Abnormal Ear Sounds – Causes and Why It Happens
Hearing is one of the five senses that we have. It allows us to detect sounds in our environment. Like any sense there is a stimulus (in this case it is sound) which is perceived through the mechanism in the ear and hearing centers in the brain. In order for us to hear a sound there must first be a sound. However, we sometimes hear sounds that do not exist. These abnormal sounds may occur due to various medical conditions.
What are abnormal sounds?
Hearing can be distorted in a number of different ways. Sounds may be perceived as louder, softer, duller or sharper than normal. This individual variation in the sense of hearing is not entirely uncommon. Some people have better hearing than others. The elderly experience diminished hearing. Similarly our hearing may appear to be different in certain instances, like when we are stressed, lacking sleep or fearful.
However, this abnormality in hearing is simply an alteration of sounds that are present in our environment. With abnormal ear sounds, a person perceives sounds that does not exist or that others around them cannot hear. It is also known as tinnitus. Most of us incorrectly think that tinnitus only refers to ringing in the ears. While ringing is commonly reported, a person with tinnitus may also hear a whooshing, hissing, wheezing, roaring, buzzing, clicking, hissing or humming sounds.
Why Abnormal Sounds Occur
In order to understand how abnormal sounds may originate, it is important to first understand how we are able to hear. There are broadly three types of structures that make hearing possible. This can be broadly divided as the ear, nerve and brain. Problems in these regions may give rise to abnormal sounds.
Ear
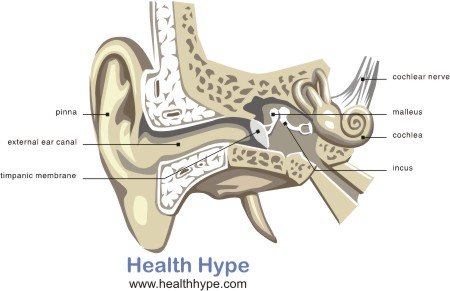
The hearing structures in the ear are responsible for conducting sound and converting it into electrical signals. First sound is directed into the ear canal by the outer conch-shaped flap on the head known as the pinna. The sound then causes the eardrum to vibrate. This vibration of the ear drum causes the tiny bones (ossicles) in the middle ear to vibrate. This vibration is then transmitted to the cochlea in the inner ear where tiny hair cells convert the mechanical energy (vibration) into electrical energy (nerve impulses).
Nerve
Nerve impulses generated in the cochlea are carried by the auditory nerve to the brain. This nerve, also known as the cochlear nerve or acoustic nerve, is part of the vestibulocochlear nerve which is a cranial nerve. Along with impulses for hearing, the vestibulocochlear nerve also transmits sensory information from the inner ear which is important for balance and coordination.
Brain
On either side of the brain, in the upper part of the temporal lobes, is the auditory cortex. It is responsible for processing signals received by the auditory nerve. The auditory cortex also works with the frontal and temporal lobes to make the sense of hearing possible.
Causes of Abnormal Ear Sounds
There are several possible causes of abnormal ear sounds. It is important to note that these sounds are not the same as auditory hallucinations which may occur in certain mental health disorders. Instead abnormal ear sounds occur for certain medical reasons where there is disturbance in the hearing apparatus within the ear, the nerve that carries signals from the ear to the brain, or in and around the hearing centers of the brain.
It is important to first exclude obvious causes of abnormal ear sounds, like a malfunctioning hearing aid, prolonged use of earphones and foreign bodies (objects) stuck in the ear. Abnormal ear sounds must be investigated by a doctor, preferably by an otorhinolaryngologist (ENT specialist), if the sound is persisting for long periods or worsening over time.
Ear, Nerve and Brain Problems
- Acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve which is carries signals from the ear to the brain.
- Acoustic trauma is where there is injury to the ear caused by loud sounds. It can occur with sudden exposure to loud sounds even if these sounds are for short periods but is more likely with regular or constant exposure.
- Aerotitis media, also known as plane ear, occurs with an air pressure imbalance between the outer and middle ear. It mainly occurs during and after air travel.
- Blood vessel abnormalities (vascular malformations) near the ear where a person may be able to hear the blood flow in these abnormal vessels.
- Earwax blockage occurs when there is an accumulation of earwax (cerumen) in the ear. It can form a plug which impedes sound entering the ear canal.
- Ear infections may involve the outer ear (otitis externa), middle ear (otitis media) or inner ear (otitis interna). Outer and middle ear infections tend to be more common.
- Eardrum rupture is another condition that may affect hearing and cause abnormal sounds. A rupture (tear or perforation) occurs with infections or injury to the ear.
- Eustachian tube dysfunction is where there is a problem with the tube that helps maintain the air pressure within the middle ear. If this tube becomes blocked for any reason then it can affect hearing.
- Meniere’s disease is where there is a disturbance in the inner ear due to increased pressure. This affects both hearing as well as the sense of balance.
- Otosclerosis is a rare condition where bone grows around one of the middle ear bones and this prevents the bone from vibrating as normal for sound conduction.
- Tumors in the brain can also cause abnormal sounds. The tumor may press on or disrupt the hearing centers in the brain thereby causing the perception of these abnormal sounds.
- Traumatic head injury refers to any injury to the head such as a blow to the head. This may occur during a fall, contact sports or as a result of an assault. Apart from a concussion it can also disrupt the perception of certain sense like hearing.
Other Causes
Abnormal ear sounds can also occur for other reasons that may not specifically affect the ear, nerve or brain. Sometimes the causes of abnormal sounds in these conditions cannot always be clearly explained. This includes:
- Psychological stress
- Thyroid disease
- Side effects of certain medication, like some types of antibiotics, antidepressants, antimalarial drugs and cancer drugs (chemotherapy).
References:
- Ear sounds. Health Grades
- Acoustic trauma. Health Line
Last updated on 11 April 2019.