Dry Skin Moisturizer Functions, Types and Directions of Use
What is a moisturizer?
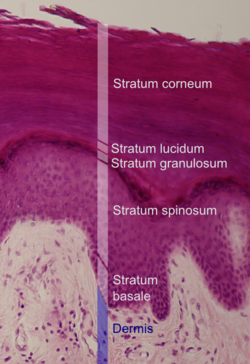
The term moisturizer refers to an application that restores moisture. In terms of the skin, it is a means of remedying dryness. This mainly refers to dryness of the outermost layer of the superficial skin – the stratum corneum of the epidermis. It is the appearance of this outermost layer of the skin that is often used to determine skin health. A moisturizer may therefore be used to treat dryness of the skin that occurs for certain non-pathological reasons such as a dry climate. It can also be used to treat dryness of the skin that occurs with certain types of skin diseases.
Moisturizers remain one of the most common topical applications to maintain skin health. It is argued that skin which cannot retain its natural moisture may therefore be unable to hold the moisture provided by these applications. However, regularly moisturizing even very dry skin does have benefits that outweigh not using a moisturizer at all. This should not detract from the fact that excessively dry skin (xerosis) or skin diseases with marked skin dryness has some underlying cause which needs to be identified, investigated and treated. Moisturizers therefore only offer short term relief for dry skin.
Functions of a Moisturizer
In order to understand the way a moisturizer works, it is important to first look at how skin retains its natural moisture.
Natural Moisture of the Skin
The skin is a barrier that prevents substances from within the environment from entering the deeper tissue. The outermost layers are composed of dead skin cells containing a high concentration of a protein known as keratin. The keratinized cell remnants are arranged in a manner that makes the skin waterproof. It also ensures that the skin is able to retain its own moisture without it evaporating into the environment. Oil (sebum) secreted by the sebaceous glands of the skin provide further protection by ensuring that the skin can resist the drying effect of environmental factors.
When the tight barrier function is impaired, the outermost layer of the skin is damaged or lost or when there is insufficient sebum to protect the outer skin, the natural moisture of the skin is lost to the environment. Sometimes internal factors and certain systemic diseases can also compromise this natural skin moisture. Dry skin has some of the following features :
- visible as skin that lacks luster
- skin that is not soft and supple
- more likely to itch
- is rough to touch
- may appear dry and whitish
Effects of Moisturizers
Depending on the type of moisturizer based on the different ingredients, it can assist with :
- Restoring the barrier function of the skin.
- Preventing water loss from the skin.
- Disallow offending agents that cause skin dryness from making contact with the skin.
- Assist with skin repair.
The effects of moisturizers is largely based on two components – a water based agent that restores skin moisture and a water-soluble fat component that acts as a barrier on the skin surface.
Types of Moisturizers
Main Ingredients
There are different types of moisturizers that can be classified according to its functional ingredients. The functional ingredients are those substances that are responsible for the functions of moisturizers. These ingredients include :
- Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs)
- Beta hydroxy acids (BHAs)
- Retinoids
- Vitamins
Other Ingredients
The vehicle ingredients are the other substances that are needed for the different properties of the moisturizer but may not have any significant benefit to the skin. These substances include :
- Emulsifiers prevent substances that do not usually mix with each other from separating.
- Preservatives prevents microbes from contaminating the moisturizer.
- Fragrances that add a pleasant scent to the moisturizer.
How to use a moisturizer?
Moisturizers should always be used as advised by a health care professional when prescribed. The directions of use are also clearly indicated on the packaging although this may vary depending on the cause of the dry skin and any underlying skin diseases. Some of the points to take into consideration when using a moisturizer includes :
- Consistent use of a moisturizer usually on a daily basis and often several times in a day.
- Using the moisturizer shortly after having a bath.
- Applying the moisturizer liberally on affected areas and especially the arms and legs.
- Moderate amounts of a moisturizer are advisable as prescribed or indicated on the packaging. Too little or too much can either be ineffective or irritate the skin.
- Always use a moisturizer with sunscreen properties, especially when outdoors.
- Avoid moisturizers with a strong scent especially where there are skin diseases.
References
1. Moisturizers. Emedicine Medscape