Pain Between Breasts (Cleavage Pain) Causes and Video
The area between the breasts, commonly referred to as the cleavage in women, is where the breastbone lies. It is covered by connective tissue and skin. The breastbone plays an important role firstly in acting as a ‘shield’ against any external force as well as serving as point where the collarbone (clavicle) and ribs can connect on either side. Pain in the area between the breasts, also referred to as cleavage pain, is therefore the same as breastbone pain.
Since women have significantly larger breasts than men, sometimes pain between the breasts may actually be breast pain on the inner side (medial aspect of the breasts. Pain in this area can arise for various reasons. Superficial pain is usually related to the skin, tissue underneath it or the breastbone itself. In most instances this is not serious. Deeper lying pain is more often of concern since the heart, great blood vessels, lower airways and parts of the lung as well as the esophagus lie in or around this region with the chest (thoracic) cavity.

Causes of Cleavage Pain
Some of the causes of cleavage pain have been discussed below. The strain of the breasts on the chest wall, especially large breasts or growing breasts, can also be a common cause of cleavage pain along with breast cancer and other breast conditions which are not discussed further. Similarly pain from the back can radiate to the chest wall as well pain referred from other organs which may not lie directly behind the breastbone (sternum).
Skin
The overlying breastbone skin is continuous with skin throughout the chest wall and the body surface as a whole. Therefore pain arising from the skin may occur for a number of different reasons. Some of the conditions that cause cause skin pain in the cleavage area includes:
- Sunburn especially when the cleavage is exposed to the sun and during long periods of sun exposure. Redness, swelling and tenderness may arise within 8 to 24 hours after exposure to intense sunlight.
- Shingles is a condition caused by reactivation of the dormant chickenpox virus. It causes a skin rash and pain within certain segments (dermatomes) particularly on the chest area.
- Acne vulgaris where the follicles becomes blocked, inflamed and sometimes infected leading to the formation of pimples. The chest area is commonly affected along with the face, scalp, shoulders and back.
- Dermatitis (eczema) which simply means skin inflammation can occur for a number of reasons. Contact dermatitis is among the more common type. It arises when some substance, like jewelry made from certain metals or even body lotions, irritates the skin or triggers an allergic reaction. An itchy skin rash is usually present.
Bone, Cartilage and Joints
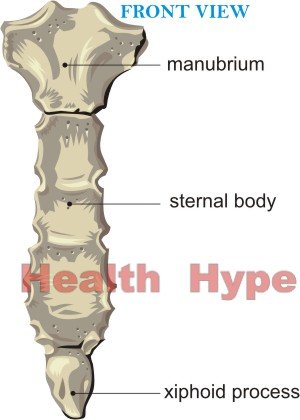
There are three parts to the breastbone – the manubrium, the body of the sternum and the xiphoid process. On either side of the breastbone the collarbone (clavicle) and ribs attach forming joints with it. Costal cartilages connect the ends of the ribs to the breastbone. Any problems with these structures will also lead to pain between the breasts.
- Fractured sternum is one of the possible cause of pain. The sternum (breastbone) may fracture with a blow to the chest and is more likely to be seen as a consequence of a car accident injury. Other bone fractures may also give rise to pain in and around this area.
- Costochondritis is inflammation of the costal cartilages which connect the ribs to the breastbone. It causes pain usually with no other symptoms. When swelling is also present then it may be Tietze syndrome.
- Arthritis is the term for joint inflammation which often presents with joint pain (arthralgia). This may be the cause of pain between the breasts as numerous joints are formed where the clavicle (collarbone) and ribs meet the sternum (breastbone). Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are the two more common forms of arthritis.
Muscle, Tendons and Ligaments
There are several muscles that lie over the ribcage or connect to different parts of it. The most prominent is the pectoral muscles on top of which lies the breasts. Muscles connect to the bones through tendons. Ligaments are bands of tissue that provide stability and support to joints and lie close to the tendons.
- Strain is where the muscle is overexerted. The muscle may go into spasm, become inflamed or even tear. The pain that arises is usually exacerbated on movements involving the use of the affected muscles.
