Toenail Fungus (Onychomycosis) Causes, Pictures, Treatment
Superficial fungal infections are common in humans. It is estimated that as much as 80% of the world’s population will experience a skin fungal infection like athlete’s foot at some point in life. While these fungal infections of the skin can extend to the nails, sometimes a nail fungus occurs entirely on its own without involving the skin. This is known as onychomycosis. The toenails are commonly affected with fungal infections.
What is a toenail fungus?
A toenail fungus is any fungus that infects the toenail(s) and is usually caused by dermatophytes although yeasts may sometimes be involved. These fungi are usually the same as those fungi that cause skin fungal infections like athlete’s foot. However, a toenail fungus can occur on its own without the skin being infected. In other words a toenail fungus (onychomycosis) may occur independently of athlete’s foot (tinea cruris).
The incidence of fungal nail infections in North America is between 2% to 13%. Toenails are more commonly affected than fingernails. It affects both genders equally. According to studies, adults are about 30 times more likely than children to develop toenail fungus. It is very prevalent in the elderly and this may be associated with certain risk factors like circulatory disorders and diabetes that is more common in seniors.
Causes of Toenail Fungus
Fungi exist in large numbers in the environment. Only some species can cause infections and a few can specifically infect the skin or nails. Dermatophytes are the main types of fungi that have a predilection for skin and only certain species will infect humans. These fungi have enzymes that can digest the protein known as keratin that make up the outer layers of the skin, the hair and the nails.
However, contact with fungi or its spores will not immediately result in an infection. There usually needs to be a break in the skin or some damage to the nail in order for fungi to establish itself an grow. These fungi cause superficial infections and do not extend into deeper lying tissue. Yeasts are uncommon causes of superficial fungal infections and tend to thrive in areas where there is exposed living tissue.
Fungi prefer warm, dark and moist environments. Naturally the feet is an ideal environment among people who wear closed shoes for long periods of time or have sweaty feet. Similarly the groin provides another ideal environment. The two main species that are responsible for fungal nail infections include Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The former, T.rubrum, is by far the most common.
Spread of Toenail Fungus
The fungi that infects the toenails are easily spread by direct contact with others who have the fungus. It is also commonly transmitted through damp public areas, like gym showers and community pools. Sharing socks, shoes and nail manicuring equipment with a person who has the fungus can also lead to its spread to uninfected individuals. People living in the same household as a person with nail fungus are at greater risk.
Risk Factors
Certain people are more at risk of developing fungal infections of the toenail, apart from the factors discussed above under spread of toenail fungus. This includes:
- Pre-existing athlete’s foot.
- Having sweaty feet.
- Wearing socks and shoes for long hours.
- Having diabetes or circulatory disorders.
- Weak immune system.
- Advancing age.
- Living or working in humid environments.
- Prolonged contact with water as part of work.
Also refer to acrylic nail fungus for information on how acrylic nails may contribute to fungal infections.
Signs and Symptoms
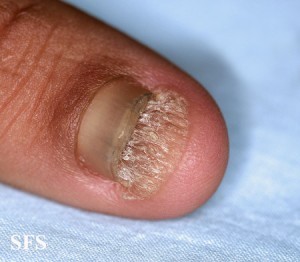
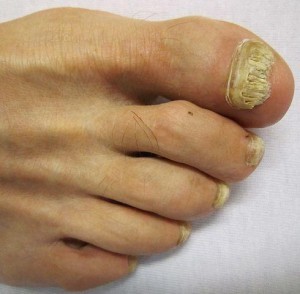
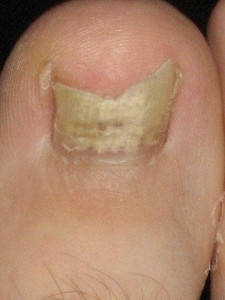
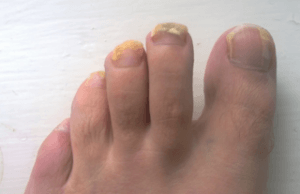
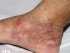
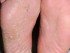
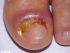
With onychomycosis, the nails become thickened, rough and weaker. It may become jagged as parts of it easily break off or crumble. Over the time the nail becomes distorted in shape. Although the infected portion becomes dull, the yellowing discoloration seen on the uninfected parts may not always be due to the fungus. In time the infected nail may separate from the nail bed and this can be painful.
Pictures of Toenail Fungus
Image sourced from atlasdermatologico.com.br
Treatment of Toenail Fungus
There are several treatment options for toenail fungus but many people first opt for over-the-counter products like antifungal ointments and medicated nail polish. These measures can be effective in many cases but if it fails to yield the desired results or if the toenail fungus is spreading the treatment by a medical professional is necessary. All fungal infections throughout the body should be treated as it is easily spread from one area to another.
The treatment for toenail fungus includes:
- Oral antifungal drugs (terbinafine or itraconazole) that are taken for 6 to 12 weeks.
- Antifungal nail polish containing ciclopirox which is applied on the nail and surrounding skin.
- Antifungal nail creams which are rubbed into the affected nail.
In some cases, these drugs are not effective and the affected toenail may have to be removed. Newer treatments involve the use of laser therapy but the effectiveness has not been thoroughly studied and verified. Many people try tea tree oil (Melaleuca alternifolia) for the treatment of toenail fungus. While this extract is known to be effective in treating skin fungal infections, there is still insufficient clinical evidence to suggest that it can be used in nail fungus.
Prevention of Toenail Fungus
As with any fungal infection, prevention is key in avoiding recurrence of the fungus. Simple lifestyle measures can be very effective.
- Remove socks and shoes when formal attire is not necessary. Let the feet air and use open shoes if the situation permits.
- Keep the nails short and immediately file down any thickened or jagged portions of the nail.
- Avoid interfering with the skin around the nails, especially if there is pre-existing athlete’s foot.
- Wash hands regularly and do not touch multiple parts of the body unnecessary. Sometimes a fungus at one part of the body can be transmitted to another area through the fingers and hands.
- Never share socks or shoes with another person. Always use rubber flip-flops when walking around a pool and while using a public shower.
- Over-the-counter antifungal sprays and powders can be helpful in preventing fungal infections.
- Do not attempt to hide a nail fungus with colored nail polish. It can worsen the infection.