
Darkening
Darkening of the skin is more likely to occur with long term tinea cruris, particularly when treatment is delayed or the infection is recurrent. The skin appears dark brown in color and this hyperpigmentation is usually irreversible. Excessive scratching also contributes to it.
Oozing
Many people with jock itch report moisture in the affected area which has a must odor. In addition, tiny blisters form which may burst and ooze. This is more likely to be worsened by vigorously scratching that leads to breaks in the skin which may then become infected with bacteria.
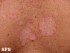
Pictures of Jock Itch
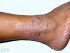
Picture 1. Jock itch – Tinea cruris (source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
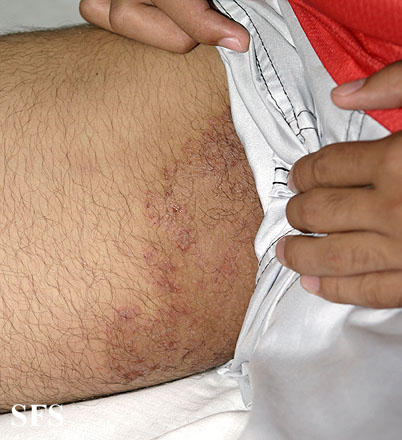
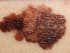
Picture 2. Jock itch with hyperpigmentation (source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D.)
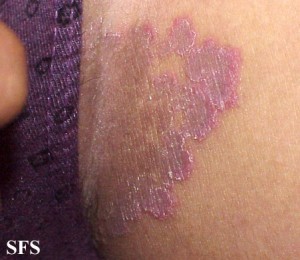
What Causes Jock Itch?
Jock itch is caused by fungi that have a predilection for human skin. These fungi are known as dermatophytes and are distinctly different from yeasts. Dermatophytes have the ability to digest the hardy protein known as keratin which is in the outermost layer of skin. It only infects and consumes these outer layers where it can thrive for months, years and even decades.
The groin region is prone to these infections because it is warm, moist and dark. The fungi therefore thrive in this region. However, this does not mean that every person will contract jock itch. It is more likely to occur under certain circumstances and mainly by close contact with people who are infected with this species of fungi. A break in the skin increases the chance of the fungi infecting the area.
In addition, jock itch often occurs along with another fungal infection of the skin elsewhere on the body like tinea pedis (foot ringworm). This foot infection is also known as athlete’s feet. Either the foot or groin infection may arise first and it is often spread from one area to the other by scratching. The fungus is carried on the fingers to any part of the body although the feet, groin and scalp are the most commonly affected areas.
How is Jock Itch Spread?
Jock itch is easily spread with sharing towels or sportswear and other personal items. There are many different species of dermatophytes that may cause jock itch. Most are specific for human skin and therefore spread from person to person but some may also infect animals like dogs and cats. The fungus is then spread from the pet to a person who is in close contact with the animal.
Who Gets Infected?
Tinea cruris (jock itch, groin ringwom) can affect any person of any age. Adult men tend to be affected more often and it is uncommon in children. Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of develop jock itch, such as:
- Moisture in the groin region, usually due to perspiration but also with immersion in water without drying.
- Tight underwear, especially where there is chaffing of the skin.
- Obesity, as skin folds increases the risk of retaining moisture.
- Hyperhidrosis where there is excessive perspiration.
- Sharing of personal items that may contact with the region, like underwear and groin guards.
- Having pre-existing skin fungal infection elsewhere on the body, like athlete’s foot (foot fungus).
- Immunodeficiency (weakened immune systems) such as in HIV infection, AIDS and diabetes.
How is Jock Itch Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of jock itch is made by examination (inspection) of the skin lesion in the groin region. In doubtful cases, rash can be scrapped and sent into microbiological laboratory. Rash in the groin may be caused by other types of fungi (Candida albicans), viruses (Herpes genitalis), bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus), allergies (itchy pants syndrome, cholinergic urticaria), inverted psoriasis, Darier’s disease, Hailey-Hailey disease (pemphigus), intertrigo, seborrheic dermatitis, and so on.
Treatment of Jock Itch with Antifungal Medications
Antifungal ointments (over-the-counter) for mild infection (1):
- Terbinafine (Lamisil)
- Naftifine (Naftin)
- Miconazole (Micatin)
- Clotrimazole (Lotrimin)
If over-the-counter ointments do not help in few days, other potent drugs should be used:
- Ointments, such as Econazole (Spectazole) or Oxiconazole (Oxistat)
- Medications by mouth, such as Itraconazole (Sporanox) or Fluconazole (Diflucan)
- Terbinafine (Lamisil)
Prevention of Jock Itch
To prevent jock itch:
- Shower or bath daily and after each sport activity or work.
- Keep groin area dry by wearing boxer pants and airy trousers.
- Do not share towels and sportswear with anyone.
Further Reading:
- Itchy Legs
- Itchy Feet and Toes
- Itchy Rash
- Causes of Itchy Skin
- Itch Diagnosis and Treatment
References:
- Jock itch treatment (mayoclinic.com)