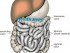
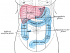
Bloody Diarrhea – Causes and Location of Bleeding
Diarrhea is a common symptom and most of us are not immediately concerned when it does arise. Usually diarrhea is short-lived, often caused by a virus or bacteria, and many cases will resolve on its own even without treatment. However, the sign of bleeding with diarrheal stool will scare most people. Often this can be a sign of a very serious underlying condition. The loss of blood coupled with the loss of fluid in diarrhea can lead complications, some of which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Why is there blood in diarrhea?
Blood in the stool is not always a cause for concern. In fact the blood is often missed in the stool either because it is very little or it has degraded to the point where it cannot be identified. Therefore tests like the fecal occult blood test (FOBT) are done to confirm the presence of blood in the feces. If positive, it means that there is some source of bleeding within the digestive tract. The walls of the digestive tract have a rich blood supply so any break in these arteries or veins will allow blood to escape and eventually be passed out in the stool.
One of the most common reasons for blood in the stool is bleeding piles (hemorrhoids). It can be very uncomfortable but is usually not serious and does not typically occur with diarrheal stool. However, when bleeding in the digestive tract occurs along with diarrhea then it is a reason for concern. The same disease that may be causing diarrhea may also be causing the bleeding. The extent of the bloody diarrhea is also an indication of the seriousness of the condition. Diarrheal stool that is entirely bloody should be considered as a medical emergency.
Location of the bleeding
Bleeding can occur anywhere in the digestive tract and eventually be passed out in the stool. However, it is usually not visible as gross blood when it occurs higher up in the upper gastrointestinal tract (throat, esophagus, stomach). Bleeding in the bowels may appear as gross blood in the stool. This means that the blood can be identified by its red color if there is sufficient bleeding. However, if the bleeding has occurred higher than the small intestine, the blood is usually degraded by the time it is expelled in the stool.
The presence of fresh blood in the stool is referred to as hematochezia. Dark blood in the stool which causes black tarry stool is known as melena. However, it does not require much time for blood to become very dark red to black and degrade. With diarrhea though, the stool is expelled so fast and so often that the blood even from the upper gastrointestinal tract (throat, esophagus or stomach) may sometimes still appear as bright red blood.
Causes of Bloody Diarrhea
Bloody diarrhea that arises suddenly in an otherwise healthy person is usually due to an infection, but may also occur in people with ischemic colitis and diverticulitis. Repeated bleeding in younger people is often due to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, frequent rectal bleeding should always raise the concern of colorectal cancer, especially when there are no other symptoms of hemorrhoids. Many other conditions that have not been discussed here can cause blood in the stool but this may not necessarily present as bloody diarrhea.
Infections
Infections are the most common cause of acute bloody diarrhea. Infectious gastroenteritis, enterocolitis or colitis resulting in bloody diarrhea may be due to:
- C. difficile (Pseudomembranous colitis)
- Campylobacter enterocolitis
- Enterohemorrhagic/enteropathic toxin (E. coli colitis)
- Amebiasis (Entameba histiolytica)
- Salmonella infection
- Shigella enteritis (bacillary dysentery)
- Aeromonas hydrophilia infection
- Balantidiasis
- Schistosomiasis
- Yersinia enterocolitica infection
- Intestinal anthrax
The recent Ebola outbreak has raised concerns about bloody diarrhea. Bleeding from the orifices in Ebola infection is a late symptom. Diarrhea may also be present and therefore bloody diarrhea could arise. This may also be seen with other viral hemorrhagic fevers.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may also lead to bloody diarrhea. Gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia infections of the rectum (infectious proctitis) may occur with anal intercourse.
Non-Infectious
A number of immune-related conditions and abnormal growths can also lead to bloody diarrhea. Immune disorders are where the activity of the immune system causes inflammation. It may be due to a hypersensitivity reaction (allergy), autoimmune disorder or with transplant rejection, such as:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) – ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease
- Graft-versus-host disease
- Celiac disease
Cancer is one of the concerns when bloody diarrhea occurs. One of the symptoms of colorectal cancer is altered bowel habit, like diarrhea, with bleeding. There may also be bleeding with anal cancer but diarrhea is not usually present as a result of the malignancy.
Injury
Injury to the rectum can occur for a number of reasons. Physical or chemical trauma may occur with certain sexual practices or colon cleansing treatments that is not done properly. It is rare for there to be an injury with a colonoscopy and related diagnostic investigations. Sometimes injury to the bowels may occur during surgery. Electromagnetic injury with radiation treatment to the area. Bloody diarrhea may also be a symptom of radiation sickness.
Poisoning
Toxins may cause gastrointestinal bleeding and diarrhea thereby resulting in blood diarrhea. It is not just poisons that are problem. Even alcoholic drinks may be an issue, especially when illegally produced alcohol brews are ingested in large quantities.
- Naturally-occurring poisons found in plants and certain animals (example croton oil, cantharidin from the blister beetle, mushroom poisoning)
- Heavy metals (example arsenic, mercury, thallium)
- Synthetic chemicals (example ricin, corrosives and acids)
Medication
Certain medication can also cause bloody diarrhea. Sometimes these drugs can irritate the lining of the bowels and result in bleeding but this is unlikely to occur if it is used within the prescribed doses and a person does not have any underlying diseases. Broad-spectrum antibiotics may cause pseudomembranous colitis (antibiotic associated diarrhea) which can lead to bloody diarrhea. Anticoagulants (blood thinners) can prevent clots from forming. Gastrointestinal bleeding may occur from ulcers that form with excessive use of NSAIDs.
Other
- Ischemic bowel disease
- Anal fissures
- Bowel obstruction
- Fecal impaction, complications
References:
www.healthgrades.com/right-care/digestive-health/bloody-diarrhea–causes
www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal_disorders/symptoms_of_gi_disorders/diarrhea.html