8 Reasons For Nighttime Urination
Having to wake at night in order to urinate is more than just an inconvenience – it can cause sleep problems and be a symptom of certain diseases. Most of us know that persistent frequent urination and nighttime urination are symptoms of conditions like diabetes. But there are number of other conditions apart from diabetes that can also cause diabetes. Some of these causes can be serious and chronic. Others may be acute or even not a disease but rather a lifestyle issue.
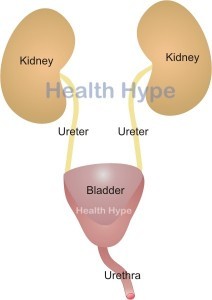
During waking hours we may easily urinate between 5 to 8 times a day, sometimes more or less and this is considered normal. The average adult will pass 1 to 2 liters of urine in a day but a volume greater than 3 liters is considered excessive. People who drink more fluids will naturally urinate more often.
However, the production of urine by the kidneys drastically decreases while we sleep. The bladder therefore fills very slowly and it should not disturb us from our sleep in order to urinate. The odd incident of waking at night to urinate is not usually a cause for concern. But when nighttime urination, which is known as nocturia, occurs on a daily basis then it needs to be investigated.
Diabetes Mellitus
It is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases across the globe and most people now know about diabetes. The problem lies with the body either producing too little insulin or not responding to insulin. As a result the blood glucose levels cannot be maintained within a normal range. Some of the common symptoms of diabetes mellitis includes excessive thirst and frequent urination. Nighttime urination is also common. However, these urinary abnormalities may decrease or return to normal with good glucose control either through medication or with dietary and lifestyle changes.
Enlarged Prostate
Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) is a common condition that will affect more than 50% of males after the age of 60 years. The prostate enlarges but this is not a malignant (cancerous) growth. BPH causes symptoms like frequent urination as it presses against the bladder. Usually the urine passed out during does not empty the bladder fully. Nighttime urination is therefore commonly seen in BPH as well as with other prostate conditions like prostatitis. However, the opposite may also occur where a person cannot pass out urine as the enlarged prostate compresses the urethra within it and occludes it completely.
Diuretic Medication
Diuretic drugs increase urine production. In this way the fluid volume within the body can be decreased. Diuretics are a widely use drug particularly for conditions like high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. However, frequent urination may mean having to awaken at night to pass urine. Although it can cause sleep disturbances, the benefits have to be weighed up against the risks. The dosage of the diuretic may be changed if the nighttime urination is causing a significant problem but the drug should not be stopped without a doctor approving it.
Excessive Fluid Intake
Naturally you will urinate more frequently if you drink larger amounts of fluids. Some fluids have a diuretic action like caffeinated beverages. This can cause frequent urination throughout the day and even into the night. Sometimes this excessive fluid intake is to quench increased thirst which can arise with certain diseases and drugs. Even having a few extra glasses of water a short while before sleeping can cause nocturia. It is best to reduce fluid intake at least 2 hours before bedtime to avoid waking at night to urinate. Remember that your urine production decreases at night so you will not need as much fluid in the evenings as you would during the course of the day.
Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common, particularly among women. In most cases microbes enter through the urethra and travel up to the bladder. Nighttime urination may be one symptom of urinary tract infections along with frequent urination and burning pain during urination. UTIs can be effectively treated with antibiotics since most are bacterial in nature. However, it is not uncommon for the infection to recur in some people. The urge to urinate should not be ignored as there is a risk of the urine pushing upwards from the bladder into the ureter and even reaching the kidney although there are valves to usually prevent this from happening.
Abnormal Circadian Rhythm
A lesser known cause of nighttime urination is a disturbance in the normal biological clock. The activity of different organs and systems in the body generally follows a 24 hour cycle and some people may have a daytime urinary pattern at night. As a result nighttime urination may disturb the sleep. This is more likely to occur with shift work as the body takes a few days to adapt to a change in the sleep and wake cycles. However, it can occur in people who usually sleep at night and are awake during the day. Simple lifestyle measures may be able to alter the cycle without the need for drugs in some cases.
Kidney Diseases
Usually in kidney diseases the production of urine is affected. This can sometimes mean that not enough water is reabsorbed in the kidney tubules leading to large volume urine output in a day which is seen as frequent urination and therefore nighttime urination. Excessive urination can occur with chronic kidney diseases although reduced urine output is more frequently seen in these cases. Some kidney problems like lithium-induced kidney disease often does present with frequent urination. This condition is caused by the use of the drug lithium in the treatment of psychiatric disorders like bipolar depression.
Bladder Diseases
Any irritation of the bladder can elicit premature urination even before the bladder is full. Apart from infectious cystitis (bladder infection), nighttime urination may be seen with other bladder conditions including interstitial cystitis, neurogenic bladder and overactive bladder syndrome. The problem is usually due to a combination of incomplete urination with some urine being retained in the bladder, and irritation of the bladder muscle wall eliciting the urge to urinate. Frequent urination occurs during the day and even into the night. It is not uncommon for urinary incontinence to occur in these cases.