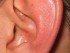
Burning Ears (Heat Sensation) Causes and Treatment
Burning is a sensation that most of us associate with being near a heat source, either too close to it or for too long a period of time. It is a warning sign of tissue damage. However, there are times when burning occurs on its own and may be due to other causes. Burning ears is one such case. It can arise with injury, infections, allergies, skin diseases and even psychologically stressful situations.
What is burning ears?
Burning ears is a sensation of the ears being hot. This may or may not be experienced as pain. While a burning sensation may be perceived when close to a source of heat, like a fire or artificial heat source, it can also occur with certain conditions particularly where inflammation is present. Sometimes it can also be perceived without it being due to factors like external heat or inflammation, and may instead just be psychogenic in origin.
The ears can be divided into three parts – the outer, middle and inner ear. With complaints of burning ear, most people are actually referring an outer ear problem. This includes the pinna, the large conch-shaped structure on the side of the head, and the ear canal. It may also include the ear drum. The middle ear can also give rise to this type of sensation but it is usually felt deeper, as is the case with problems of the inner ear.
Causes of Burning Ears
There are a number of different causes of burning ears. The most obvious, like being close to a heat source, should first be excluded. Other symptoms like redness, swelling of the ears or skin rashes may also accompany the burning sensation. It is therefore important to seek medical advice for intense burning of the ears or ongoing burning sensation, especially if it is accompanied by an ear discharge or changes in hearing.
Injury
Injury to the ear is one of the common causes of a burning sensation. It can be caused mechanically by a blow to the ear, pulling on the pinna aggressively, with sharp force trauma like ear piercings, insect bites or injury to the ear canal when attempting to clean it with a cotton bud. Chemical injury may arise with cosmetics and hair care products that make contact with the pinna, or even enter the ear canal.
Infections
Ear infections are fairly common, especially in children. It may affect the outer or middle ear in most cases and only sometimes involves the inner ear. A burning ear sensation is more likely to be due to an infection of the outer ear. An outer ear infection is known as otitis externa (swimmer’s ear) while a middle ear infection is known as otitis media. These infections may be caused by bacteria, viruses of fungi. Ringworm infections of the scalp may also extend to the ears.
Skin Conditions
While several skin conditions can affect the ear, like atopic dermatitis or psoriasis, the more likely cause of acute skin irritation of the ear leading to burning is contact dermatitis. This is skin inflammation that arises when some substances irritates the ear (irritant contact dermatitis) or when a substance triggers an allergic reaction at the point of contact (allergic contact dermatitis).
Common irritants include sweat or water that lingers on or in the ears, soaps, chlorine and chaffing with ear wear like earphones or spectacles. Allergies to certain metal earrings, contact with hair dyes to which a person is sensitive to and plant material are examples of allergic contact dermatitis. In children, seborrheic dermatitis should also be considered as a possible cause of burning ears especially when there are lesions on the scalp as well.
Allergies
Apart from allergic contact dermatitis, ear burning often accompanied by swelling and redness may be seen with systemic allergic reactions. The most serious of these reactions is anaphylaxis. It is an acute reaction with exposure to certain substances, mainly foods lead to itching and burning with the mouth, throat and ears. Urticaria (hives) is another cause especially when accompanied by angioedema although the exact trigger is unclear.
Sunburn
The skin of the ears are just as prone to sunburn as skin elsewhere on the body. Often people do not use the same protective measures for the ears as they would for the skin on the face. The irritation and even damage to the skin by UV light, commonly referred to as sunburn, is more likely to occur in bright sunlight but may even arise in tanning booths or other sources of UV light.
Psychological
We all know the feeling of our ears heating up when angry or embarrassed. This is due to changes in superficial blood flow. People undergoing psychological stress or people suffering with anxiety may therefore experience a burning ear sensation and there may even be accompanying ear redness. Acoustic phobia is an irrational fear of loud noises and a person may irritate or injure the ears trying to prevent exposure to these noises on a daily basis.
Treatment of Burning Ears
A burning sensation of the ears has to be treated in the context of the underlying ear problem. This may require lifestyle changes, medication and sometimes even surgery. There burning ears has to be investigated by a medical professional to determine the underlying cause.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs may be used to reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics or antifungals may be used to treat bacterial and fungal infections, respectively.
- Corticosteroids may be used for severe inflammation and allergies, either in topical or oral form.
Simple measures can also be helpful:
- Minimize contact with the ears by tugging at it, scratching or attempting to clean it can help in reducing injury and inflammation.
- Sunscreen should be applied to the pinna when in bright sunlight or tanning booths.
- Trigger foods that lead to burning ears should be noted and avoided.
- Discontinue using ear jewelry and avoid further piercings of the ears.
- Reduce contact with harsh hair care products, like hair dyes and even hair sprays.
- Use ear plugs when swimming or even when having a shower.