Tinnitus – Causes, Symptoms of Ringing Sound in the Ears
Tinnitus is the perception of a sound or noise, usually described as a ringing noise in the ears, in the absence of any external noise source (lack of acoustic stimulus). Tinnitus is often associated with the elderly but can affect younger persons, especially those exposed to excessively loud sounds (music) on a regular basis. In most cases of tinnitus is accompanied by hearing loss of varying degrees, mild to severe.
Tinnitus itself is not a disease but is a common symptom associated with many ear disorders.
Tinnitus Symptoms
The sounds or noise experienced in tinnitus varies among sufferers. In most cases of tinnitus, the sound is reported as a ‘ringing noise’ in the ears which is more clear when in a silent environment. Other descriptions of the noise experienced in tinnitus include :
- Buzzing
- Roaring
- Whistling
- Hissing
- Beeping
Some sufferers may experience and describe more complex sounds as a combination of one or more sounds. The noise in the ears associated with tinnitus may also be described as :
- Continuous
- Intermittent – episodes of ringing sounds in the ears that come and go with no clear contributing factors.
- Pulsating noise in the ear which may seem to be synchronized with the heartbeat and may also be described as ‘beating’.
In cases where the pulsating or beating noise can be heard by your doctor during examination, the cause may be linked to a bruit. A bruit is an abnormal sound of arterial blood flow usually heard by the sufferer or during auscultation (using a stethoscope) by the examining physician. A bruit is usually associated with vascular disorders like atherosclerosis, aneurysm, thromboembolism or certain physical abnormalities of the arteries or veins.
A bruit is a verifiable sign of a specific vascular disorder or abnormality and should not be confused with the symptom of a ringing sound in the ear associated with tinnitus.
Common complaints from tinnitus sufferers is that the ringing in the ears affects sleep, concentration when focusing on reading, studying or other mental activities and communication with others during a conversation. However some of these complaints may be due to associated hearing loss that accompanies many cases of tinnitus. Also refer to sudden hearing loss.
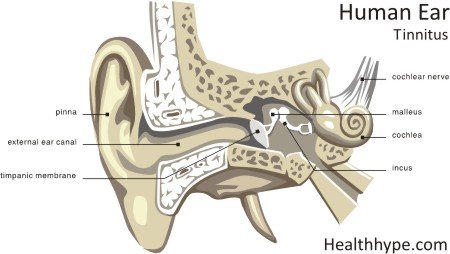
Tinnitus Causes
The exact cause and processes contributing towards tinnitus is unknown. However tinnitus is a symptom associated with many disorders including :
- Obstruction :
- Outer ear canal (external auditory canal) obstruction.
- Obstruction of the Eustachian tube – the tube connecting the middle ear with the nasopharynx (back of the throat) and responsible for maintaining ear pressure within the middle ear.
- Infections :
- Otitis externa or otitis media – infection and inflammation of the outer ear canal or middle ear.
- Myringitis – inflammation of the tympanic membrane (ear drum).
- Labyrinthitis – inflammation of the labyrinth of the inner ear also referred to as otitis interna.
- Petrositis – inflammation of the petrous portion of the temporal bone of the skull (at the temples of the head).
- Syphilis – a sexually transmitted (STD) and congenital disease caused by Treponema pallidum.
- Meningitis – inflammation of the lining of the brain (meninges).
- Neoplasms of the ear
- Meniere’s disease – other symptoms include recurret attacks of dizziness and/or hearing loss.
- Arachnoiditis
- Drug or chemical toxicity – certain NSAID’s (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories), antibiotics, malaria drugs, diuretics, carbon monoxide, heavy metals and alcohol.
- Cardiovascular diseases including hypertension although these disorders may cause a bruit.
- Anemia – Refer to Low Iron in the Blood
- Hypothyroidism
- Noise induced hearing loss or acoustic trauma which may be caused by exposure to excessively loud music especially within a small, closed environment (nightclubs, cars), use of head or earphones, gunshots fired close to the ear.
- Injury to the head, ear or eardrum.
- Hereditary hearing disorders
- Stress (including post traumatic stress disorder) and/or depression
- Age related hearing disorders
Tinnitus Diagnosis & Investigation
Diagnosis should focus on identifying possible causes of tinnitus as outlined above. This may involve a CT scan or MRI of the head, audiology tests and testing for sensory and neural (nerve) associated hearing loss. A cardiovascular examination and relevant tests should be conducted to identify or exclude cardiovascular causes of tinnitus. In cases of suspected drug induced tinnitus, the medication may be changed by your medical practitioner . If drug therapy is not essential, it may be stopped altogether to exclude drug induced tinnitus. The presence of concomitant symptoms like dizziness or vertigo with tinnitus may be indicative of an inner ear disorder.
Tinnitus Treatment & Management
Severe cases of tinnitus can be very disturbing for the sufferer and there is no known cure for tinnitus. Medical treatment should be directed at the causative factor if other disorders are diagnosed after further investigation. Conservative management should be the focus of dealing with tinnitus and self resolution is possible in certain cases, especially in young persons or noise induced trauma.
- In cases of partial or complete hearing loss (deafness), a hearing aid or cochlear implant may resolve the hearing loss and tinnitus. However a cochlear implant should only be considered as a measure for hearing loss and not as a treatment for tinnitus itself.
- Using noise devices for creating other, more pleasant sounds may be useful in certain cases. This can vary from playing music on a radio to using a white noise machine or tinnitus masking device.
- The drug acamprosate calcium which is used for treatment of alcohol addiction has been reported to provide varying degrees of relief for tinnitus but its use in tinnitus itself has not been verified in clinical trials.