- Tendonitis is one of the common tendon problems. It is inflammation of the tendon and is also often associated with muscle strain and excessive stretching. Sometimes the tendons can tear as well.
- Sprain is where a ligament is injured or inflamed usually be excessive stretching. There are several ligaments that attach in and around the breastbone like the costo-clavicular ligament, sterno-clavicular ligament and chondro-sternal ligament.
Heart and Blood Vessels
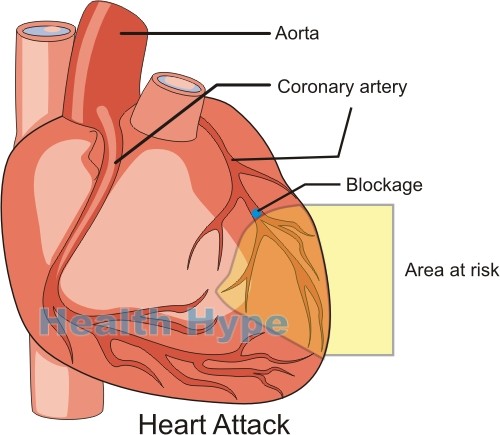
The heart lies behind the breastbone and protrudes from either side of it, with more of the heart extending to the left than the right side. From the heart arises the great blood vessels like the aorta. Cardiac pain is therefore usually in the center of the chest although it can be slightly to the left of the sternum and even to the right of it.
- Angina pectoris is heart muscle pain that arises when there is insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. It is usually associated with coronary artery disease. If left untreated it can progress to a heart attack.
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack) is where a portion of the heart muscle dies due to insufficient blood flow to it. Apart from central chest pain, dizziness, excessive sweating and left arm pain may also be present.
- Pericarditis is inflammation of the lining around the heart (pericardium). It can occur for a number of different reasons, including infections, non-infectious inflammation and with trauma to the chest wall.
- Aortic aneurysm is where a portion of the wall of the aorta bulges abnormally. It can lead to an aortic dissection where there is a tear in the inner lining of the aorta with blood accumulating inside the wall. This may the progress to a rupture. Aortitis is where the aorta becomes inflamed. Pain behind the breastbone may be present in all of these conditions.
Airway and Lungs
The airway continues down the throat (larynx and trachea) to give rise to two bronchi (singular ~ bronchus) which carries air to and from the lungs. Problems in the lower airways like the bottom part of the trachea, bronchi or the inner side (medial aspect) of the lungs can give rise to pain between the breasts. Breathing is usually affected to some degree.
- Tracheitis and bronchitis refer to inflammation of the trachea (windpipe) and bronchi respectively. Bronchitis is usually due to infections. Asthma may sometimes also cause pain in this area as the bronchi constrict abnormally and mucus impedes airflow.
- Pneumonia is inflammation of the lung that is most often due to infections. Other lung disease like pneumoconiosis and pneumonitis may arise with exposure to organic or inorganic dust and allergic reactions.
- Pleuritis or pleurisy is inflammation of the lining around the lungs (pleura). It is also often due to infections. Apart from pain that is worse when breathing there may also be fluid accumulation in the space round the lungs (pleural effusion).
Cancer of the lower airways or lungs is relatively common. Pain may be a late feature to arise.
Esophagus
The esophagus or food pipe carries food from the throat to the stomach. It runs down the length of the chest to pierce the diaphragm and join the stomach. The esophagus lies somewhat in the middle of the chest. A number of conditions can affect the esophagus and due to its close proximity to the heart, it may be mistaken for cardiac conditions.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is where the rising stomach acid enters the esophagus and irritates it. The typical symptom is heartburn (burning chest pain) and is usually accompanied by nausea.
- Esophagitis is inflammation of the esophagus. While it can arise with infections, consumption of toxic substances or mechanical injury, the more common cause is acid reflux as is seen in GERD.
- Esophageal ulcers are open sores that form in the inner wall of the esophagus. It is also commonly caused by recurrent acid reflux but may also be associated with the same causes as stomach ulcers.
Reviewed and updated on 12 August 2018.