Peripheral Neuropathy (Nerve Disease) Symptoms, Causes, Types
What is peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is any disease or disorder of a nerve outside of the brain and spinal cord. It is also known as peripheral neuritis, although the word neuritis specifically refers to inflammation of the nerve and not all neuropathies are inflammatory in nature. Another common term for peripheral neuropathy is peripheral nerve disease. There are several different types of peripheral neuropathies that are classified according to the disease mechanism or cause of the nerve disease.
Anatomy of a peripheral nerve
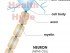
Nerves are located throughout the body either within the central nervous system (in the brain and spinal cord) or peripheral nervous system (outside of the brain and spinal cord). Peripheral nerves are conduits between the central nervous system and different parts of the body. Most nerves are made up of nerve fibers which are the collections of axons – long projections of the nerve cells (neurons). Collections of the cell bodies of these neurons are ganglion. In order to transmit electrical signals efficiently, some nerves are surrounded by an insulating layer known as the myelin sheath (myelinated nerves). Those nerves that lack this insulation are known as unmyelinated nerves.
Peripheral nerves are classified as :
- Afferent or sensory fibers when it carries impulses from a part of the body to the central nervous system.
- Efferent or motor fibers it carries impulses from the central nervous system to a part of the body.
- Mixed fibers contain a combination of both afferent and efferent fibers.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
There are various ways in which these peripheral diseases may become diseased or damaged. Depending on the type of nerve that is affected and the extent of the disease, it may cause a host of different signs and symptoms.
Sensory nerves
These are the peripheral nerves that relay sensations from receptors throughout the body to central nervous system.
- Burning
- Pain
- Tingling
- Numbness
- Diminished sensation
Motor nerves
These are the peripheral nerves that relays signals from the central nervous system to muscles throughout the body. It may control the muscles that are voluntary or involuntary (autonomic nervous system) contol.
- Muscle weakness
- Paralysis
- Lack of coordination
- Bowel and bladder problems
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
There are a number of different causes of peripheral neuropathy. The way in which the nerve is damaged may vary with each cause thereby contributing to different symptoms. It includes autoimmune disorders, infections, inherited disorders, metabolic diseases, nutritional deficiencies, toxins, trauma to the nerve and nerve tumors. This has been discussed in greater details under types of peripheral neuropathies.
Types of Peripheral Neuropathies
Inflammatory Neuropathy
Inflammatory neuropathies occur as part of an autoimmune mechanism. Here immune responses are directed at the entire nerve or specific parts of the nerve. The reason why this occurs is not always clear as with many types of autoimmune diseases. Sometimes it occurs after an infection but is not infectious neuropathy. Instead the infectious agent may trigger an abnormal immune response that can persist long after the infection resolves. The main inflammatory neuropathies includes :
- Acute inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy (Guillain-Barré Syndrome)
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy
Infectious Neuropathy
Nerve damage can occur as part of an infection at a site but some infectious agents tend to target nerve tissue specifically. It may occur as infection isolated only to a nerve or be part of a systemic infection where multiple organs are affected. These infections are mainly viral or bacterial in nature with some bacterial toxins also specifically affecting the nerve tissue. Some types of nerve infections include :
- Diptheria – bacteria
- Epstein-Barr – virus
- Leprosy (Hansen disease) – bacteria
- Lyme disease – bacteria
- Varicella zoster (shingles) – virus
Hereditary Neuropathy
This type of peripheral nerve disease is inherited. Genetic errors may cause any number of disturbances of the peripheral nerves mainly by damaging the myelin sheath or the axons that make up the nerve fibers. These types of neuropathy can be classified as :
- Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies (HMSNs)
- Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies (HSANs)
- Familial amyloid polyneuropathies
- Peripheral neuropathy accompanying inherited metabolic disorders
Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies (HMSNs) are the most common type of hereditary peripheral neuropathies. The main types of HMSNs include :
- HMSN I (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease)
- HMSN II
- HMSN III (Dejerine-Sottas neuropathy)
Metabolic or Toxic Neuropathy
Certain metabolic disorders or toxins can affect nerve function or structure. These substances damage the nerves to varying degrees thereby affecting nerve function in different ways. It includes :
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Metabolic and nutritional neuropathies including alcoholic neuropathy, uremic neuropathy or neuropathic beri beri
- Neuropathies associated with malignancy
- Toxic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a complication of long term and poorly controlled diabetes mellitus (sugar diabetes). It affects about half of all diabetics and mainly occurs after having diabetes mellitus for 15 years or more. Diabetic neuropathy affects both the sensory and motor nerves particularly in the limbs.
Uremic neuropathy occurs in renal failure. It is often reversible with dialysis. Nutritional neuropathy is nerve damage that arises with deficiencies of vitamins B6, B12 or vitamin E. Alcoholic neuropathy arises with long term alcohol abuse but is more likely associated with vitamin deficiencies such as thiamine deficiency in alcoholism rather than the toxic effects of alcohol on the nerves. Peripheral neuropathy can also occur with diseases involving the liver, thyroid and respiratory system.
Cancer neuropathy is nerve disease that occurs with cancer. Here the cancer may infiltrate the nerve or compress it. Sometimes the nerve is disrupted through an unknown mechanism seen with certain types of cancer, particularly small cell lung cancer. This is known as paraneoplastic autonomic neuropathy and the exact cause is not known but it is believed to be associated with an autoimmune mechanism.
Toxic neuropathies arise with exposure to certain industrial chemicals and drugs. It is mainly seen with heavy metals like arsenic and lead. One of common neuropathies associated with drugs is that of statin-induced neuropathy. These cholesterol-lowering drugs have often been implicated as a cause of neuropathy by patients but there is insufficient evidence to corroborate this side effect of statins.
Traumatic Neuropathy
Neuropathy due to trauma can arise with many different types of injuries and musculoskeletal disorders. It may compress the nerve (entrapment), stretch it or even sever the nerve. This has been discussed in detail under nerve injury.
Peripheral Nerve Tumors
Various benign and malignant tumors may arise in the nerve tissue. This includes :
- Schwannoma
- Neurofibroma
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
These tumors develop from nerve tissue unlike paraneoplastic syndrome and metastatic spread of cancer to the nerve as discussed above under cancer neuropathy.