Shoulder Pain Causes and Other Symptoms
Shoulder problems are common conditions and mainly present as pain and/or limited mobility. Although the more persistent problems tend to affect middle-aged and older people, any person can be afflicted with a shoulder problem like shoulder pain. This is largely due to the strain that the shoulder joint has to bear at times. It is a highly mobile joint allowing the upper limbs a large degree of movement to carry out various tasks in everyday like.
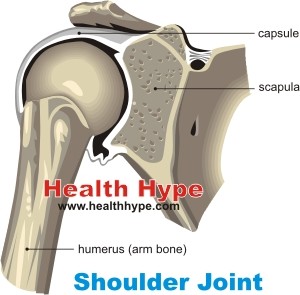
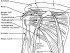
The shoulder is the area containing the joint, surrounding muscles and supporting tendons that connects the upper limbs (arms) to the torso of the body. It lies between the neck and arm. Three important bones make up the shoulder – the shoulder blade (scapula), humerus (upper arm bone) and clavicle (collarbone). The main joint of the shoulder is a ball and socket joint known as the glenohumeral joint. The rounded head of the humerus is the “ball” while the glenoid fossa of the scapula serves as the socket. The other joint at this site is formed by the scapula and clavicle ans is known as acromioclavicular (AC) joint.
The shoulder is highly mobile but the shallow glenoid fossa does not make for the most stable of joints. Therefore a group of muscles and its tendons stabilize the shoulder ad are collectively known as the rotator cuff. The four muscles of the rotator cuff are the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor muscles. Apart from these main structures of the shoulder, there are several other parts of the shoulder including muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves and blood vessels.
Picture from Wikimedia Commons
Signs and Symptoms
Shoulder pain is a symptom of an underlying disease. It may vary in nature from a bruised feeling to an ache or severe pain that can radiate to parts of the arm, back or neck. The pain may be constant but is usually exacerbated by movement or the pain may only be present with movement. The shoulder may also be tender to touch particularly firm pressure.
Other symptoms may including a grinding sensation with arm movement. There may also be the feeling that the joint is about to ‘pop’. Movement may be associated with several abnormal noises like clicking, grinding or even a popping sound. Muscle stiffness and arm weakness may also be present.
Swelling of the area, with redness of the skin that is typically warmer than surrounding areas indicates severe inflammation and more likely an infection. Malaise and fever are generalized symptoms that may accompany shoulder pain especially in infectious cases.
Causes of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain is not always due to a problem with the shoulder. It can be associated with some disease of the organs in the thoracic cavity or be referred to the shoulder from distant sites. Pathology in the shoulder itself is unlikely to cause severe complications and is rarely life threatening except for cancer. It is therefore important to first exclude these diseases before investigating the shoulder itself for problems with the joints or muscles.
Thoracic, Abdominal and Referred Pain
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack) typically presents with centralized chest pain although the pain may radiate to the shoulder and arm, particularly on the left side.
- Angina pectoris presents in a similar manner to a myocardial infaction pain but with angina, the pain usually eases fully with rest.
- Biliary disease may include gallstones, bile duct stones, cholecystitis and cholangitis which presents with mid upper abdominal pain and sometimes referred pain to the shoulder, particularly the right shoulder.
- Spleen trauma which may rest in severe inflammation or hemorrhage (bleeding).
- Lung cancer particularly when it affects the apex of the lung.
- Subphrenic abscess is a collection of pus lying between the diaphragm and liver (right side) or spleen (left side).
- Diaphragmatic irritation may cause shoulder pain and if the phrenic nerve is also affected, the pain may be accompanied by hiccups. Disease of the lower lobe of the lung and/or pleura may also irritate the diaphragm or phrenic nerve and therefore lead to shoulder pain.
- Peritonitis is an inflammation of the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum) and may case shoulder pain particularly when associated with ascites (fluid accumulation in the cavity).
Painful Shoulder Problems
- Fractures are usually associated with significant force in injuries such as falls. In children, the clavicle is more likely to be fractured while in adults, particularly the elderly, the proximal humerus (upper arm bone) is more prone to fractures. A fracture may also occur on the scapula. Sometimes the shoulder joint may be dislocated along with the fracture.
- Contusion is also associated with force, like falls or impact to the area. The soft tissue is injured and the small blood vessels in the area may rupture typically presenting as swelling with a red to purple discoloration of the skin along with pain.
- Bursitis is inflammation of the fluid-filled sac around the shoulder joint that aims to reduce friction with movement. It may become inflamed with an injury or with certain inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Rotator cuff disorders like rotator cuff tendinitis (inflammation of the muscle tendon like supraspinatus tendinitis)or rotator cuff tear.
- Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) is one of the common shoulder problems that is associated with pain. The connective tissue capsule surrounding the shoulder joint becomes inflamed and thickened, thereby restricting movement.
- Shoulder joint instability may either be acute or chronic. It is associated with a partial (subluxation) or complete joint dislocation (dislocated shoulder).
- Acromioclavicular joint injuries can vary from localized inflammation of the AC joint to joint separation (dislocation). AC joint dislocation is not the same as shoulder joint dislocation (dislocated shoulder).
- Bicipital tendinitis is inflammation of the long head of the biceps tendon. This tendon attaches to the coracoid process of the scapula and also helps to stabilize the movement of the humerus (upper arm bone) at the shoulder joint.
- Arthritis is a broad term for joint inflammation which is typically associated with joint pain (arthralgia). This can include rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, septic arthritis or crystal-induced arthritis.
- Cancer may affect any of the shoulder bones and the more common types of primary cancers that affects these sites are an osteosarcoma or chondrosarcoma. Sometimes the cancer may spread from elsewhere to affect the shoulder structures (secondary / metastatic).
Other Causes
- Cervical radiculopathy (pinched nerve in the neck)
- Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Costoclavicular syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Arthralgia
- Hyperabduction syndrome
- Psychogenic pain
- Sleep dysesthesia
- Postural