Solar Urticaria (Sun-Induced Hives)
What is solar urticaria?
Solar urticaria is a skin condition known as hives that specifically develops after exposure to sunlight. It can also occur with artificial light sources within specific wavelengths. Solar urticaria is a type of photodermatosis – a skin condition that arises with light exposure. It tends to develop on the sun exposed areas in hypersensitive people and resolves spontaneously within minutes and hours after moving away from the sunlight. However, the areas of the body that are usually exposed to sun on a daily basis, like the face and arms, are often spared. Solar urticaria should not be confused with sunburn as it is an immune-mediated reaction and not due to UV radiation damage. The condition tends to arise with less than 30 minutes of sun exposure.
Reasons for Sun-Induced Hives
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a condition where the body’s inflammatory response is triggered for no apparent reason. Sometimes it can be associated with contact with certain substance but hives in most people comes and goes without any trigger or treatment. Substances that cannot be identified in every case triggers the immune system’s activity and inflammation ensues. In solar urticaria, it appears to be an antigen-antibody complex that triggers the reaction.
Antigens and antibodies
Antigens are protein substances that are almost unique to each organism. For example, bacteria and viruses have proteins on their surface which are considered as antigens. A part of the immune system functions by making antibodies, another type of protein, which will bind with specific amtigens. When an antigen-antibody complex is formed, it triggers the immune system to act and release chemicals and cells which are responsible for inflammation.
Mast cells
It appears that in solar urticaria, there are substances within the bloodstream that are photosensitive or are only formed after light exposure. Sometimes it arises with the use of certain drugs. These substances, either new or altered, are the antigens which binds with antibodies. One type of immune cells that responds to this complex is a mast cell which is distributed throughout the body. Mast cells are known for playing a major role in allergies. When activated, these mast cells release large amounts of histamine.
Histamine
Histamine and possibly other inflammatory chemical mediators causes the blood vessels at om the affected are to dilate. The blood flow increases to the affected area and fluid leaks into the tissue from the bloodstream thereby leading to swelling. It irritates receptors at the site and causes immune cells to aggregate at the area. This leads to typical symptoms like itching with swelling and redness, as is seen in urticaria. Although urticaria is primarily a skin condition, it can affect any tissue in the body like the airways.
Solar Urticaria Symptoms
The most prominent symptoms in solar urticaria are the skin lesions. It is similar to acute urticaria except that it is distributed along the sun-exposed areas. The characteristic feature is that the skin rash develops after even short exposure to sunlight, usually less than 30 minutes. If the swelling of the skin is very severe, there may be other systemic symptoms like lightheadedness. This occurs when excessive amounts of fluid leave the bloodstream and enter into the skin.
Skin rash
- Varies from a red flat patch to a raised swollen lesion (wheal).
- Tends to appear on areas of the body that are usually shielded from sunlight.
- Sun-exposed areas often spared probably due to acclimatization to sunlight.
- Itching and stinging sensation of the affected skin.
Other symptoms
Additional symptoms may not always be present.
- Swelling of the tongue or lips.
- Wheezing.
- Lightheadedness.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
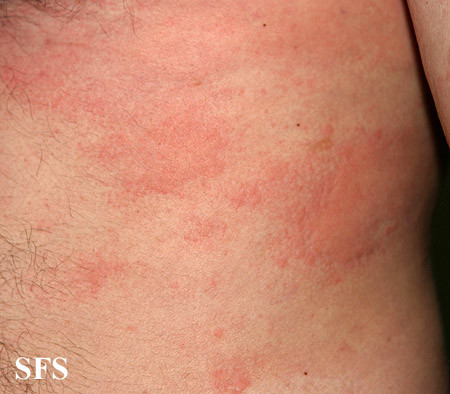
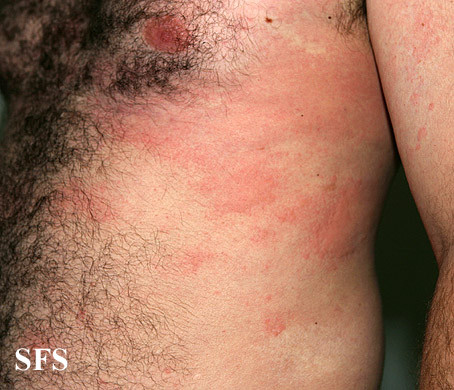
Pictures and Photos
Pictures sourced from Dermatology Atlas Brazil courtesy of Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D.
