How Does Cancer Spread (Metastasize) to Other Parts of the Body
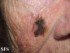
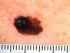
One of the greatest dangers of cancer is that it can spread anywhere in the body. When cancer starts, it is usually isolated to one body part, organ or certain type of tissue. It grows, infiltrates and destroys surrounding tissue. However, it can break away and travel to distant parts of the body where the cancer continues to grow. The cancer will then ‘consume’ the area where it relocates. The cancer cells at the site of origin will still grow and destroy healthy tissue while the cancer that has spread may do the same at a distant part of the body.
What is metastasis?
Metastasis is the medical term for cancer spread beyond the organ where it started to other parts of the body. The cancer is said to have metastasized when this occurs. The “new” cancer that starts at the distant body part is referred to as metastatic cancer. This means that there is cancer in the organ but it did not start in that organ. The distant spread may occur when cancer cells enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
The term metastasis can sometimes be confused with malignant. It is important to understand the difference. A malignant tumor means that the growth or abnormal cells are cancerous. If it is non-cancerous then it is known as a benign tumor. All metastatic cancers are malignant because metastasis simply means that the cancer (malignancy) has spread to distant sites.
Read more on benign and malignant tumors.
Local and Regional Cancer Spread
However, cancer spread is not always to distant sites. As a cancer grows, it spreads to surrounding healthy tissue and destroys it. This is referred to as local spread. The cancer may also spread to neighboring organs or lymph nodes. This is known as regional spread. Different cancers spread at different rates. Some spread rapidly while others are slower. Faster-spreading cancers generally have a poorer prognosis unless it is diagnosed and treated early.
How is metastatic cancer named?
Metastatic cancer means cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body from its site of origin. For example, bladder cancer can spread to the liver. In this case the cancer is referred to as metastatic bladder cancer. This can be confusing as it is expected for the cancer to be named according to the organ where it is located.
Instead with metastatic cancer it is named according to its site of origin. The terms primary and secondary cancer may also be used. Primary cancer refers to cancer that is located where it has originated. Secondary cancer means cancer that originated in one part of the body but spread elsewhere.
Is metastatic cancer the same as stage IV cancer?
Staging of a cancer describes whether the cancer is localized, has spread regionally or metastasized. Stage IV (4) cancer is where the cancer has metastasized. Therefore stage IV cancer is the same as metastatic cancer. However, it should not be confuse with the grading of a cancer. The grading system describes how abnormal the cancer cells are and if it is very abnormal (grade 4) then it is also referred to as an aggressive cancer.
Read more on staging and grading of cancer.
How Do Cancers Spread?
It is important to understand how cancers spread. When a cancer is diagnosed, it does not mean that it has already spread or will spread immediately. Several factors have to be present for the cancer to metastasize. Firstly cancer cells are abnormal in structure, grow rapidly and destroy surrounding tissue as it grows. It has to be able to break away from its site of origin in order to spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
Then these cancer cells that have broken off must gain entry into a blood vessel or lymphatic vessel. It can then be carried to distant parts of the body. Once it reaches a distant site where it lodges, the cancer may still not survive at this site. It may not have a sufficient blood supply to establish itself at the new location or it may be unable to withstand the immune system which can destroy it.
However, if the cancer cells can thrive at the new site, it will grow and destroy the healthy tissue surrounding it. The cancer cells will need a constant supply of nutrients to enable it to grow and spread rapidly. It secretes special chemicals that encourage the growth of new blood vessels to supply it. The cancer cells may also undergo certain changes to survive at the new site. This metastatic cancer may not always remember the cancer cells at the location where it originated.
Why Does Cancer Spread?
The nature of cancer is to spread. Normally cells die and may then be replaced by new cells that resemble it. However, cancers do not die as would be expected. It also does not develop as normal. This uncontrolled growth and abnormal development of cancer cells are due to defective genes. The cancer cells need space to grow and will therefore destroy the surrounding healthy tissue. It keeps spreading because it does not have the same control measures in place as normal cells do.
Firstly it must be understood that cancer cells arise from pre-cancerous cells which in turn arose from normal cells. Some factor has to damage these genes although some genes may be inherited. It causes the normal cells to become abnormal in growth and development. Initially the cancer cells may resemble the normal cells in the area from which is arose. This is where the grading system of cancer is relevant.
However, as the cancer progresses it less resenbles the normal cells of origin. It can reach a point where it shows little to no resemblance to the normal cells. Cancer cells that are very poorly differentiated tend to be very aggressive. It is usually less responsive to cancer treatments. Without the immune system being able to stop these cancerous cells and with treatment not being effective or with no treatment, the cells will spread rapidly.