Thrombophlebitis – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention
Veins carry blood away from different areas of the body and transport it back to the heart. The movement of blood in some veins, particularly in the limbs, can become sluggish and even obstructed by a blood clot. This can cause a host of problems, both at the site where the clot forms and even sometimes in the vital organs like the lungs.
What is thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is inflammation of a vein that results in a blood clot formation. This clot blocks the flow of blood through the affected vein. Most of the time thrombophlebitis affects the vein in the legs. The problem may arise in the superficial vein of the legs and then spread to the deep veins. The latter, a blood clot in the deep veins, can cause serious complications which may even be fatal.
Causes of Thrombophlebitis
Blood flowing through the veins and arteries remains in a liquid state due to severa factors. When the situation demands, a blood clot may form in order to plug a break in a blood vessel. This is a life-saving mechanism to prevent loss of blood. Clotting factors (a type of chemical) are activated to achieve this formation of the blood clot at the desired site until the blood vessel wall is repaired.
Read more on varicose veins.
The main causes of thrombophlebitis are injury to a vein, usually superficial vein of the leg, as a result of trauma including surgery. It is also more likely to occur when a person is inactive for prolonged periods of time. This inactivity causes blood flow to slow down and this can also trigger premature blood clot formation.
Dehydration is another contributing factor as the blood becomes “thicker” due to a lower fluid volume. Blood clotting disorders can also increase the risk of thrombophlebitis. This causes a blood clot to form abnormally due to a problem with blood clotting factors that control when a clot should arise. Usually these clotting disorders are genetic.
There are various other risk factors that increase the risk of thrombophlebitis. This includes:
- Having varicose veins.
- Being pregnant or using hormone drugs like birth control pills or HRT.
- Being overweight or obese.
- Having cancer.
- Being older than 60 years of age.
- Being a tobacco smoker.
- Having a previous history of conditions like thrombophlebitis or a stroke.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of thrombophlebitis are due to the inflammatory process as well as the blood clot preventing the blood flow back to the heart.
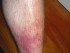
Inflammation causes pain, swelling, redness and warmth over the affected area. Redness and warmth are usually noticeable when inflammation is affecting a superficial part of the body. Pro-inflammatory chemicals causes arteries to widen and become leaky. This brings immune cells to the affected area but also increases blood flow to the site (redness and heat) and causes fluid to leak out (swelling).
A blood clot is s physical obstruction to blood flow. Venous blood (blood within the veins) carries wastes substances, excess tissue fluid and carbon dioxide away from different parts of the body. It is transported back to the liver and heart where wastes are removed and blood is reoxygenated. However, these substances as well as fluid builds up in the affected region when a vein is obstructed by a blood clot.
Thrombophlebitis may present with the following signs and symptoms:
- Swelling of the limb (superficial or deep clots).
- Pain at the site of the clot (superficial) or throughout the limb (deep).
- Tenderness (usually with a superficial clot).
- Warmth and redness (superficial clot).
Superficial thrombophlebitis rarely progresses to any complications. However, when the clot affects the deep vein of the legs then serious and even deadly complications can arises.
Deep Leg Clot
DVT or deep vein thrombosis is where there is a blood clot in the deep vein of the leg. Apart from all of the localized symptoms of the clot, there is also a possibility that the clot may dislodge. It can the travel up the venous system and through the heart. Eventually it may become lodged in a blood vessel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism). This prevents blood flow through the lungs and can result in death.
The signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism includes:
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Cough
- Pale or bluish skin discoloration
- Excessive sweating
Read more on signs of DVT.
Treatment of Thrombophlebitis
The choice of treatment for thrombophlebitis depends on the severity of the condition, whether the superficial or deep veins are affected as well as individual factors that may prohibit the use of certain medication.
- Anticoagulants are drugs that prevent blood clotting. These drugs are also known as blood thinners. It includes drugs like heparin and warfarin.
- Thrombolytics are drugs that dissolve clots. It is also referred to as clot busters. These drugs include substances like alteplase.
- Blood filters are devices that filter blood flowing through the large vein to the heart. It prevents the clot from reaching teh heart and lungs.
- Vein stripping is where a varicose vein is surgically removed. This can only be done on the superficial veins. Varicose veins are enlarged veins with weakened walls.
Prevention of Thrombophlebitis
People who are at risk of thrombophlebitis may be able be able to prevent it with certain lifestyle measures and medical applications. Medication like antixoagulants can also help to prevent blood clot formation. Once thrombophlebitis occurs the focus should be on preventing complications like DVT.
- Compression stockings can prevent thrombophlebitis in people at risk as well as prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis. It also helps with reducing symptoms like swelling. The stockings provide physical support fr the veins in the legs.
- Regular physical activity of the legs can help with blood circulation and prevent blood clot formation. Walking around or doing leg exercises may be useful, especially during prolonged periods of physical inactivity such as during a long flight.
- Drink plenty of water and other fluids such as fruit juices to avoid dehydration. Oral rehydrating solutions are ideal for hydration when dehydration occurs. Avoid caffeinated and alcoholic beverages which can lead to dehydration.