The skin rash in these photos are of acute urticaria which is largely the same type of rash seen in solar urticaria. Sometimes the affected area in solar urticaria may be clearly demarcated from the neighboring unaffected areas that were adequately protected by clothing.
Sun Hives Causes
The exact cause of solar urticaria is unclear. Sunlight and other artificial light sources emitting light within a certain wavelength range are the triggering factor but not the actual cause. As explained above it appears to be an antigen-antibody reaction. The reason why some people are hypersensitive and others are not is not known. The photoallergen in solar urticaria may be chemicals within the body that are altered by sunlight. It is also believed that sometimes the use of certain drugs may cause the development of photoallergens. However, these photoallergens will not affect every person to lead to solar urticaria. Individual hypersensitivity is therefore a factor.
Solar urticaria is triggered by light in the wavelength range of around 290 to 800 nm. The reaction is more likely to occur in areas that are not usually exposed to sunlight like the back whereas other areas, such as the face and hands, which are usually exposed to sunlight daily tend not to be affected. These areas may have acclimatized to sunlight and are therefore unaffected with solar urticaria. Sunlight may be able to penetrate light clothing and cause solar urticaria even on covered areas of the body. Solar urticaria is a very uncommon condition accounting for less than 5% of all photodermatoses.
Solar Urticaria Types
There are two types of solar urticaria – type I and type II.
Type I solar urticaria
In this type of solar urticaria, the specific photoallergens responsible for the development of the condition are only present in hypersensitive individuals. A type of antibody known as IgE (immunoglobulin-E) binds to the photoallergen and mediates the reaction.
Type II solar urticaria
In this type, the photoallergens may be present in both solar urticaria patients and healthy individuals. It is also an IgE mediated reaction. However, the reason why only certain people will develop the condition and not others who also have the photoallergen within their body is unclear.
Tests and Diagnosis
Solar urticaria may closely resemble other skin conditions caused by sunlight exposure (photodermatoses). The rash develops within 30 minutes of sun exposure and resolves within minutes or hours once out of the light. Further diagnostic investigations are necessary for a conclusive diagnosis. Phototesting is the definitive investigation for diagnosing solar urticaria. Blood tests are useful for excluding other conditions or causes of photodermatoses. A skin biopsy and microscopic examination of the sample is rarely necessary.
Phototesting
Phototesting is the investigation to test the sensitivity of skin to light. The light sources to be used includes ultraviolet light (less than 400nm) and visible light (between 400 to 800nm). There are number of different light sources that can be used for this purpose. A person should be exposed to the light source for not more than one hour. Sunlight should not be considered as a light source during phototesting for solar urticaria.
Treatment of Solar Dermatitis
The treatment regimen for solar dermatitis has variable results in individual patients. There is no cure for the condition and it has to be managed appropriately. This involves :
- Avoiding sunlight or minimizing exposure.
- Medication for symptomatic relief and some degree of prevention.
- Phototherapy for desensitization.
Sun Avoidance
It is not practical for any person to avoid the sun completely. Even if sun exposure is minimized, it should not be to the point where it is hampering a person’s social and occupational commitments. Vitamin D deficiencies may also be a factor in patients who become obsessive with regards to sun exposure. Proper protective wear may be of use.
Medication
Antihistamines are the main drugs used for relieving symptoms of solar urticaria. It may also be useful to some degree as a preventative measure (prophylaxis) but has limited efficacy in this regard. Histamine receptor blockers and antimalarials may also be of some use in treating and preventing solar dermatitis eruptions.
Phototherapy
Light therapy (phototherapy) is done as a means to desensitize the skin to sunlight. Just as the sun-exposed areas become acclimatized to sunlight in solar urticaria, phototherapy may be able to desensitize affected areas to some degree. This involves the use of just UV-A and/or UV-B (phototherapy) or UV-A light may be used in conjunction with psoralens (photochemotherapy). It does not have permanent results and may have to be repeated frequently.
References :
dermnetnz.org/reactions/solar-urticaria.html